MP5001 MPS, MP5001 Datasheet - Page 9

MP5001
Manufacturer Part Number
MP5001
Description
5v, 1a- 5a Programmable Current Limit Switch
Manufacturer
MPS
Datasheet
1.MP5001.pdf
(12 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MP5001
Manufacturer:
ZV
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MP5001DQ-LF-Z
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MP5001DQ-LF-Z
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MP5001S
Manufacturer:
ZV
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MP5001W
Manufacturer:
ZV
Quantity:
20 000
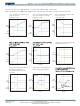
CURRENT LIMIT
The desired current limit is a function of the
external current limit resistor.
The hold current refers to the current limit.
However, the current limit is set to the “trip
current” level when the output (source voltage) is
near Vcc. As the output decreasing, the current
limit is decreased to the “hold current” level.
Output Current (Amps)
In a typical application using a current limit
resistor of 22Ω, the trip current will be 3.3A and
the hold current will be 2.1A. If the device is in its
normal operating state and passing 2.1A it will
need to dissipate only 194mW with the very low
on resistance of 44mΩ. For the package
dissipation of 50°C/Watt, the temperature rise will
only be + 9.7°C. Combined with a 25°C ambient,
this is only 34.7°C total package temperature.
During a short circuit condition, the device now
has 5V across it and the hold current clamps at
2.1A and therefore must dissipate 10.5W. At
50°C/watt, if uncontrolled, the temperature would
rise above the thermal protection threshold
(+175°C) and the device will shutdown to cause
the temperature to drop.
Proper heat sink must be used if the device is
intended to supply the hold current and not
shutdown. Without a heat sink, hold current
should be maintained below 600mA at + 25°C
and below 360mA at +85°C to prevent the device
from activating the thermal shutdown feature.
MP5001 Rev.0.92
10/15/2009
Table 1—Current Limit vs. Current Limit Resistor
Current Limit Resistor
Hold Current
Figure 2—Load Current vs. Voltage Drop
Trip Current
Hold Current
Trip Current
(A)
(A)
(Ω)
(V
MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
V
CC
IN -
3.3
2.1
V
22
V
=5V)
OLTS
OUT
2.1
50
1
MP5001 – 5V, 1A- 5A PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT SWITCH
1.75
100
0.6
© 2009 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
www.MonolithicPower.com
RISE TIME
The rise time is a function of the capacitor
(Cdv/dt) on the dv/dt pin.
*
The “start-up rise time” is measured by taking the
10% to 90% time and multiplied by 1.25 to get
the “interpolated” 0% to 100% rise time.
FAULT AND ENABLE PIN
The Enable/Fault Pin is a Bi-Directional three
levels I/O with a weak pull up current (25uA
typical). The three levels are low, mid and high. It
functions to enable/disable the part and to relay
Fault information.
Enable pin as an input:
Enable pin as an output:
The Enable/Fault line must be above the mid
level for the output to be turned on.
100%
90%
10%
Notes: Rise Time = K
Rise Time*
(TYPICAL)
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
Cdv/dt
(ms)
Low and mid disable the part.
Low, in addition to disabling the part,
clears the fault flag.
High enables the part (if the fault flag is
clear).
The pull up current may (if not over
ridden) allow a “wired nor” pull up to
enable the part.
An under voltage will cause a low on the
enable pin, and will clear the fault flag.
A thermal fault will cause a mid level on
the enable pin, and will set the fault flag.
Figure 3—Start-up Rise Time
Table 2—Rise Time vs. Cdv/dt
10_90 Rise Time
Start-Up Rise
RT
none
1.4
*(50pF+C
50pF
2.8
dv/dt
), K
RT
=28E6
500pF
15.4
1nF
29.4
Enable
Output
Supply
9