ELANSC400-66AI AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), ELANSC400-66AI Datasheet

ELANSC400-66AI
Specifications of ELANSC400-66AI
Available stocks
Related parts for ELANSC400-66AI
ELANSC400-66AI Summary of contents
Page 1
Single-Chip, Low-Power, PC/AT-Compatible Microcontrollers DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers E86 family of x86 embedded processors TM – Offers improved time-to-market, software migration, and field-proven development tools Highly integrated single-chip CPU with a complete set of common ...
Page 2
... Combination) is formed by a combination of the elements below. ELANSC400 –33 A Valid Combinations ELANSC400–33 AC, AI ELANSC400–66 ELANSC400–100 ELANSC410–33 AC, AI ELANSC410–66 ELANSC410–100 2 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet With its low-voltage Am486 form factor, the ÉlanSC400 microcontroller is highly op- timized for mobile computing applications. The É ...
Page 3
Table 1. Product Comparison—ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Feature Core CPU L1 Cache System management mode (SMM) Floating-point unit Data Bus ISA Interface ISA bus mastering VESA Local Bus VL bus mastering Power Management Mode timers Activity detection SMI/NMI generation Battery ...
Page 4
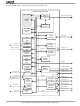
BLOCK DIAGRAM—ÉlanSC400 MICROCONTROLLER Am486 CPU Dual DMA Controllers 8237 Power Management Unit Clock Clock I/O Generation Real-Time 32-kHz Crystal Clock Boundary Scan AT Port Logic Timer 8254 Dual Interrupt Controllers 8259 PC Card Socket A Ctrl Controller GPIOs or Parallel ...
Page 5
BLOCK DIAGRAM—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER Am486 Dual DMA Controllers 8237 Power Management Clock Clock I/O Generation Real-Time 32-kHz Crystal Clock Boundary AT Port Logic Timer Dual Interrupt Controllers GPIOs or Parallel Port Serial Port Infrared Infrared Port Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data ...
Page 6
LOGIC SYMBOL—ÉlanSC400 MICROCONTROLLER LCDD7 [VL_BE3] LCDD6 [VL_LDEV] LCDD5 [VL_D/C] LCDD4 [VL_LRDY] LCDD3 [VL_M/IO] LCDD2 [VL_W/R] LCD Graphics LCDD1 [VL_ADS] Controller or LCDD0 [VL_RST] VESA Local Bus M [VL_BE2] LC [VL_BE1] SCK [VL_BE0] FRM [VL_LCLK] LVEE [VL_BRDY] LVDD [VL_BLAST] DTR, RTS, ...
Page 7
LOGIC SYMBOL—ÉLANSC410 MICROCONTROLLER VL_BE3 VL_LDEV VL_D/C VL_LRDY VL_M/IO VL_W/R VESA Local Bus VL_ADS VL_RST VL_BE2 VL_BE1 VL_BE0 VL_LCLK VL_BRDY VL_BLAST DTR, RTS, SOUT 8-Pin Serial Port CTS, DCD, DSR RIN, SIN SIROUT Infrared Interface SIRIN Power ACIN Management BL2–BL1 Interface ...
Page 8
TABLE OF CONTENTS Distinctive Characteristics ............................................................................................................ 1 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers ...................................................................... 1 ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only ............................................................................................. 1 General Description ..................................................................................................................... 2 Block Diagram—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller .............................................................................. 4 Block Diagram—ÉlanSC410 Microcontroller .............................................................................. 5 Logic Symbol—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller ................................................................................. 6 Logic Symbol—ÉlanSC410 Microcontroller ...
Page 9
High-Speed PLL .................................................................................................................... 81 Band Gap Block .................................................................................................................... 81 RTC Voltage Monitor ............................................................................................................. 81 Clock Specifications .............................................................................................................. 83 Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................................................................................... 86 Operating Ranges ...................................................................................................................... 86 DC Characteristics Over Commercial and Industrial Operating Ranges .................................... 86 Capacitance ............................................................................................................................... 87 ...
Page 10
Figure 35. DRAM Page Hit Read, Non-Interleaved .............................................................. 100 Figure 36. DRAM Page Hit Write, Non-Interleaved .............................................................. 101 Figure 37. DRAM Page Miss Read, Non-Interleaved ........................................................... 101 Figure 38. EDO DRAM Page Hit Read, Non-Interleaved ..................................................... 102 Figure 39. EDO ...
