CS9211-VNG National Semiconductor, CS9211-VNG Datasheet
CS9211-VNG
Specifications of CS9211-VNG
Available stocks
Related parts for CS9211-VNG
CS9211-VNG Summary of contents
Page 1
... GX1, GXLV, GXm) along with the CS5530A I/O companion, also members of the Geode fam- ily of products. The CS9211 converts the digital pixel stream output of the CS5530A to the digital RGB inputs used by standard single and dual-scan STN LCD display panels. Support is pro- ...
Page 2
... Pixel Port Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 2.2.2 Serial Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 2.2.3 Flat Panel Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 2.2.4 Memory Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 2.2.5 Reset, Crystal, and GPIO Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 2.2.6 National Semiconductor Internal Test Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 2.2.7 Power and Ground Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 3.0 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 3.1 SYSTEM INTERCONNECTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 3.1.1 CS550A Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 3.1.2 Panel Connections ...
Page 3
Table of Contents (Continued) 5.0 Electrical Specifications ...
Page 4
... Architecture Overview The major functional blocks, as shown in Figure 1-1, of the CS9211 graphics companion flat panel display controller: • Serial Interface • Dither Engine • Frame Rate Modulator (FRM) • Control Registers 4 Serial Configuration 18 Pixel Dither Data Engine 4 Pixel DSTN Timing ...
Page 5
... Signal Definitions This section defines the signals and external interface of the CS9211. Figure 2-1 shows the pins organized by their functional groupings (internal test and electrical pins are not shown). 2.1 PIN ASSIGNMENTS The tables in this section use several common abbrevia- tions ...
Page 6
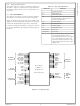
... LD1 28 LD0 29 SHFCLK 30 LP/HSYNC 31 LDE 32 FLM/VSYNC 33 FP_VDDEN 34 FP_VCONEN 35 VDD 36 Figure 2-2. 144-Pin LQFP Pin Assignment Diagram Order Number: CS9211-VNG www.national.com Geode™ CS9211 Graphics Companion Top View 6 108 VDDIO 107 MD2 106 MD13 105 MD1 104 MD14 103 MD0 102 MD15 ...
Page 7
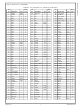
Signal Definitions (Continued) Table 2-2. Pin Assignments - Sorted by Pin Number Pin Drive No. Signal Name Type (mA) 1 VDDIO PWR -- 2 VSSIO GND -- 3 UD11 UD10 UD9 ...
Page 8
Signal Definitions (Continued) Table 2-3. Pin Assignments - Sorted Alphabetically by Signal Name Drive Pin Signal Name Type (mA) No. BLUE0 BLUE1 BLUE2 BLUE3 BLUE4 ...
Page 9
... This signal is the pixel clock from the video controller within the CS550A. It clocks data in from the pixel port on the rising edge. Additionally, this signal is used as the input clock for the entire CS9211 device. This clock must be running at all times after reset for the CS9211 to function correctly. ...
Page 10
Signal Definitions (Continued) 2.2.2 Serial Interface Signals Type Signal Name Pin No. (Drive) SCLK 40 SDIN 41 SDO 42 (8 mA) SCS 43 2.2.3 Flat Panel Interface Signals Type Signal Name Pin No. (Drive) SHFCLK 30 UD[11:0] 3:14 (8 mA) ...
Page 11
Signal Definitions (Continued) 2.2.3 Flat Panel Interface Signals (Continued) Type Signal Name Pin No. (Drive) FLM 33 (8 mA) VSYNC DISPOFF mA) FP_VDDEN 34 (8 mA) FP_VCONEN 35 (8 mA) 2.2.4 Memory Interface Signals Type Signal Name Pin ...
Page 12
... O Write Enable The write enable output for DRAM/SDRAM. O Memory Clock (12 This clock output from the CS9211 should be connected to the SDRAM mA) not used for EDO DRAM. O Clock Enable This output signal should be connected to the SDRAM. When CKE is active (high), the MCLK signal is low. Deactivating the clock provides precharge ...
Page 13
... Reset, Crystal, and GPIO Pins Type Signal Name Pin No. (Drive) RESET# 44 XTALIN 48 XTALOUT 49 GPIO0-GPIO7 70:63 (4 mA) 2.2.6 National Semiconductor Internal Test Pins Type Signal Name Pin No. (Drive) TEST_SE 47 MBIST_EN 45 SCAN_EN 46 2.2.7 Power and Ground Pins Type Signal Name Pin No. ...
Page 14
... SYSTEM INTERCONNECTIONS The system-level discussion topics revolve around events that affect the device as a whole unit and how the CS9211 connects/interfaces with other system devices (i.e., CS5530A, panel, memory, and crystal oscillator). 3.1.1 CS550A Connections ...
