MAX5003EEE-T Maxim Integrated Products, MAX5003EEE-T Datasheet - Page 9

MAX5003EEE-T
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX5003EEE-T
Description
Voltage Mode PWM Controllers PWM Power-Supply Controller
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Datasheet
1.MAX5003CEE.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MAX5003EEE-T
Topology
Flyback, Forward
Output Current
1000 mA
Switching Frequency
300 KHz
Duty Cycle (max)
75 %
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Package / Case
QSOP-16
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Synchronous Pin
Yes
V
nel MOSFET driver output to ground if the V
not regulating. V
lockout logic, the undervoltage lockout, and the power
regulators.
The preferred method for powering the MAX5003 is to
start with the high-voltage power source (at V+ or ES,
depending on the application), then use a bootstrap
source from the same converter with an output voltage
higher than the V
to power V
of the V
MAX5003 with no bootstrap source from ES or V+, but
do not exceed the maximum allowable power dissipa-
tion. The current consumption of the part is mostly a
function of the operating frequency and the type of
external power switch used—in particular, the total
charge to be supplied to the gate.
A reference output of 3V nominal is externally available
at the REF pin, with a current sourcing capability of
1mA. A lockout circuit shuts off the oscillator and the
output driver if REF falls 200mV below its set value.
Minimize loading at REF, since the REF voltage is the
source for the FB voltage, which is the regulator set
point when the error amplifier is used. Any changes in
V
output voltage of the converter.
The undervoltage lockout feature disables the controller
when the voltage at INDIV is below 1.2V (120mV hys-
teresis). When INDIV rises higher than 1.2V plus the
hysteresis (typically 1.32V), it allows the controller to
start. An external resistive divider connected between
the power line and AGND generates the INDIV signal.
INDIV is also used as the signal for the fast input volt-
age feed-forward circuit.
Always connect INDIV to a voltage divider. It is not a
“don’t care” condition; the signal is used to set the fast
feed-forward circuit (see the Oscillator and Ramp
Generator section).
Choose R2 (Figure 2) between 25kΩ to 500kΩ and cal-
culate R1 to satisfy the following equation:
where V
V
The undervoltage lockout function allows the use of the
INDIV pin as a shutdown pin with an external switch to
CC
REF
INDIVLO
regulator has a lockout line that shorts the N-chan-
will be proportionally reflected in the regulated
Undervoltage Lockout, Feed Forward,
DD
SUL
= I
DD
NDIV
LDO. It is also possible to power the
. This will disable the power consumption
R
= system undervoltage lockout and
1
CC
=
undervoltage lockout.
DD
_______________________________________________________________________________________
R
feeds all circuits except the V
2
regulator turn-off voltage (10.75V)
V
INDIVLO
V
SUL
1 -
and Shutdown
CC
LDO is
CC
Power-Supply Controller
ground. The shutdown circuit must not affect the resis-
tive divider during normal operation.
The current-sense (CS) comparator and its associated
logic limit the current through the power switch. Current
is sensed at CS as a voltage across a sense resistor
between the external MOSFET source and PGND.
Connect CS to the external MOSFET source through a
100Ω resistor or RC lowpass filter (Figures 2 and 3).
See CS Resistor in the Component Selection section.
A blanking circuit shunts CS to ground when the power
MOSFET switch is turned off, and keeps it there for
70ns after turn-on. This avoids false trips caused by the
switching transients. The blanking circuit also resets
the RC filter, if used. When V
MOSFET is switched off. The propagation delay from
the time the switch current reaches the trip level to the
driver turn-off time is 240ns. If the current limit is not
used, the CS pin must be connected to PGND.
The internal error amplifier is one of the building blocks
that gives the MAX5003 its flexibility. Its noninverting
input is biased at 1.5V, derived from the internal 3V ref-
erence. The inverting input is brought outside (FB pin)
and is the regulation feedback connection point. If the
error amplifier is not used, connect this pin to ground.
The output is available for the frequency compensation
network and for connection to the input of the PWM
comparator (CON). Unity-gain frequency is 1.2MHz,
open-circuit gain is 80dB, and the amplifier is unity-
gain stable. To eliminate long overload recovery times,
there are clamps limiting the output excursions close to
the range limits of the PWM ramp. The voltage at the
noninverting input of the error amplifier is the regulator
set point, but is not accessible.
Set-point voltage can be measured, if needed, by con-
necting COMP and FB and measuring that node with
respect to ground. The error amplifier is powered from
the V
The pulse-width modulator (PWM) comparator stage
transforms the error signal into a duty cycle by comparing
the error signal with a linear ramp. The ramp levels are
0.5V min and 2.5V max. The comparator has a typical
hysteresis of 5.6mV and a propagation delay of 100ns.
The output of the comparator controls the external FET.
The soft-start feature allows converters built using the
MAX5003 to apply power to the load in a controllable
soft ramp, thus reducing start-up surges and stresses.
CC
rail.
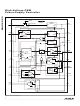
High-Voltage PWM
Current-Sense Comparator
CS
PWM Comparator
> 100mV, the power
Error Amplifier
Soft-Start
9