Page 11
Table 22. CFG0 and CFG1 Configuration ............................................................................. 74 Table 23. CFG2 Configuration (ÉlanSC400 microcontroller only) ......................................... 74 Table 24. CFG3 Configuration ............................................................................................... 75 Table 25. BNDSCN_EN Configuration .................................................................................. 75 Table 26. Integrated Peripheral Clock Sources ..................................................................... 77 Table 27. Frequency ...
Page 12
RELATED AMD PRODUCTS ™ E86 Family Devices Device Description 80C186 16-bit microcontroller 80C188 16-bit microcontroller with 8-bit external data bus 80L186 Low-voltage, 16-bit microcontroller 80L188 Low-voltage, 16-bit microcontroller with 8-bit external data bus Am186™EM High-performance, 80C186-compatible, 16-bit embedded microcontroller Am188™EM ...
Page 13
SC400 Microcontroller Evaluation Board The Élan™SC400 microcontroller evaluation board is a stand-alone evaluation platform for the ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers test and development platform for designs based on the ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers, this AMD product is ...
Page 14
The ROM/Flash memory interface provides the flex- ibility to optimize the performance of ROM cycles, including the support of burst-mode ROMs. This is ben efi ci al bec aus duc ts bas ÉlanSC400 ...
Page 15
ROM/Flash Memory Interface The integrated ROM/Flash memory interface supports the following features: 8-, 16-, and 32-bit ROM/Flash memory interfaces Three ROM/Flash memory chip selects Burst-mode ROMs ROM accesses at both ISA and CPU speeds (normal and fast-speed modes) Dedicated ROM ...
Page 16
The interrupt controller block is functionally compatible with the standard cascaded 8259A controller pair as implemented in the PC/AT system. The master control- ler drives the CPU’s interrupt input signal based on the highest priority interrupt request pending at the ...
Page 17
Serial Port The ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers in- clude an industry-standard 16550A UART. The UART can be used to drive a standard 8-pin serial interface or a 2-pin infrared interface. The serial interface and infra- red interface signals are available ...
Page 18
The graphics controller is not supported on the ÉlanSC410 microcontroller. The graphics controller includes the following features: Supports multiple panel resolutions Provides internal ...
Page 19
The ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers sup- port the data bus configurations listed below. External transceivers or buffers can be used to isolate the buses. 16-bit DRAM bus, 8-/16-bit ROM, 32-bit VL-bus disabled, internal graphics controller enabled/ disabled 16-/32-bit DRAM bus, ...
Page 20
ISA Bus Interface For External ISA Peripherals The ISA interface consists of a subset of ISA-compati- ble bus signals, allowing for the connection 16-bit devices supporting ISA-compatible I/O, memory, and DMA cycles. The following features are supported: ...
Page 21
Bank 0 Bank 1 Ctrl D15–D0 Low Word MA11–MA0 Low MA D Ctrl ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller 32-kHz Crystal Loop Filters Ctrl Backup Battery Power Supply Pwr Conn Speaker Battery Matrix Keyboard Ctrl Row Column Conn Conn Rows Columns LCD SA25–SA0 GPIO_CS12–GPIO_CS0 ...
Page 22
Bank 0 Bank 1 Bank 2 High DRAM DRAM DRAM Word Low DRAM DRAM DRAM Word Low MA Ctrl D Rows Columns ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller LCD 32-kHz High D Crystal Ctrl SA Loop Filters Ctrl PC Card A Ctrl PC Card ...
Page 23
Bank 0 Bank 1 Bank 2 High DRAM DRAM DRAM Word Low DRAM DRAM DRAM Word DRAM Low MA Ctrl D Rows Columns ÉlanSC410 Microcontroller VL-Bus Ctrl 32-kHz High D Crystal ISA Ctrl SA Loop Filters ROM Ctrl Parallel Ctrl ...
Page 24
CONNECTION DIAGRAM—ÉlanSC400 AND ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLERS 292 Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package Top View (from component side looking through to bottom ...
Page 25
PIN DESIGNATIONS This section identifies the pins of the ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers and lists the signals asso- ciated with each pin. Several different tables are included in this section. The Pin Designations (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller table beginning on page ...