Page 15
... Figure 3-3. The output of the CS9211 is a 24-bit data bus that is artifi- cially split into two 12-bit data buses by the CS9211’s adopted nomenclature (UD/LD). The output data presented on these buses “ ...
Page 16
... Functional Description (Continued) 3.2 FUNCTIONAL BLOCKS The block diagram of the CS9211, along with the basic sys- tem interconnections are shown in Figure 3-4. Details of each block will be discussed in this section. The CS9211 interfaces directly to industry standard 8-, 16- and 24-bit color or monochrome single or dual-scan STN flat panels (not all combinations are supported) ...
Page 17
... The read and write proto- cols are summarized in Table 3-1. Figure 3-5 on page 18 shows the write cycle timing, and Figure 3-6 on page 18 shows the read cycle timing. In order for the CS9211 to properly receive commands through the serial interface, the DOTCLK input signal must be active. ...
Page 18
Functional Description (Continued) SCLK 1 SCS A2...A9 SDIN SDO Figure 3-5. Serial Interface Write Cycle Timing Diagram I SCLK 1 SCS 2 3 SDIN A2...A9 4 SDO Figure 3-6. ...
Page 19
... Section 3.2.3 "Timing Signals" on page 22). 3.2.2.3 Output Data Mapping The output of the CS9211 is a 24-bit data bus that is artifi- cially split into two 12-bit data buses by the CS9211’s adopted nomenclature (UD/LD). The output data presented on these buses “moves” from pin to pin depending on the type of panel being used, as determined by the contents of Offset 404h[21:16] (see Table 3-2) ...
Page 20
Functional Description (Continued) Bit Name Description Offset 404h-407h 21:20 DSTN_TFT Panel Type Select: Selects panel type. The selection of the panel type in conjunction with the PIX_OUT (bits [18:16]) setting determines how pixel data is mapped on the output LD/UD ...
Page 21
Functional Description (Continued) DSTN DSTN Pin Name 24-Bit 16-Bit LD0 UD9 LD1 UD10 LD2 UD11 LD3 UD6 LD4 UD7 UD0 LD5 UD8 UD1 LD6 UD3 UD2 LD7 UD4 UD3 LD8 UD5 LD9 UD0 LD10 UD1 UD4 LD11 UD2 UD5 UD0 ...
Page 22
... Input Timing Signals The internal logic of the CS9211 is designed to operate from the leading edge of the incoming VSYNC and HSYNC pulses. This internal logic is triggered from the rising edge of the input pulses after inversion (or not) by Offset 400h bits 30 and 29, as shown in Figure 3-7 ...
Page 23
Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.3.2 Output Timing Signals There are two separate pass-through bits to select internal or external generation of the output timing signals. The PASS_THRU bit, Offset 404h[30] is global and affects whether Offset 400h[7:0], Offset 404h[29], and Offset ...
Page 24
... Table 3-8). The first FLM (First Line Marker) is generated at the beginning of the first line. Then the CS9211 counts the number of lines. A second FLM is generated when half number of total lines has been reached. This is required because in DSTN Table 3-7 ...
Page 25
... Pass-Through: Activates the Pass-Through mode. In Pass-Through mode, the input timing and the pixel data are passed directly onto the panel interface timing and the panel data pins to drive the panel; the internal CS9211 logic and timing is not used. In normal mode, Offset 400h[7:0], 404h[29], and 404h[27:24] are effective. ...
Page 26
... The sequence repeats itself every 64 frames. The CS9211 contains one 64-bit x 32-bit FRM memory for each of the three primary pixel colors, red, green, and blue. These three memories can be pro- grammed simultaneously or individually ...
Page 27
Functional Description (Continued) Table 3- example of one of the three FRM- Sequence tables that is addressed by the most significant bit of the incoming pixel value. The ”n” most-significant bits (as chosen by Offset ...
Page 28
... MSB’s of row “0” FRM RAM. To update the entire RAM location, the index is programmed only once with the starting value, “00”. This is used inside the CS9211 to auto increment the FRM RAM locations for every FRM RAM data access using the Offset 41Ch. ...
Page 29
Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.6 Dithering Dithering creates intermediate color intensities by mixing available colors. Human vision sees an average of the intensities of adjacent pixels on a screen. Although dither- ing provides additional shades, it does so by sacrificing spatial ...
Page 30
... The values are given in hexadecimal. The CS9211 also supports 5-bit dithering but that pattern is not shown. The patterns shown in Figure 3-10 are stored in the CS9211’s internal ROM. These patterns will be used when the dither ROM is selected by Offset 40Ch[12 3.2.6.3 Controlling Dithering Table 3-13 " ...
