MCIMX6S5EVM10AB Freescale Semiconductor, MCIMX6S5EVM10AB Datasheet - Page 99
MCIMX6S5EVM10AB
Manufacturer Part Number
MCIMX6S5EVM10AB
Description
Processors - Application Specialized i.MX6 Solo rev 1.1
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Type
Multimedia Applicationsr
Datasheet
1.MCIMX6S5DVM10AB.pdf
(167 pages)
Specifications of MCIMX6S5EVM10AB
Rohs
yes
Core
ARM Cortex A9
Processor Series
i.MX6
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Maximum Clock Frequency
1 GHz
Data Ram Size
16 KB
Operating Supply Voltage
1.175 V to 1.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
MAPBGA-624
Interface Type
I2C, I2S, UART, USB
Memory Type
L1/L2 Cache, ROM, SRAM
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 20 C
Number Of Timers
2
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MCIMX6S5EVM10AB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MCIMX6S5EVM10AB
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MCIMX6S5EVM10ABR
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
124
Electrical Characteristics
4.11.10.2 Sensor Interface Timings
There are three camera timing modes supported by the IPU.
4.11.10.2.1 BT.656 and BT.1120 Video Mode
Smart camera sensors, which include imaging processing, usually support video mode transfer. They use
an embedded timing syntax to replace the SENSB_VSYNC and SENSB_HSYNC signals. The timing
syntax is defined by the BT.656/BT.1120 standards.
This operation mode follows the recommendations of ITU BT.656/ ITU BT.1120 specifications. The only
control signal used is SENSB_PIX_CLK. Start-of-frame and active-line signals are embedded in the data
stream. An active line starts with a SAV code and ends with a EAV code. In some cases, digital blanking
is inserted in between EAV and SAV code. The CSI decodes and filters out the timing-coding from the data
stream, thus recovering SENSB_VSYNC and SENSB_HSYNC signals for internal use. On BT.656 one
component per cycle is received over the SENSB_DATA bus. On BT.1120 two components per cycle are
received over the SENSB_DATA bus.
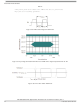
4.11.10.2.2 Gated Clock Mode
The SENSB_VSYNC, SENSB_HSYNC, and SENSB_PIX_CLK signals are used in this mode. See
Figure
62.
Figure 62. Gated Clock Mode Timing Diagram
A frame starts with a rising edge on SENSB_VSYNC (all the timings correspond to straight polarity of the
corresponding signals). Then SENSB_HSYNC goes to high and hold for the entire line. Pixel clock is valid
as long as SENSB_HSYNC is high. Data is latched at the rising edge of the valid pixel clocks.
SENSB_HSYNC goes to low at the end of line. Pixel clocks then become invalid and the CSI stops
receiving data from the stream. For next line the SENSB_HSYNC timing repeats. For next frame the
SENSB_VSYNC timing repeats.
i.MX 6Solo/6DualLite Applications Processors for Consumer Products, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor
99