CY8C3866LTI-065 Cypress Semiconductor Corp, CY8C3866LTI-065 Datasheet - Page 45
CY8C3866LTI-065
Manufacturer Part Number
CY8C3866LTI-065
Description
CY8C3866LTI-065
Manufacturer
Cypress Semiconductor Corp
Series
PSOC™ 3 CY8C38xxr
Datasheet
1.CY8C3865LTI-058.pdf
(129 pages)
Specifications of CY8C3866LTI-065
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
67MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, I²C, LIN, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
CapSense, DMA, LCD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
25
Program Memory Size
64KB (64K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
2K x 8
Ram Size
8K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.71 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 2x20b, D/A 4x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
*
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Independent of the ALU operation, these functions are available:
7.2.2.3 Conditionals
Each datapath has two compares, with bit masking options.
Compare operands include the two accumulators and the two
data registers in a variety of configurations. Other conditions
include zero detect, all ones detect, and overflow. These
conditions are the primary datapath outputs, a selection of which
can be driven out to the UDB routing matrix. Conditional
computation can use the built in chaining to neighboring UDBs
to operate on wider data widths without the need to use routing
resources.
7.2.2.4 Variable MSB
The most significant bit of an arithmetic and shift function can be
programmatically specified. This supports variable width CRC
and PRS functions, and in conjunction with ALU output masking,
can implement arbitrary width timers, counters and shift blocks.
7.2.2.5 Built in CRC/PRS
The datapath has built-in support for single cycle CRC
computation and PRS generation of arbitrary width and arbitrary
polynomial. CRC/PRS functions longer than 8 bits may be
implemented in conjunction with PLD logic, or built in chaining
may be use to extend the function into neighboring UDBs.
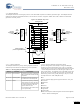
7.2.2.6 Input/Output FIFOs
Each datapath contains two four-byte deep FIFOs, which can be
independently configured as an input buffer (system bus writes
to the FIFO, datapath internal reads the FIFO), or an output
buffer (datapath internal writes to the FIFO, the system bus reads
from the FIFO). The FIFOs generate status that are selectable
as datapath outputs and can therefore be driven to the routing,
to interact with sequencers, interrupts, or DMA.
Figure 7-9. Example FIFO Configurations
Document Number: 001-11729 Rev. *R
System Bus
System Bus
Shift left
Shift right
Nibble swap
Bitwise OR mask
A0/A1/ALU
D0/D1
TX/RX
F0
F1
A0/A1/ALU
F0
Dual Capture
System Bus
A0/A1/ALU
F1
D0
F0
A0
Dual Buffer
System Bus
F1
D1
A1
7.2.2.7 Chaining
The datapath can be configured to chain conditions and signals
such as carries and shift data with neighboring datapaths to
create higher precision arithmetic, shift, CRC/PRS functions.
7.2.2.8 Time Multiplexing
In applications that are over sampled, or do not need high clock
rates, the single ALU block in the datapath can be efficiently
shared with two sets of registers and condition generators. Carry
and shift out data from the ALU are registered and can be
selected as inputs in subsequent cycles. This provides support
for 16-bit functions in one (8-bit) datapath.
7.2.2.9 Datapath I/O
There are six inputs and six outputs that connect the datapath to
the routing matrix. Inputs from the routing provide the
configuration for the datapath operation to perform in each cycle,
and the serial data inputs. Inputs can be routed from other UDB
blocks, other device peripherals, device I/O pins, and so on. The
outputs to the routing can be selected from the generated
conditions, and the serial data outputs. Outputs can be routed to
other UDB blocks, device peripherals, interrupt and DMA
controller, I/O pins, and so on.
7.2.3 Status and Control Module
The primary purpose of this circuitry is to coordinate CPU
firmware interaction with internal UDB operation.
Figure 7-10. Status and Control Registers
The bits of the control register, which may be written to by the
system bus, are used to drive into the routing matrix, and thus
provide firmware with the opportunity to control the state of UDB
processing. The status register is read-only and it allows internal
UDB state to be read out onto the system bus directly from
internal routing. This allows firmware to monitor the state of UDB
processing. Each bit of these registers has programmable
connections to the routing matrix and routing connections are
made depending on the requirements of the application.
7.2.3.1 Usage Examples
As an example of control input, a bit in the control register can
be allocated as a function enable bit. There are multiple ways to
enable a function. In one method the control bit output would be
routed to the clock control block in one or more UDBs and serve
as a clock enable for the selected UDB blocks. A status example
is a case where a PLD or datapath block generated a condition,
such as a “compare true” condition that is captured and latched
by the status register and then read (and cleared) by CPU
firmware.
8-bit Status Register
(Read Only)
Routing Channel
System Bus
PSoC
8-bit Control Register
®
(Write/Read)
3: CY8C38 Family
Data Sheet
Page 45 of 129
[+] Feedback