Page 26
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Pin No. Signal Name A1 KBD_COL5/PIRQ6 A2 KBD_COL2/PIRQ3 A3 KBD_ROW13 [[R32BFOE]] A4 D15 A5 D12 A10 D1 A11 MWE A12 MA2 {CFG2} A13 V CC A14 ...
Page 27
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller (Continued) Pin No. Signal Name H17 SA25 H18 SA23 H19 SA20 H20 SA18 J1 SD10 [D26] J2 SD7 [D23 GND J8 GND J9 GND J10 GND J11 GND J12 GND J13 ...
Page 28
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller (Continued) Pin No. Signal Name U17 GND U18 V CC U19 ROMWR U20 IOR V1 BVD1_A V2 GPIO31 [STRB] [MCEL_B] V3 GPIO21 [PPDWE] V4 GPIO27 [ERROR] [CD_B] V5 LF_HS V6 BBATSEN V7 SPKR V8 SIROUT ...
Page 29
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Signal Name Pin No. ACIN W12 [ACK] [BVD1_B] GPIO25 U2 [AEN] GPIO_CS10 V17 [AFDT] [MCEH_B] GPIO30 W1 [BALE] KBD_ROW10 D2 BBATSEN V6 BL0 [CLK_IO] W14 BL1 Y13 BL2 W13 BNDSCN_EN Y11 [[BNDSCN_TCK]] MCEL_A P2 [[BNDSCN_TDI]] ...
Page 30
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller (Continued) Signal Name Pin No. GND M8 GND M9 GND M10 GND M11 GND M12 GND M13 GND N8 GND N9 GND N10 GND N11 GND N12 GND N13 GND R17 GND T17 GND U5 ...
Page 31
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller (Continued) Signal Name Pin No. MA6 B13 MA7 C12 MA8 A15 MA9 B14 MA10 C13 MA11 A16 [MA12] KBD_ROW6 B17 MCEH_A [[BNDSCN_TMS]] N3 [MCEH_B] GPIO30 [AFDT] W1 MCEL_A [[BNDSCN_TCK]] P2 [MCEL_B] GPIO31 [STRB] V2 [MCS16] ...
Page 32
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller (Continued) Signal Name Pin No B16 E17 CC V G17 J17 CC V L17 ...
Page 33
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER Pin No. Signal Name A1 KBD_COL5/PIRQ6 A2 KBD_COL2/PIRQ3 A3 KBD_ROW13 [[R32BFOE]] A4 D15 A5 D12 A10 D1 A11 MWE A12 MA2 A13 V CC A14 MA5 ...
Page 34
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER (Continued) Pin No. Signal Name H17 SA25 H18 SA23 H19 SA20 H20 SA18 J1 SD10 [D26] J2 SD7 [D23 GND J8 GND J9 GND J10 GND J11 GND J12 GND J13 ...
Page 35
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Number)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER (Continued) Pin No. Signal Name U17 GND U18 V CC U19 ROMWR U20 IOR V1 Reserved V2 GPIO31 [STRB] V3 GPIO21 [PPDWE] V4 GPIO27 [ERROR] V5 LF_HS V6 BBATSEN V7 SPKR V8 SIROUT V9 DCD ...
Page 36
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER Signal Name Pin No. ACIN W12 [ACK] GPIO25 U2 [AEN] GPIO_CS10 V17 [AFDT] GPIO30 W1 [BALE] KBD_ROW10 D2 BBATSEN V6 BL0 [CLK_IO] W14 BL1 Y13 BL2 W13 BNDSCN_EN Y11 [[BNDSCN_TCK]] P2 [[BNDSCN_TDI]] R1 [[BNDSCN_TDO]] M2 ...
Page 37
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER (Continued) Signal Name Pin No. GND N11 GND N12 GND N13 GND R17 GND T17 GND U5 GND U6 GND U7 GND U8 GND U9 GND U10 GND U11 GND U12 GND U13 GND U14 ...
Page 38
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER (Continued) Signal Name Pin No. PIRQ7/KBD_COL6 B2 [PPDWE] GPIO21 V3 [PPOEN] GPIO22 T3 [[R32BFOE]] KBD_ROW13 A3 RAS0 C15 RAS1 D14 [RAS2] KBD_ROW4 D15 [RAS3] KBD_ROW5 C16 Reserved M3 Reserved N2 Reserved P1 Reserved P3 Reserved ...
