MAX1678EUA Maxim Integrated Products, MAX1678EUA Datasheet - Page 8

MAX1678EUA
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX1678EUA
Description
DC/DC Switching Converters
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Datasheet
1.MAX1678EUA.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of MAX1678EUA
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MAX1678EUA
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MAX1678EUA+T
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
The MAX1678 employs a proprietary constant-peak-
current control scheme that combines the ultra-low qui-
escent current of traditional pulse-skipping PFM
converters with high-load efficiency.
When the error comparator detects that the output volt-
age is too low, it turns on the internal N-channel
MOSFET switch for an internally calculated on-time
(Figure 2). During the on-time, current ramps up in the
inductor, storing energy in the magnetic field. When the
MOSFET turns off during the second half of each cycle,
the magnetic field collapses, causing the inductor volt-
age to force current through the synchronous rectifier,
transferring the stored energy to the output filter
capacitor and the load. The output filter capacitor
stores charge while the current from the inductor is
high, then holds up the output voltage until the second
half of the next switching cycle, smoothing power flow
to the load. The ideal on-time of the N-channel MOSFET
changes as a function of input voltage. The on-time is
determined as follows:
where K is typically 8V-µs.
The peak inductor current (assuming a lossless circuit)
can be calculated from the following equation:
The P-channel MOSFET (synchronous rectifier) turns on
when the N-channel MOSFET turns off. The circuit oper-
ates at the edge of discontinuous conduction; therefore,
the P-channel synchronous rectifier turns off immediately
after the inductor current ramps to zero. During the dead
time after the P-switch has been turned off, the damping
switch connects LX and BATT. This suppresses EMI noise
due to LC ringing of the inductor and parasitic capaci-
tance at the LX node (see Damping Switch section). The
error comparator starts another cycle when V
below the regulation threshold. With this control scheme,
the MAX1678 maintains high efficiency over a wide range
of loads and input/output voltages while minimizing
switching noise.
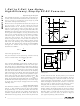
The MAX1678 contains a low-voltage start-up oscillator
(Figure 1). This oscillator pumps up the output voltage
to approximately 1.7V, the level at which the main DC-
DC converter can operate. The 150kHz fixed-frequency
oscillator is powered from the BATT input and drives an
NPN switch. During start-up, the P-channel synchronous
1-Cell to 2-Cell, Low-Noise,
High-Efficiency, Step-Up DC-DC Converter
8
_______________________________________________________________________________________
t
ON
I
PEAK
=
V
=
BATT
Operating Principle
K
Start-Up Operation
K
L
OUT
falls
rectifier remains off and its body diode (or an external
diode, if desired) is used as an output rectifier. The mini-
mum start-up voltage is a function of load current (see
Typical Operating Characteristics ). In normal operation,
when the voltage at the OUT pin exceeds 1.7V, the DC-
DC converter is powered from the OUT pin (boot-
strapped) and the main control circuitry is enabled.
Once started, the output can maintain the load as the
battery voltage decreases below the start-up voltage.
To improve start-up capability with heavy loads, add a
Schottky diode in parallel with the P-channel synchro-
nous rectifier (from LX to OUT) as shown in Figure 3
(see Typical Operating Characteristics ).
Figure 2. Switching Waveforms
Figure 3. External Schottky Diode to Improve Start-Up with
Heavy Load
V
I
V
BATT
PEAK
OSCILLATOR
V
OUT
START-UP
LX
CIRCUIT
I
TIMING
L
PDRV
NDRV
MAX1678
V
t
ON
BATT
K
V
I
OUT
PEAK
t
OFF
K
- V
=
BATT
K
OUT
L
N
P
GND
LX
OR DEAD TIME
t
ON
(ON TIME)
(DEAD TIME)
V
V
(DEAD TIME)
IN
BATT
(ON TIME)
t
t
L1
V
OUT
C
OUT