Page 31
... Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.7 User-defined Dither Patterns The CS9211 allows the user to define custom dither pat- terns, should the pre-programmed patterns prove to be insufficient. As shown in Table 3-13, this memory is accessed through Offset 424h (control and address) and 428h (data). The dither RAM structure is 32 columns x 64 rows, in which each column represents one 8x8 dither pattern matrix, like one of the matrices shown in Figure 3-10 ...
Page 32
... Dither RAM or ROM Select: This bit selects either internal ROM or internal RAM as the source of the ROM_SEL dither patterns Selects fixed (internal to CS9211) ROM for dither patterns (Default Selects programmable (internal to CS9211) RAM for dither patterns. To update the dither RAM, this bit must = 1. ...
Page 33
... Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.8 CRC Signature The CS9211 contains hardware logic that performs Cycli- cal Redundancy Checks (CRCs) on the panel data digital 3 pipeline, using the polynomial used for error detection during silicon and design valida- tion and makes it possible to capture a unique 24-bit signa- ture for any given mode setup ...
Page 34
Functional Description (Continued) Table 3-16 provides the mapping for the panel data bits as inputs to the CRC. Where: RU1/BU1/GU1 -> pixel 1 RU2/GU2/BU2 -> pixel 2 and so on for the Upper Display from line 1 to line 240 ...
Page 35
... EDO_LATE EDO DRAM Late Latch Bit: When this bit is set, the data is latched into the CS9211, one clock after the data arrives from the DRAM. Since SSTN and TFT panels do not use any frame buffer, this bit is used only for DSTN panels. This bit is effective only if EDO RAM is used, as selected by bit ...
Page 36
... Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.12 Power Sequence Control The CS9211 contains a power-sequence controller that manages the application of the power and control voltages to the panel in a specified order compatible with most panel types. Table 3-18 shows the register control bits for power sequencing and Figure 3-13 on page 37 identifies the power sequence and the various delays ...
Page 37
Functional Description (Continued) Table 3-18. Power Sequence Control Bits (Continued) Bit Name Description 23 PWRUP_PHASE_2 Panel Power-Up Phase 2: Selects the interval between enabling FP_VDDEN to enabling panel data and control signals ±1.0 ms ...
Page 38
... Functional Description (Continued) 3.2.13 General Purpose I/O Pins The CS9211 provides eight GPIO (General Purpose I/O) pins. There are two 32-bit registers used for programming the GPIO pins: • GPIO Control Register (Offset 438h): — TYPE Bits [7:0] - Allows for setting each GPIO pin’s direction (i.e., input or output). — ...
Page 39
Functional Description (Continued) Table 3-19. GPIO Pin Programming Registers (Continued) Bit Name Description 9 GPIO1_MODE GPIO1 Pin Mode Normal mode Weak pull-up or weak pull-down mode. 8 GPIO0_MODE GPIO0 Pin Mode Normal mode; 1 ...
Page 40
... The value can be compared with the software simulation results or a previously generated signature for the same image and settings. 430h-433h RO Device and Revision ID Register Reads the CS9211’s device ID and revision ID. 434h-437h R/W GPIO Data Register Status and levels of GPIO pins. ...
Page 41
Register Descriptions (Continued) Bit Name Description Offset 400h-403h 31 RSVD Reserved: This bit is not defined. 30 FP_VSYNC_POL FP_VSYNC Input Polarity: Selects positive or negative polarity of the FP_VSYNC input signal (pin 99). Program this bit to match the polarity ...
Page 42
... Pass-Through: Activates the Pass-Through mode. In Pass-Through mode, the input timing and the pixel data are passed directly onto the panel interface timing and the panel data pins to drive the panel; the internal CS9211 logic and timing is not used. In normal mode, Offset 400h[7:0], 404h[29], and 404h[27:24] are effective. ...
Page 43
... Continuous Line Pulses: This bit selects whether line pulses are continuously output or are output only during the active display time. In most cases, DSTN panels require continuous line pulses (LPs). This bit will have no effect if the CS9211 is set to TFT mode Continuous line pulses. ...
Page 44
... Dither RAM or ROM Select: This bit selects either internal ROM or internal RAM as the source of the ROM_SEL dither patterns Selects fixed (internal to CS9211) ROM for dither patterns (Default Selects programmable (internal to CS9211) RAM for dither patterns. To update the dither RAM, this bit must = 1. ...
Page 45
... EDO Data Latch Edge Select: This bit controls which clock edge is used to latch data. When this bit is set, the data from the DRAM is latched into the CS9211 on the negative edge of the memory clock. Since SSTN and TFT panels do not use any frame buffer, this bit is used only for DSTN panels. This bit is effective only if EDO RAM is used, as selected by bit ...