Page 39
PIN DESIGNATIONS (Pin Name)—ÉlanSC410 MICROCONTROLLER (Continued) Signal Name Pin No. VL_BE0 F19 VL_BE1 E20 VL_BE2 F18 VL_BE3 D20 VL_BLAST A19 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet Signal Name Pin No. VL_BRDY A20 VL_D/C E18 VL_LCLK E19 VL_LDEV F17 VL_LRDY D19 ...
Page 40
PIN STATE TABLES The pin state tables beginning on page 42 are grouped alphabetically by function and show pin states during reset, normal operation, and Suspend mode, along with output drive strength, maximum load, supply source, and power-down groups. Pin ...
Page 41
Table 4. Power Pin Type Abbreviations Symbol Meaning A Pin is an analog input CPU CPU power input RTC Real-time clock input V Power input CC Power-Down Group: The signals on the chip are grouped together by interface for the ...
Page 42
Table 6. Pin State Table—System Interface Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] IOR U20 O IOW R19 O MEMR W20 O MEMW T18 O RSTDRV V12 O SA0 T20 O C–E SA1 P19 O C–E SA2 R20 ...
Page 43
Table 6. Pin State Table—System Interface Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] SD11 [D27 [B] C–E SD12 [D28 [B] C–E SD13 [D29 [B] C–E SD14 [D30 [B] C–E SD15 ...
Page 44
Table 7. Pin State Table—Memory Interface Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] CASH0 D13 O CASH1 A17 O CASL0 B15 O CASL1 C14 O D0 B10 B C–E D1 A10 B C– C–E D3 ...
Page 45
Table 7. Pin State Table—Memory Interface Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] MA10 C13 O C–E MA11 A16 O C–E MWE A11 O C–E RAS0 C15 O C–E RAS1 D14 O C–E ROMCS0 R18 O ROMCS1 T19 ...
Page 46
The CFG2 pin is not supported on the ÉlanSC410 microcontroller. 8. Memory Address MA11–MA4 Suspend state of the pins: Will be three-stated with a pulldown resistor. This will work for CAS-before-RAS refresh, self-refresh, and the DRAM powered down. Summary: ...
Page 47
Table 8. Pin State Table—GPIOs/Parallel Port/PC Card Socket B Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] GPIO15 Y15 B B [PCMA_VPP2] [O] GPIO16 V15 B B [PCMB_VCC] [O] GPIO17 W15 B B [PCMB_VPP1] [O] GPIO18 Y14 B B ...
Page 48
Notes: 1. The shared GPIO20–GPIO15, GPIO_CS14–GPIO_CS13, and PC Card battery signals: As GPIO_CSxs, the signals are active in Suspend mode: that is, if they are inputs before Suspend, they are still inputs during Suspend (the GPIO_CSs can be used to ...
Page 49
Table 9. Pin State Table—GPIOs/ISA Bus Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] GPIO_CS5 W19 B B [IOCS16] [I] GPIO_CS6 V18 B B [IOCHRDY] [STI] GPIO_CS7 Y19 B B [PIRQ1] [I] GPIO_CS8 W18 B B [PIRQ0] [I] GPIO_CS9 ...
Page 50
Notes: 1. The shared GPIO_CS12–GPIO_CS5 and ISA signals: As GPIO_CS signals, they are active in Suspend mode: that is, if they are inputs before Suspend, they are still inputs during Suspend (they can be used to wake up the system); ...
Page 51
Table 10. Pin State Table—GPIOs/System Data (SD) Buffer Control Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] GPIO_CS2 C18 B [[DBUFRDL]] [[O]] GPIO_CS3 D17 B [[DBUFRDH]] [[O]] GPIO_CS4 C4 B [[DBUFOE]] [[O]] KBD_ROW13 A3 STI-OD [[R32BFOE]] [O] Notes: 1. ...
Page 52
Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] GPIO_CS0 V19 B GPIO_CS1 Y20 B Notes: 1. The GPIO_CS signals become inputs in Suspend mode with either a pullup resistor for devices that are left powered pulldown resistor ...
Page 53
Table 14. Pin State Table—Keyboard Interface Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] KBD_COL0 E2 OD-STI D [XT_DATA] [B] KBD_COL1 D1 OD-STI D [XT_CLK] [B] KBD_COL2/ A2 OD-STI D PIRQ3 [I] KBD_COL3/ B3 OD-STI D PIRQ4 [I] KBD_COL4/ ...
