ADA4851-1YRJZ Analog Devices Inc, ADA4851-1YRJZ Datasheet - Page 13

ADA4851-1YRJZ
Manufacturer Part Number
ADA4851-1YRJZ
Description
OP AMP, HIGH SPEED RRO/P, SMD, 4851
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.ADA4851-1YRJZ.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of ADA4851-1YRJZ
Op Amp Type
High Speed
No. Of Amplifiers
1
Bandwidth
130MHz
Slew Rate
375V/µs
Supply Voltage Range
2.7V To 12V
Amplifier Case Style
SOT-23
No. Of Pins
6
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ADA4851-1YRJZ-R2
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ADA4851-1YRJZ-RL7
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4 feature a high slew rate input
stage that is a true single-supply topology, capable of sensing
signals at or below the minus supply rail. The rail-to-rail output
stage can pull within 70 mV of either supply rail when driving
light loads and within 0.17 V when driving 150 Ω. High speed
performance is maintained at supply voltages as low as 2.7 V.
HEADROOM CONSIDERATIONS
This amplifier is designed for use in low voltage systems. To
obtain optimum performance, it is useful to understand the
behavior of the amplifier as input and output signals approach
the amplifier’s headroom limits. The ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4’s
input common-mode voltage range extends from the negative
supply voltage (actually 200 mV below this), or ground for
single-supply operation, to within 2 V of the positive supply
voltage. Therefore, at a gain of 3, the ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4
can provide full rail-to-rail output swing for supply voltages as
low as 3.3 V, assuming the input signal swing is from −V
ground) to +V
can provide a rail-to-rail output range down to 3 V total
supply voltage.
Exceeding the headroom limit is not a concern for any inverting
gain on any supply voltage, as long as the reference voltage at
the amplifier’s positive input lies within the amplifier’s input
common-mode range.
The input stage is the headroom limit for signals when the
amplifier is used in a gain of 1 for signals approaching the
positive rail. Figure 38 shows a typical offset voltage vs. the
input common-mode voltage for the ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4
amplifiers on a ±5 V supply. Accurate dc performance is
maintained from approximately 200 mV below the minus
supply to within 2 V of the positive supply. For high speed
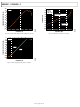
signals, however, there are other considerations. Figure 39 shows
−3 dB bandwidth vs. dc input voltage for a unity-gain follower.
As the common-mode voltage approaches the positive supply,
the amplifier responds well, but the bandwidth begins to drop at
2 V within +V
S
S
.
/2. At a gain of 4, the ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4
S
(or
Rev. A | Page 13 of 16
This can manifest itself in increased distortion or settling time.
Higher frequency signals require more headroom than the
lower frequencies to maintain distortion performance. Figure 40
illustrates how the rising edge settling time for the amplifier
configured as a unity-gain follower stretches out as the top of a
1 V step input approaches and exceeds the specified input
common-mode voltage limit.
For signals approaching the minus supply and inverting gain
and high positive gain configurations, the headroom limit is the
output stage. The ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4 amplifiers use a
common emitter output stage. This output stage maximizes the
available output range, limited by the saturation voltage of the
output transistors. The saturation voltage increases with the
drive current the output transistor is required to supply, due to
the output transistors’ collector resistance.
Figure 39. Unity-Gain Follower Bandwidth vs. Input Common-Mode
440
460
480
500
520
540
560
580
600
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
–6
1
0
2
0.1
–6
G = +1
R
V
Figure 38. V
L
S
–5
= 1k Ω
= 5V
–4
1
OS
–3
vs. Common-Mode Voltage, V
FREQUENCY (MHz)
–2
ADA4851-1/ADA4851-4
V
CM
–1
10
(V)
0
1
100
2
S
V
V
V
V
= ±5 V
CM
CM
CM
CM
= 3.0V
= 3.1V
= 3.2V
= 3.3V
3
1000
4