BA50BC0WT-V5 Rohm Semiconductor, BA50BC0WT-V5 Datasheet - Page 7
BA50BC0WT-V5
Manufacturer Part Number
BA50BC0WT-V5
Description
IC REG LDO 5V 1A TO220FP-5(V5)
Manufacturer
Rohm Semiconductor
Series
-r
Datasheet
1.BA00BC0WCP-V5E2.pdf
(10 pages)
Specifications of BA50BC0WT-V5
Regulator Topology
Positive Fixed
Voltage - Output
5V
Voltage - Input
Up to 16V
Voltage - Dropout (typical)
0.3V @ 200mA
Number Of Regulators
1
Current - Output
1A (Max)
Current - Limit (min)
-
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 105°C
Mounting Type
*
Package / Case
*
Number Of Outputs
1
Polarity
Positive
Input Voltage Max
16 V
Output Voltage
5 V
Output Type
Fixed
Output Current
1 A
Line Regulation
35 mV
Load Regulation
75 mV
Voltage Regulation Accuracy
2 %
Maximum Power Dissipation
2 W
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Reference Voltage
1.28 V
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Notes for use
© 2010 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
BA□□BC0 Series,BA□□BC0W Series,BA00BC0W Series
www.rohm.com
1. Absolute maximum ratings
2. GND voltage
3. Thermal design
4. Inter-pin shorts and mounting errors
5. Actions in strong electromagnetic field
6. Testing on application boards
7. Regarding input pin of the IC
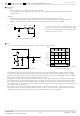
8. Ground Wiring Pattern
9. Thermal shutdown circuit
10. Overcurrent Protection Circuit
11. Damage to the internal circuit or element may occur when the polarity of the Vcc pin is opposite to that of the other pins in
Diode for preventing back current flow
An excess in the absolute maximum ratings, such as supply voltage, temperature range of operating conditions, etc., can break
down the devices, thus making impossible to identify breaking mode, such as a short circuit or an open circuit. If any over rated
values will expect to exceed the absolute maximum ratings, consider adding circuit protection devices, such as fuses.
The potential of GND pin must be minimum potential in all operating conditions.
Use a thermal design that allows for a sufficient margin in light of the power dissipation (Pd) in actual operating conditions.
Use caution when positioning the IC for mounting on printed circuit boards.
The IC may be damaged if there is any connection error or if pins are shorted together.
Use caution when using the IC in the presence of a strong electromagnetic field as doing so may cause the IC to malfunction.
When testing the IC on an application board, connecting a capacitor to a pin with low impedance subjects the IC to stress.
Always discharge capacitors after each process or step. Always turn the IC's power supply off before connecting it to or
removing it from a jig or fixture during the inspection process. Ground the IC during assembly steps as an antistatic
measure. Use similar precaution when transporting or storing the IC.
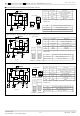
This monolithic IC contains P+ isolation and P substrate layers between adjacent elements in order to keep them isolated.
P-N junctions are formed at the intersection of these P layers with the N layers of other elements, creating a parasitic diode
or transistor. For example, the relation between each potential is as follows:
Parasitic diodes can occur inevitable in the structure of the IC. The operation of parasitic diodes can result in mutual
interference among circuits, operational faults, or physical damage. Accordingly, methods by which parasitic diodes
operate, such as applying a voltage that is lower than the GND (P substrate) voltage to an input pin, should not be used.
When using both small signal and large current GND patterns, it is recommended to isolate the two ground patterns,
placing a single ground point at the ground potential of application so that the pattern wiring resistance and voltage
variations caused by large currents do not cause variations in the small signal ground voltage. Be careful not to change the
GND wiring pattern of any external components, either.
The IC incorporates a built-in thermal shutdown circuit (TSD circuit). The thermal shutdown circuit (TSD circuit) is designed
only to shut the IC off to prevent thermal runaway. It is not designed to protect the IC or guarantee its operation. Do not continue
to use the IC after operating this circuit or use the IC in an environment where the operation of this circuit is assumed.
An overcurrent protection circuit is incorporated in order to prevention destruction due to short-time overload currents.
Continued use of the protection circuits should be avoided. Please note that the current increases negatively impact the temperature.
applications. (I.e. Vcc is shorted with the GND pin while an external capacitor is charged.) Use a maximum capacitance of
1000μF for the output pins. Inserting a diode to prevent back-current flow in series with Vcc or bypass diodes between Vcc
and each pin is recommended.
When GND > Pin A and GND > Pin B, the P-N junction operates as a parasitic diode.
When GND > Pin B, the P-N junction operates as a parasitic transistor.
Fig.23 Bypass Diode
Bypass Diode
VCC
Output pin
(PIN A)
(端子 A)
P substrate
P 基板
N
P
+
Resistor
抵抗
N
P
GND
Fig.24 Example of Simple Bipolar IC Architecture
Parasitic elements
7/8
寄生素子
P
+
N
(端子 B)
(PIN B)
Parasitic elements
N
P
+
C
Transistor (NPN)
トランジスタ(NPN)
B
N
N
N
E
P substrate
P
P
GND
P 基板
N
P
+
N
(PINB)
GND
(PINA)
Technical Note
2010.02 - Rev.B
GND
B
E
C
GND
Parasitic elements
Parasitic elements or
transistors