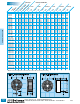
Power Toroids -
Horizontal or Vertical Mount
Inductance tested at 1 KHz, <10 gauss and 0 Adc
DC Resistance at 25°C
Rated Idc based on 40°C maximum rise from 25°C
ambient with 0 Arms
Windings single layered to maximize operating
frequency and minimize board space
Self leads solder coated to within .050" of seating plane
Other values available on request
Packaging Bulk only
Mounting Standard mounting is self-lead radial per
Figure “1”. Optional mounting methods are self-leaded
horizontal per Figure “2” or vertical base mounted per
Figures “3” and “4”.
Notes to Figure 5 (Page 102) The PT Toroid Series inductance is specified at AC and DC signal levels which have no significant effect
on the permeability of the powdered iron toroidal core. Superimposed AC and DC voltages will change the permeability and therefore
the inductance, under operating conditions. Typically, DC currents will reduce the inductance, while AC signals will increase the
inductance up to a point, before beginning to decrease. Supporting information is provided, detailing the AC or DC effects upon each
part. Saturation resulting from DC currents is specified with waveform having less than a 1% ripple content. When considering the AC
waveform, both the frequency and voltage level must be taken into account. As an aid in defining what effect the alternating sine wave
signal will have, the voltage/frequency factor curve can be used. To determine what change of inductance can be expected at a given
voltage level and frequency, simply divide the sinusoidal RMS voltage by the frequency. The voltage is in volts and the frequency is in
hertz. As an example, if using part number PT25-680 at a 1VRMS signal level, and a frequency of 25KHz, the voltage/frequency factor
is calculated to be: 1VRMS/25,000Hz = 40 x 10–6. Referring to the graph, a 39% increase in inductance would be expected.
Notes to Figure 6 (Page 102) Typical saturation effects as a function of DC flowing through the part. Data is representative of a DC
waveform with less than 1% ripple, and an AC waveform less than 10 gauss.
Note This information is intended to be used in assisting the designer in part selection. Each operating application may contain other
variables which must be considered in part selection; such as temperature effects, waveform distortion, etc.…
Delevan Sales/Engineering staff is available to provide information as needed to fit each application.
4/2005
FIGURE
1
FIGURE
3
Series
270 Quaker Rd., East Aurora NY 14052 • Phone 716-652-3600 • Fax 716-652-4814
STANDARD
VERTICAL
VERTICAL
PTxxxxR
PT
2-LEAD
FIGURE
2
4
FIGURE
VERTICAL
4-LEAD
www
HORIZONTAL
.
delevan
.
com
PT5-530
PT5-700
PT5-800
PT5-1000
PT10-530
PT10-680
PT10-820
PT10-990
PT25-680
PT25-800
PT25-900
PT25-1000
PT50-780
PT50-900
PT50-1020
PT50-1320
PT75-900
PT75-980
PT75-1260
PT75-1550
PT100-1000
PT100-1100
PT100-1260
PT100-1550
PT150-1040
PT150-1250
PT150-1500
PT150-2050
PT250-1200
PT250-1500
PT250-1800
PT300-1200
PT300-1500
PT300-1750
PT400-1200
PT400-1500
PT400-1750
PT500-1450
PT500-1750
PT500-2000
PT750-1400
PT750-1700
PT750-2050
PT1000-1400
PT1000-1750
PT1000-2050
E-mail: apisales@delevan . com
*Complete part # must include series # PLUS the dash #
refer to TECHNICAL section of this catalog.
For further surface finish information,
1000
1000
1000
100
100
100
100
150
150
150
150
250
250
250
300
300
300
400
400
400
500
500
500
750
750
750
PT SERIES POWER TOROIDS
10
10
10
10
25
25
25
25
50
50
50
50
75
75
75
75
5
5
5
5
0.015
0.012
0.010
0.008
0.020
0.015
0.010
0.008
0.035
0.025
0.020
0.014
0.050
0.030
0.025
0.020
0.060
0.040
0.035
0.025
0.080
0.050
0.035
0.028
0.100
0.060
0.050
0.040
0.130
0.080
0.055
0.150
0.100
0.075
0.250
0.180
0.110
0.220
0.160
0.090
0.350
0.280
0.150
0.620
0.420
0.200
10.6
12.8
13.2
10.4
11.0
10.6
10.3
12.3
6.1
7.4
4.9
6.8
9.3
4.4
6.6
7.0
3.8
5.6
7.0
3.9
5.2
7.4
3.5
5.1
7.8
3.4
5.7
7.7
3.8
6.1
9.1
3.3
5.5
7.3
2.4
4.7
6.0
3.4
5.0
8.0
2.6
3.7
6.4
1.8
3.1
5.9
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
MOUNTING AVAILABLE
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
PAGE
99