Page 54
Notes: 1. The keyboard column signals are shared with the programmable IRQs and XT keyboard signals. As keyboard column signals and XT keyboard signals, they are inputs and open drain outputs with pullup or pulldown resistors in normal operation and ...
Page 55
Table 15. Pin State Table—PC Card Socket A Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] BVD1_A V1 I BVD2_A R3 I CD_A R2 I ICDIR M3 O MCEH_A N3 O [[BNDSCN_TMS]] [[I]] MCEL_A P2 O [[BDNSCN_TCK]] [[I]] OE ...
Page 56
Table 16. Pin State Table—Graphics Controller/VESA Local Bus Control Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] FRM E19 O [VL_LCLK] [O] LC E20 O [VL_BE1] [O] LCDD0 B20 O [VL_RST] [O] LCDD1 C19 O [VL_ADS] [O] LCDD2 D18 ...
Page 57
Notes: 1. The shared graphics controller interface and VESA local bus pins: These signals default to three-state with pulldown resistors and remain this way until an LCD or VL-bus interface is selected (all except LVEE and LVDD). When the graphics ...
Page 58
Table 17. Pin State Table—Miscellaneous Signal Name Pin Output [Alternate Type # Drive Function] 32KXTAL1 Y6 32KXTAL2 Y4 ACIN W12 STI BBATSEN V6 A BL1 Y13 STI BL2 W13 STI BLO W14 STI[B] [CLK_IO] BNDSCN_EN Y11 I LF_HS V5 A ...
Page 59
Table 18. Pin State Table—Power Signal Name (Alternate Function) GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND ...
Page 60
Table 18. Pin State Table—Power Signal Name (Alternate Function) GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND_A ...
Page 61
Table 18. Pin State Table—Power Signal Name (Alternate Function _RTC _CPU CC V _CPU CC V _CPU CC V _CPU CC V _CPU CC V _CPU ...
Page 62
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS The descriptions in Table 19 are organized in alphabetical order within the functional group listed here. System Interface on page 62 Configuration Pins on page 63 Memory Interface on page 64 VL-Bus Interface on page 64 Power Management ...
Page 63
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description MEMR O Memory Read Command indicates that the current cycle is a read of the currently addressed memory device. When this signal is asserted, the memory device can drive data onto ...
Page 64
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description Memory Interface CASH3–CASH0 O Column Address Strobe High indicates to the DRAM devices that a valid column address is asserted on the MA lines. These CAS signals are for the odd ...
Page 65
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description VL_BRDY I Local Bus Burst Ready is asserted by the VL-bus target to indicate that it is terminating the current burst transfer. The chip samples this signal on the rising edge ...
Page 66
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description Clocks 32KXTAL1 32.768-kHz Crystal Interface Signals are used for the 32.768-kHz crystal. This is the main 32KXTAL2 clock source for the chip and drives the internal Phase-Locked Loops (PLLs) that generate ...
Page 67
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description RTS O Request To Send indicates to the external DCE that the internal serial port controller is ready to send data. SIN I Serial Data In receives the serial data from ...
Page 68
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description ICDIR O Card Data Direction controls the direction of the card data buffers or voltage translators. It works with the MCEL and MCEH card enable signals to control data buffers on ...
Page 69
Table 19. Signal Description Table (Continued) Signal Type Description LC O LCD Panel Line Clock is activated at the start of every pixel line commonly referred to by LCD data sheets as CL1 or CP1. This signal is ...
Page 70
Multiplexed Pin Function Options Table 20 shows how to configure each multiplexed É É ...
Page 71
Table 20. Multiplexed Pin Configuration Options (Continued) Signal You Want Signals You Give Up VL-Bus Interface 1 VL_ADS LCDD1 1 VL_BE0 SCK 1 VL_BE1 LC 1 VL_BE2 M 1 VL_BE3 LCDD7 1 VL_BLAST LVDD 1 VL_BRDY LVEE 1 VL_D/C LCDD5 ...
Page 72
Table 20. Multiplexed Pin Configuration Options (Continued) Signal You Want Signals You Give Up GPIO_CS11 PDACK0 GPIO_CS12 PDRQ0 1 GPIO_CS13 PCMA_VCC 1 GPIO_CS14 PCMA_VPP1 Parallel Port ACK GPIO25, BVD1_B AFDT GPIO30, MCEH_B BUSY GPIO24, BVD2_B 1 ERROR GPIO27, CD_B 1 ...
Page 73
Table 20. Multiplexed Pin Configuration Options (Continued) Signal You Want Signals You Give Up 1 MCEL_B GPIO31, STRB 1 PCMA_VCC GPIO_CS13 1 PCMA_VPP1 GPIO_CS14 1 PCMA_VPP2 GPIO15 1 PCMB_VCC GPIO16 1 PCMB_VPP1 GPIO17 1 PCMB_VPP2 GPIO18 1 RDY_B GPIO26, PE ...
Page 74
Using the Configuration Pins to Select Pin Functions The configuration pins are used only for those func- tions that must be selected at reset, prior to firmware execution. All other I/O functions are selected using configuration registers. Table 21 provides ...
Page 75
CFG3 Pin This configuration pin is used for selecting between the GPIO_CS4–GPIO_CS2 I/O pins and the SD bus buffer control signals: DBUFOE, DBUFRDL, and DBUFRDH. When the buffer control signal configuration is selected using the CFG3 pin, the DBUFOE, DBUFRDL, ...
Page 76
CLOCKING Clock Generation The ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers re- quire only one 32.768-kHz crystal to generate all the other clock frequencies required by the system. The output of the on-chip crystal oscillator circuit is used to generate the various frequencies ...
Page 77
Integrated Peripheral Clock Sources Table 26 and Figure 5 show the primary peripheral clocks internal to the microcontroller and the PLL and divider sources that are used in the generation of these clocks. Note that several of the peripheral clocks ...
Page 78
Oscillator 32.768 kHz Enable Intermediate PLL Enable Low-Speed PLL PMU Enable Graphics Dot Clock PLL Enable High-Speed PLL Graphics Dot Clock Select PLL Block Notes: The graphics controller and the PC Card controller are not supported on the ...
Page 79
Crystal Oscillator The 32-kHz oscillator circuit is shown in Figure 6; the only external component required for operation is a 32.768-kHz crystal. The inverting amplifier (AMP) is in- tegrated on-chip together with the feedback resistor and the load capacitors. ...
Page 80
Reference Phase Frequency Detector (Fr) Feedback Frequency (Ff) Divider Frequency Output (Fo) Figure 8. Intermediate and Low-Speed PLLs Block Diagram Graphics Dot Clock PLL (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) The input clock to the Graphics Dot Clock PLL is the output clock ...
Page 81
MHz /16 Ff Figure 9. Graphics Dot Clock PLL Block Diagram High-Speed PLL The High-Speed PLL generates a 66.3552-MHz clock for the DRAM controller. Figure 10 on page 82 shows the block diagram for the High-Speed PLL. The input ...
Page 82
MHz /5 Figure 10. High-Speed PLL Block Diagram BBATSEN – Band Gap Voltage + RESET D 32 kHz CK 82 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet Fr Up Charge Phase Pump Detector Down Ff Fo 66.3552 MHz Divider (9) ...
Page 83
RESET kHz Notes: 1. These timings apply only when powering down the chip while leaving only the RTC powered. 2. Applies to all V except for the Guarantees at least one rising edge ...
Page 84
Table 28. Loop-Filter Component Specification for PLLs Parameter Intermediate PLL C1 0. 0.001 F R 4.7 K Table 29. Analog V Parameter Peak-to-peak noise on VCCA Current consumption in High-Speed mode Current consumption in Low-Speed mode Current consumption ...
Page 85
RESET (Wakeup) t1 Intermediate PLL Lock Low-Speed PLL Lock High-Speed PLL Lock PLLRATIO[2:0] Graphics Dot Clock PLL Lock Figure 13. PLL Enabling Timing Sequence PLL Intermediate PLL frequency Intermediate PLL cycle-to-cycle jitter Low-Speed PLL frequency Low-Speed PLL cycle-to-cycle jitter Graphics ...
Page 86
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . – +125 C Ambient Temperature Under Bias . . – +110 C Supply Voltage V with Respect CC to ...