Page 46
Register Descriptions (Continued) Table 4-2. Configuration Registers (Continued) Bit Name Description 1 SDRAM_CLK SDRAM Clock: Inverts the clock to the SDRAM interface. Since SSTN and TFT panels do not use _INVERT any frame buffer, this bit is used only for ...
Page 47
Register Descriptions (Continued) Table 4-2. Configuration Registers (Continued) Bit Name Description 5 GPIO5_DATA GPIO5 Pin Configuration: Reflects the level of GPIO5 Low High. (Note) 4 GPIO4_DATA GPIO4 Pin Configuration: Reflects the level of GPIO4 ...
Page 48
... AC characteristics. All voltage values in the Electrical Specifications are with respect to V erwise noted. 5.1 TEST MODES The CS9211 can be forced into different test modes. Table 5-1 summarizes the test mode selection process. Mode NAND tree test Signal Name Pin No. ...
Page 49
... Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.2 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Table 5-3 lists absolute maximum ratings for the CS9211. Stresses beyond the listed ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to conditions beyond these limits may (1) reduce device reliability and (2) result in premature failure even when there is no immediate apparent sign of failure ...
Page 50
... Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.4 DC CHARACTERISTICS Table 5-5 lists the DC characteristics for the CS9211. All DC parameters and current measurements in this section were measured under the operating conditions listed in Symbol Parameter I Supply Current (dynamic Output Low Voltage OL V Output High Voltage OH I Static I ...
Page 51
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5 AC CHARACTERISTICS The following tables list the AC characteristics including output delays, input setup requirements, input hold require- ments and output float delays. The rising-clock-edge refer- ence level V and other reference levels are shown in ...
Page 52
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5.1 Pixel Port Timing Symbol Parameter t DOTCLK period D t DOTCLK high pulse width DHP t RED[5:0], GREEN[5:0], BLUE[5:0] setup to DIS rising DOTCLK t RED[5:0], GREEN[5:0], BLUE[5:0] hold DIH from rising DOTCLK 1. All AC ...
Page 53
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5.2 Serial Interface Timing Symbol Parameter t SCLK period S t SCLK high pulse width SHP t SCS, SDIN setup to rising SCLK SIS t SCS, SDIN hold from rising SCLK SIH t SDO valid from rising ...
Page 54
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5.3 Flat Panel Timing Table 5-9. Flat Panel Interface Timing (50 pF Output Load) Symbol Parameter t SHFCLK period P t SHFCLK rise/fall transition time PT t SHFCLK high pulse width PHP t SHFCLK low pulse width ...
Page 55
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5.4 Memory Interface Timing Symbol Parameter t OE# and WE# setup to falling RAS# OWS t OE# and WE# hold from rising RAS# OWH t RAS# precharge time RP t Falling RAS# to falling CASH#, CASL# RCD ...
Page 56
Electrical Specifications (Continued) Symbol Parameter t Clock Cycle Time 1 t CS# Setup Time 2 t CS# Hold Time 3 t RAS# Setup Time 4 t RAS# Hold Time 5 t CAS# Setup Time 6 t CAS# Hold Time 7 ...
Page 57
Electrical Specifications (Continued MCLK RAS CAS WE COL ...
Page 58
Electrical Specifications (Continued) 5.5.5 Panel Timings Table 5-13. DSTN Color Panel Timing Characteristics Symbol Parameter T SHFCLK period P1 T SHFCLK high time P2 T SHFCLK low time P3 T SHFCLK rise time P4 T SHFCLK fall time P5 T ...
Page 59
Electrical Specifications (Continued) Table 5-14. Active Matrix TFT Color Panel Timing Characteristics Symbol Parameter T SHFCLK period P1 T SHFCLK high time P2 T SHFCLK low time P3 T SHFCLK rise time P4 T SHFCLK fall time P5 T Valid ...
Page 60
Mechanical Package Outline 22.00 +0.25 TYP 108 109 144 1 PIN #1 0.50 TYP IDENT 0.17-0.27 TYP NOTE 3 NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED 1. STANDARD LEAD FINISH 7.62 MICROMETERS MINIMUM SOLDER PLATING (85/15) THICKNESS ON ALLOY 42 / COPPER ...
Page 61
... Appendix A Support Documentation A.1 REVISION HISTORY This document is a report of the revision/creation process of the data book for the Geode™ CS9211 graphics com- Revision # (PDF Date) Revisions / Comments 0.1 (9/24/99) First release for web posting. 0.2 (12/1/99) Second preliminary release for web posting. Added table of contents and two new chapters (func- tional and registers) ...
Page 62
... NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein: 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the ...