AMIS30622C6228G ON Semiconductor, AMIS30622C6228G Datasheet
AMIS30622C6228G
Specifications of AMIS30622C6228G
Available stocks
Related parts for AMIS30622C6228G
AMIS30622C6228G Summary of contents
Page 1
AMIS-30622 Micro-Stepping Motor Driver INTRODUCTION The AMIS−30622 is a single−chip micro−stepping motor driver with a position controller and control/diagnostic interface ready to build intelligent peripheral systems where drivers can be 2 connected ...
Page 2
... AMIS30622C6223RG 800 mA AMIS30622C6227G 800 mA AMIS30622C6227RG 800 mA AMIS30622C6228G 800 mA AMIS30622C6228RG 800 mA *For additional information on our Pb−Free strategy and soldering details, please download the ON Semiconductor Soldering and Mounting Techniques Reference Manual, SOLDERRM/D. †For information on tape and reel specifications, including part orientation and tape sizes, please refer to our Tape and Reel Packaging Specification Brochure, BRD8011/D ...
Page 3
Table of Contents General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Product Features . . . . . ...
Page 4
SDA 1 SCK 2 VDD 3 4 GND TST1 5 TST2 6 GND CPN 9 CPP 10 SOIC−20 Table 4. PIN DESCRIPTION Pin Name 2 SDA I C serial data line 2 SCK I C serial clock ...
Page 5
The AMIS−30622 is available in SOIC−20 or optimized NQFP−32 packages. For cooling optimizations, the NQFP has an exposed thermal pad which has to be soldered to the PCB ground plane. The ground plane needs thermal vias to conduct the head ...
Page 6
The DC parameters are guaranteed overtemperature and V currents flowing into the circuit are defined as positive. Table 5. DC PARAMETERS Symbol Pin(s) Parameter MOTORDRIVER I Max current through motor coil MSmax,Peak in normal operation I Max rms current through ...
Page 7
Table 5. DC PARAMETERS Symbol Pin(s) Parameter SUPPLY AND VOLTAGE REGULATOR V Regulated internal supply DD (Note 12) V Digital supply reset level @ ddReset V power down (Note 13 Current limitation ddLim SWITCH INPUT AND HARDWIRE ADDRESS ...
Page 8
The AC parameters are guaranteed for temperature and V Table 6. AC PARAMETERS Symbol Pin(s) Parameter POWERUP T Power−up time pu INTERNAL OSCILLATOR f Frequency of internal oscillator osc TRANSCEIVER (STANDARD MODE) f SCL clock frequency SCL ...
Page 9
Table 6. AC PARAMETERS Symbol Pin(s) Parameter SWITCH INPUT AND HARDWIRE ADDRESS INPUT T Scan pulse period (Note 19) sw SWI T Scan pulse duration HW sw_on (Note 19) MOTORDRIVER F PWM frequency (Note 19) pwm T Turn−on transient time ...
Page 10
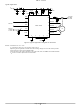
Typical Application V BAT 100 mF 100 nF VDD SDA Bus SCK Connect BAT C 2 GND 1 TST2 Figure 6. Typical Application Diagram for SO ...
Page 11
Stepping Modes One of four possible stepping modes can be programmed: • Half−stepping • 1/4 micro−stepping • 1/8 micro−stepping • 1/16 micro−stepping Table 7. MAXIMUM VELOCITY SELECTION TABLE Vmax Index Vmax Hex Dec (full step/s) Group ...
Page 12
Minimum Velocity Once the maximum velocity is chosen, 16 possible values can be programmed for the minimum velocity Vmin. The table below provides the obtainable values in full−step/s. The accuracy of Vmin is derived from the internal oscillator. Table 8. ...
Page 13
Acceleration and Deceleration Sixteen possible values can be programmed for Acc (acceleration and deceleration between Vmin and Vmax). The table below provides the obtainable values in 2 full−step/s . One observes restrictions Table 9. ACCELERATION AND DECELERATION SELECTION TABLE Vmax ...
Page 14
Position Ranges A position is coded by using the binary two’s complement format. According to the positioning commands used and to the chosen stepping mode, the position range will be as shown in the following table. Table 11. POSITION RANGE ...
