OP471GS-REEL Analog Devices Inc, OP471GS-REEL Datasheet - Page 9

OP471GS-REEL
Manufacturer Part Number
OP471GS-REEL
Description
IC,Operational Amplifier,QUAD,BIPOLAR,SOP,16PIN,PLASTIC
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.OP471GSZ-REEL.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of OP471GS-REEL
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Amplifier Type
General Purpose
Number Of Circuits
4
Slew Rate
8 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product
6.5MHz
Current - Input Bias
25nA
Voltage - Input Offset
1000µV
Current - Supply
9.2mA
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
±4.5 V ~ 18 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-SOIC (0.300", 7.5mm Width)
Output Type
-
Current - Output / Channel
-
-3db Bandwidth
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Noise Measurements - Peak-to-Peak Voltage Noise
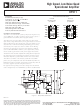
The circuit of Figure 7 is a test setup for measuring peak-to-peak
voltage noise. To measure the 500 nV peak-to-peak noise speci-
fication of the OP471 in the 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz range, the following
precautions must be observed:
1. The device must be warmed up for at least five minutes. As
2. For similar reasons, the device must be well-shielded from
3. Sudden motion in the vicinity of the device can also “feedthrough”
4. The test time to measure 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz noise should not exceed
5. A noise voltage density test is recommended when measuring
6. Power should be supplied to the test circuit by well bypassed,
REV. A
shown in the warm-up drift curve, the offset voltage typically
changes 13 mV due to increasing chip temperature after
power-up. In the 10-second measurement interval, these
temperature-induced effects can exceed tens-of-nanovolts.
air currents. Shielding also minimizes thermocouple effects.
to increase the observed noise.
10 seconds. As shown in the noise-tester frequency-response curve
of Figure 8, the 0.1 Hz corner is defined by only one pole. The
test time of 10 seconds acts as an additional pole to eliminate
noise contribution from the frequency band below 0.1 Hz.
noise on a large number of units. A 10 Hz noise voltage density
measurement will correlate well with a 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
peak-to-peak noise reading, since both results are determined
by the white noise and the location of the 1/f corner frequency.
low noise supplies, e.g, batteries. These will minimize output
noise introduced through the amplifier supply pins.
1/4
OP471
Figure 9. Noise Voltage Density Test Circuit
1/4
OP471
1/4
OP471
–9–
100
Figure 8. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Peak-to-Peak Voltage Noise
Test Circuit Frequency Response
Noise Measurement - Noise Voltage Density
The circuit of Figure 9 shows a quick and reliable method of
measuring the noise voltage density of quad op amps. Each
individual amplifier is series connected and is in unity-gain, save
the final amplifier which is in a noninverting gain of 101. Since
the ac noise voltages of each amplifier are uncorrelated, they
add in rms fashion to yield:
The OP471 is a monolithic device with four identical amplifiers.
The noise voltage density of each individual amplifier will
match, giving:
R1
e
V
OUT
S
=
100
(nV Hz) = 101(2e
80
60
40
20
15V
0
0.01
e
1/4
OP471
OUT
10k
R2
e
OUT
= 101
TO SPECTRUM ANALYZER
=
n
0.1
)
101
Ê
Ë
e
e
OUT
Ê
Ë
FREQUENCY – Hz
nA
2
4e
+ e
n
1
2
nB
ˆ
¯
2
= 101 2e
+
e
nC
2
10
( )
+
e
n
nD
OP471
2
ˆ
¯
100