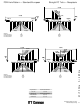
121073-0151 ITT Cannon, 121073-0151 Datasheet - Page 278

121073-0151
Manufacturer Part Number
121073-0151
Description
DSUB BACKSHELL SIZE 25 STR 5PCS
Manufacturer
ITT Cannon
Datasheet
1.053513-1611.pdf
(301 pages)
Specifications of 121073-0151
Accessory Type
Two Piece Backshell
Number Of Positions
25
Cable Type
Round
Cable Exit
180°
Shielding
Shielded
Plating
Nickel over Copper
Hardware
Cable Clamp
Color
Silver
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Features
-
Other names
1003-1085
DB121073-151
DB121073-151
- Current page: 278 of 301
- Download datasheet (10Mb)
D Subminiature
Glossary of Terms
Closed Socket Contact — A socket contact in
which the mating cavity limits the entry of a contact
or probe having a diameter larger than the mating
pin.
Coax — Abbreviation for coaxial.
Coaxial Cable — A cable that comprises a single
copper wire surrounded by insulating material,
wire shielding or mesh, and a plastic protective
sheath.
Component — An essential functional part of the
connector.
Contact — The conductive element in a connector
which makes the actual connection between the
wire and the mating connector for the purpose of
transferring electrical energy. Ideally the contact
should add nothing to the circuit. In the real world,
however, contacts typically have a small
CONTACT RESISTANCE and associated potential
drop.
Contact Alignment — The overall play that a
contact has in the insulator cavity to allow the
mating contacts to self align. Also called contact
float.
Contact Arrangement — See LAYOUT.
Contact Cavity — A defined hole in the connector
insulator into which the contacts fit. The cavities
are generally marked with a unique designation or
number for ease of identification.
Contact Resistance — The maximum amount of
resistance which a contact introduces into the
connection when carrying a specified current
(usually stated in milliohms). When not stated,
values are typically given for ‘‘Initial’’ or ‘‘new’’
contacts. Most specifications also limit the
maximum resistance during or after each of a
series of extreme tests, such as ‘‘Contact
Resistance After Corrosion Test’’. These figures
are typically slightly higher than ‘‘Initial’’.
Contact Retention — The maximum allowable
axial load which can be applied to a contact from
either direction without it being dislodged from the
insulator. Usually stated in Newtons or pounds of
force.
Contact Separation Force — The force required
to separate a pair of mated contacts. Usually
stated in Newtons or pounds of force.
Contact Size — This usually relates to the
maximum size wire this contact can nominally
accommodate. It is based on that AWG size most
closely corresponds to the circular mil area of the
engaging end of a pin contact for that size. For
example, a size 16 contact can accomodate a size
16 AWG wire maximum and the pin corresponds to
the CMA of a size 16 AWG. Note, however, that
oversized crimp pots are available for some crimp
contacts which will allow, for example, a size 16
contact to accommodate a size 14 AWG wire.
Contact Spacing — The distance between the
centers of adjacent contacts.
Creepage — The conduction of electricity across
the surface of an insulator.
Creepage Distance — The shortest distance
between contacts of opposite polarities, or
between a live contact and ground, measured over
the surface of the insulator.
Creepage Path — A path across the surface of the
insulator between two conductors. Lengthening
the path reduces the possibility of arc damage.
Crimp — A method of attaching a contact to a wire
through the application of pressure.
Crimp Contact — A contact which is terminated to
a wire by means of crimping with an appropriate
die and tool. After termination, an insertion tool is
normally used to insert the crimped contact into
the connector. Removable crimp contacts can be
FRONT RELEASE or REAR RELEASE. An
extraction tool is usually required to remove the
contact.
Crosstalk — Undesired electrical currents in
conductors caused by electromagnetic or
electrostatic coupling from other conductors or
from external sources. Also, leakage of optical
power from one optical conductor to another.
CSA — Abbreviation for Canadian Standards
Association.
Current — The movement of electrons through a
conductor. Current is measured in amperes. Its
symbol is L.
Current Rating — The maximum current that a
particular wire, contact, or connector can
accommodate. NOTE: When several wires are
used in a single connector or elevated temperature
or altitude is involved, derating curves must be
applied to these ratings. A typical derating system
is MIL-W-5088 which allows the user to calculate
the derating effects of current, ambient
temperature, number of wires in the bundle, and
altitude.
Decibel — A standard unit of measure for
transmission gain or loss. It expresses the ratio of
power input to power output. Abbreviated dB. The
term dBm is used when 1 milliwatt is the reference
level.
Derating — To reduce the voltage, current, or
power rating of a connector to improve its
reliability or to permit operation at high ambient
temperatures or altitudes.
Derating Curve — A graph of the change in power
handling capability of a connector as a function of
ambient temperature or altitude. Typically the
graphed function is curved, hence the name.
Diallyl Phthalate — A thermosetting plastic used
for insulators and some types of connector
housings. It has outstanding resistance to
chemicals, excellent dimensional stability, and
superior electrical insulating properties.
Dielectric — An insulator used to isolate two
conductors having a low loss factor (RF cables).
The perfect insulator is a vacuum.
Dielectric Constant — That property (K) of an
insulating material which is the ratio of the parallel
capacitance (C) of a given configuration of
electrodes with the material as the dielectric, to the
capacitance of the same electrode configuration
with a vacuum as the dielectric.
Digital — A signal comprising discrete elements.
DIN — Abbreviation for Deutsche Industrie Norm,
a German standards organization.
Direct Current — An essentially constant value of
current that flows in only one direction.
Abbreviated dc.
Dust Cap — A cover used in place of a mating
connector to seal it against dirt and moisture.
Usually secured to the connector by a captive
chain, wire, or rope.
Electroplating — To deposit a metal on the
surface of a conductor using electrolysis.
EMI/RFI — Electro-Magnetic Interference and
Radio Frequency Interference. This is unwanted
stray electronic radiation which may enter, and/or
be emitted by an electronic system. The most
common method of shielding interconnections
against this radiation is to use wires with a metallic
braided shield and a connector system which will
extend the shield through the interconnection. This
type of design will keep radiation from entering, or
being emitted by the system. Backshells for
shielded cable and connectors with threads or
grounding fingers are typically used for this
purpose.
accommodations of the connectors in this catalog.
Glossary of Terms
Call
for
Dimensions are shown in mm (inch)
the
Dimensions subject to change
specific
EMI/RFI
277
Related parts for 121073-0151
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
DSUB BACKSHELL SIZE 9 STR 5PC
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DSUB BACKSHELL SIZE 37 STR 5PC
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DSUB BACKSHELL SIZE 15 KIT 5PCS
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DSUB BACKSHELL SIZE9 40DEG 5PCS
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INDUCTOR FERRITE CORE 15UH SMD
Manufacturer:
API Delevan Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
EMI SHIELDED ENDBELL WITH 4-40 EXTENDED JACKSCREW
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
UNIVERSAL CONTACT 1.8MM SMD
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
UNIVERSAL CONTACT 2.5MM SMD
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
UNIVERSAL CONTACT 3.5MM SMD
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PLUG STR CRIMP SMB RG174/U 316/U
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TRI TNM RECP M FLG SEAL 0-12
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CONN RCPT 6POS JAM NUT W/SCKT
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TRI R E/B STR C/C SEAL SZ 18
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CAB CON 16S PIN 18/16 F80 SILVER
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TRI CON SKT 16-18 TIN ST/LO
Manufacturer:
ITT Cannon
Datasheet: