LMV824M National Semiconductor, LMV824M Datasheet - Page 11
LMV824M
Manufacturer Part Number
LMV824M
Description
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) IC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LMV824M.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of LMV824M
No. Of Amplifiers
1
Bandwidth
5MHz
Slew Rate
2V/µs
No. Of Pins
14
Single Supply Voltage Min (+v)
2.7V
Amplifier Type
Operational
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Peak Reflow Compatible (260 C)
No
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LMV824M
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LMV824MT
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
4 162
Part Number:
LMV824MT
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LMV824MTX
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
61 000
Part Number:
LMV824MTX
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LMV824MTX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LMV824MTX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
15 047
Part Number:
LMV824MX
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
APPLICATION NOTE
This application note is divided into two sections: design
considerations and Application Circuits.
1.0 Design Considerations
This section covers the following design considerations:
1. Frequency and Phase Response Considerations
2. Unity-Gain Pulse Response Considerations
3. Input Bias Current Considerations
1.1 Frequency and Phase Response Considerations
The relationship between open-loop frequency response
and open-loop phase response determines the closed-loop
stability performance (negative feedback). The open-loop
phase response causes the feedback signal to shift towards
becoming positive feedback, thus becoming unstable. The
further the output phase angle is from the input phase angle,
the more stable the negative feedback will operate. Phase
Margin (
at the unity-gain crossover point. Zero degrees of phase-
margin means that the input and output are completely in
phase with each other and will sustain oscillation at the unity-
gain frequency.
The AC tables show
changes with load. The Gain and Phase margin vs Fre-
quency plots in the curve section can be used to graphically
determine the
examine the phase angle portion of the plot, find the phase
margin point at the unity-gain frequency, and determine how
far this point is from zero degree of phase-margin. The larger
the phase-margin, the more stable the circuit operation.
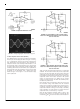
The bandwidth is also affected by load. The graphs of Figure
1 and Figure 2 provide a quick look at how various loads af-
fect the
These graphs show capacitive loads reducing both
bandwidth, while resistive loads reduce the bandwidth but in-
crease the
parallel with 220 picofarads capacitance, to increase the
20˚(approx.), but at the price of about a 100 kHz of band-
width.
Overall, the LMV821/822/824 family provides good stability
for loaded condition.
FIGURE 1. Phase Margin vs Common Mode Voltage for
m
m
) specifies this output-to-input phase relationship
and the bandwidth of the LMV821/822/824 family.
m
. Notice how a 600
m
for various loaded conditions. To do this,
Various Loads
m
for a no load condition. But
resistor can be added in
DS100128-60
m
and
m
m
11
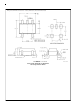
1.2 Unity Gain Pulse Response Considerations
A pull-up resistor is well suited for increasing unity-gain,
pulse response stability. For example, a 600
tor reduces the overshoot voltage by about 50%, when driv-
ing a 220 pF load. Figure 3 shows how to implement the
pull-up resistor for more pulse response stability.
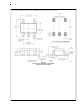
Higher capacitances can be driven by decreasing the value
of the pull-up resistor, but its value shouldn’t be reduced be-
yond the sinking capability of the part. An alternate approach
is to use an isolation resistor as illustrated in Figure 4 .
Figure 5 shows the resulting pulse response from a LMV824,
while driving a 10,000pF load through a 20
resistor.
FIGURE 4. Using an Isolation Resistor to Drive Heavy
FIGURE 3. Using a Pull-up Resistor at the Output for
FIGURE 2. Unity-Gain Frequency vs Common Mode
Stabilizing Capacitive Loads
Voltage for Various Loads
Capacitive Loads
DS100128-61
DS100128-41
DS100128-43
pull-up resis-
www.national.com
isolation