Page 15
Control Logic (Position Controller and Main Control) The control logic block stores the information provided by 2 the I C interface (in a RAM or ...
Page 16
Table 13. POSITION RELATED PARAMETERS Parameter Pmax – Pmin Zero Speed Hold Current Maximum Current Acceleration and Deceleration Vmin Vmax Different positioning examples are shown in the table below. Table 14. POSITIONING EXAMPLES Short motion. New positioning command in same ...
Page 17
Dual Positioning A SetDualPosition command allows the user to perform a positioning using two different velocities. The first motion is done with the specified Vmin and Vmax velocities in the SetDualPosition command, with the acceleration (deceleration) parameter already in RAM, ...
Page 18
ActPos = +30000 0 Motion direction TagPos = −30000 −10000 −20000 Figure 9. Motion Direction is Function of Difference between ActPos and TagPos R2GND 2 = R2VBAT 3 = OPEN Figure ...
Page 19
Table 15. STATE DIAGRAM OF THE HW COMPARATOR Previous State DriveLS Float 1 Float 1 Float 0 Float 0 Low 1 Low 1 Low 0 Low 0 High 1 High 1 High 0 High 0 The logic is controlling the ...
Page 20
Condition R2 VBAT Tsw = 1024 ms DriveLS Tsw_on = 64 ms DriveHS “R”−Comp R th HW_Cmp State Figure 11. Timing Diagram Showing the Change in States for HW Comparator R2VBAT A resistor is connected between VBAT and HW. Every ...
Page 21
R2GND 2 = R2VBAT 3 = OPEN Figure 12. Simplified Schematic Diagram of the SWI Comparator As illustrated in the drawing above, a change in state is always synchronized with DriveHS or DriveLS. ...
Page 22
DriveHS DriveLS “R”−Comp R th SWI_Cmp ESW ActPos Figure 13. Simplified Timing Diagram Showing the Change in States for SWI Comparator Main Control and Register, OTP memory + ROM Power−up Phase Power−up phase of the AMIS−30622 will not exceed 10 ...
Page 23
Thermal Shutdown Mode When thermal shutdown occurs, the circuit performs a <SoftStop> command and goes to motor shutdown mode (see Figure 14: State Diagram Temperature Management). Temperature Management The AMIS−30622 monitors temperature by means of two thresholds and one shutdown ...
Page 24
T shutdown level T T warning level T <tw> bit T < T getfullstatus1 T <tsd> bit Figure 15. Illustration of Thermal Management Situation Battery Voltage Management The AMIS−30622 monitors the battery voltage by means of one threshold and one ...
Page 25
In Stop mode 1 the motor is put in shutdown state. The <UV2> flag is set. In case V > UV1, AMIS−30622 accepts BB updates of the target position by means of the reception of SetPosition or GotoSecurePosition commands, only ...
Page 26
Irun[3:0] Current amplitude value to be fed to each coil of the stepper−motor. The table below provides the 16 possible values for <IRUN>. Index Irun Run Current (mA ...
Page 27
Note: The Secure Position is coded on 11 bits only, providing actually the most significant bits of the position, the non coded least significant bits being set to ‘0’. Vmax[3:0] Maximum velocity Index Vmax Vmax(full step/ ...
Page 28
Table 19. RAM REGISTERS Length Register Mnemonic Actual position ActPos Last programmed Pos/TagPos Position Acceleration shape AccShape Coil peak current Irun Coil hold current Ihold Minimum Velocity Vmin Maximum Velocity Vmax Shaft Shaft Acceleration/ Acc deceleration Secure Position SecPos Stepping ...
Page 29
Table 20. FLAGS TABLE Length (bit) Flag Mnemonic Charge pump failure CPFail 1 Electrical defect ElDef 1 External switch ESW 1 status Electrical flag HS 1 Motion status Motion 3 Over current in coil X OVC1 1 Over current in ...
Page 30
Priority Encoder The table below describes the simplified state management performed by the main control block. Table 21. PRIORITY ENCODER State " Standby Stopped Motor Command Stopped, O Ihold in Coils GetOTPparam OTP refresh slave response 2 ...
Page 31
After power−on−reset, the <Standby> state is entered. 31. A DualPosition sequence runs with a separate set of RAM registers. The parameters that are not specified in a DualPosition command ...
Page 32
Motordriver Current Waveforms in the Coils Figure 18 below illustrates the current fed to the motor coils by the motordriver in half−step mode Coil Y Figure 18. Current Waveforms in Motor Coils X and Y in Halfstep Mode ...
Page 33
Motor Starting Phase At motion start, the currents in the coils are directly switched from <Ihold> to <Irun> with a new sine/cosine ratio corresponding to the first half (or micro−) step of the motion Charge Pump Monitoring If ...
Page 34
This can be illustrated in the following sequence given as an application example. The master can check whether there is a problem or not and decide which application strategy to adopt. Table 23. Example of Possible Sequence used to Detect ...
Page 35
General Description AMIS−30622 uses a simple bi−directional 2−wire bus for efficient inter−ic control. This bus is called the Inter C−bus. Features include: • Only two bus lines are required; a serial data line (SDA) and a ...
Page 36
General Characteristics Serial Data Line Serial Clock Line SCK 2 Clock IN Data IN Clock OUT Data OUT AMIS−30624, NCV70624 Figure 22. Connection of a Device to the I Both SDA and SCK are bi−directional lines connected to a positive ...
Page 37
Transferring Data Byte Format Every byte put on the SDA line must be 8−bits long. The number of bytes that can be transmitted per transfer to AMIS−30622 is restricted to eight. Each byte has to be followed by an acknowledge ...
Page 38
Clock Generation The master generates the clock on the SCK line to transfer 2 messages on the I C−bus. Data is only valid during the HIGH period of the clock. Data Formats with 7−bit Addresses Data transfers follow the format ...
Page 39
S Figure 29. Master Reading Data from AMIS−30622: First Transmission is Addressing 2. The second transmission consists of the slave address and the read bit. Then the master can read the data bits on the SDA line on every rising ...
Page 40
Introduction Communications between the AMIS−30622 and a 2−wire serial bus interface master takes place via a large set of commands. Reading commands are used to: Get actual status information, e.g. error flags ♦ Get actual position of the stepper motor ...
Page 41
Application Commands GetFullStatus1 This command is provided to the circuit by the master to get a complete status of the circuit and of the stepper motor. Refer to Tables 19 and 20 to see the meaning of the 2 parameters ...
Page 42
GetFullStatus2 This command is provided to the circuit by the master to get the actual, target and secure position of the stepper motor. Both the actual and target position are returned in signed two’s complement 16−bit format. Secure position is ...
Page 43
GetOTPParam This command is provided to the circuit by the I to read the content of the OTP memory. More information can be found in OTP Memory Structure corresponds to the 2 following I C command frame:. GetOTPParam Table 30. ...
Page 44
HardStop This command will be internally triggered when an electrical problem is detected in one or both coils, leading to shutdown mode. If this occurs while the motor is moving, the <StepLoss> flag is raised to allow warning of the ...
Page 45
SetDualPosition This command is provided to the circuit by the I in order to perform a positioning of the motor using two different velocities. See Section Dual Positioning. Note: This sequence cannot be interrupted by another positioning command. Important: If ...
Page 46
SetMotorParam This command is provided to the circuit by the I to set the values for the stepper motor parameters (listed below) in RAM. Refer to Table 19 to see the meaning of the 2 parameters sent by the I ...
Page 47
SetPosition This command is provided to the circuit by the I to drive the motor to a given absolute position. See Positioning (see Priority Encoder) for more details. The SetPosition corresponds to the following I Table 40. SetPosition COMMAND FRAME ...
Page 48
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS SOIC 20 W CASE 751AQ−01 ISSUE O http://onsemi.com 48 ...
Page 49
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS NQFP−32, 7x7 CASE 560AA−01 ISSUE O http://onsemi.com 49 ...
Page 50
... Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer. This literature is subject to all applicable copyright laws and is not for resale in any manner. PUBLICATION ORDERING INFORMATION LITERATURE FULFILLMENT: Literature Distribution Center for ON Semiconductor P.O. Box 5163, Denver, Colorado 80217 USA Phone: 303−675−2175 or 800−344−3860 Toll Free USA/Canada Fax: 303− ...