Page 87
Table 33. Operating Voltage (Commercial and Industrial) Power Pin Type Min Analog 2.7 CPU 2.7 RTC 2.7 V 2.7 CC CAPACITANCE Symbol Parameter Descriptions C Input Capacitance IN Clock Capacitance C Output Capacitance OUT C I/O Pin Capacitance I/O Notes: ...
Page 88
TYPICAL POWER NUMBERS Power Requirements Under Different Power Management Modes Table 34 shows the maximum and typical power dissipation for the ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers. Hyper-Speed (100 MHz) Maximum at 3.3 V 2194 mW (~665 mA) Typical at 3.3 V ...
Page 89
DERATING CURVES This section describes how to use the derating curves on the following pages to determine potential specified timing variations based on system capacitive loading. The Pin State Tables beginning on page 42 in this doc- ument have a ...
Page 90
Load (pF) Figure 18. 3.3-V I/O Drive Type C Rise Time 100 Load (pF) Figure 20. ...
Page 91
AC SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS AND WAVEFORMS The AC specifications provided in the AC characteris- tics tables that follow consist of output delays, input setup requirements, and input hold requirements. AC specifications measurement is defined by the figures that follow each timing ...
Page 92
AC Switching Characteristics over Commercial and Industrial Operating Ranges Symbol Parameter Description t1 V _RTC valid hold before all other RESET valid hold from all _RTC valid to BBATSEN active CC t4 CFGx setup ...
Page 93
Table 36. ROM/Flash Memory Cycles Symbol Parameter Description t1 SA3–SA0 delay from SA31–SA4 t2a SA stable to ROMCSx assertion t2b SA stable to ROMCSx assertion when qualified with command (ROMRD or ROMWR) t2c SA stable to ROMCSx assertion when qualified ...
Page 94
Notes: 1. The ROMCSx address decode is programmable for an early decode (via bit 5 in CSC index 23h, 25h, and 27h). The early address-decode is available to provide the ROMCSx by qualifying the address signals only not ...
Page 95
SA25–SA4 t1 SA3–SA0 t2a ROMCSx ROMWR ROMRD SD7–SD0 Notes: The ROM controller fetches the number of bytes requested by the CPU as dictated by the CPU BE (Byte Enable) signals and returns the data as a single transfer. In this ...
Page 96
SA25–SA4 t1 SA3–SA1 t2a ROMCSx ROMWR ROMRD SD15–SD0 Figure 28. Fast Mode 16-Bit Burst ROM Read Cycles t2b SA25–SA4 t1 SA3–SA2 t2a ROMCSx ROMWR ROMRD SD15–SD0 DBUFOE R32BFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 29. Fast Mode CPU Burst Read from 32-Bit ...
Page 97
SA25–SA4 t1 SA3–SA0 t2a ROMCSx t8 t27 ROMRD ROMWR SD15–SD0 DBUFOE R32BFOE IOCHRDY DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 30. Normal Mode 8-/16-Bit ROM/Flash Memory Read Cycles SA25–SA4 t1 SA3–SA0 t2a ROMCSx t27 ROMWR ROMRD SD15–SD0 DBUFOE R32BFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH IOCHRDY ...
Page 98
Symbol Parameter Description t1 Row address setup time t2 RAS to CAS delay t3 Row address hold time t4 Column address setup time t5 Column address hold time t6a CAS pulse width (CPU, Fast Page mode) t6a CAS pulse width ...
Page 99
RAS t4 t2 CASL3–CASL0 CASH3–CASH0 t3 t15 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 32. DRAM Page Hit Read, Interleaved t1 RAS t2 t17 t4 t19 CASL3– CASL0 CASH3– CASH0 t3 t15 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 33. DRAM Page Hit Write, Interleaved ...
Page 100
RAS CASL3–CASL0 CASH3–CASH0 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 34. DRAM Page Miss Read, Interleaved t1 RAS t2 CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 t3 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 35. DRAM Page Hit Read, Non-Interleaved 100 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t8a t4 ...
Page 101
RAS t19 CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 t3 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 36. DRAM Page Hit Write, Non-Interleaved t1 RAS CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Figure 37. DRAM Page Miss Read, Non-Interleaved Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t2 t8a t4 t17 ...
Page 102
RAS CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 MA12–MA0 MWE D31–D0 Notes: The EDO DRAM page hit write timing is similar to DRAM page hit write timing. See Figure 36 on page 101 for more information. Figure 38. EDO DRAM Page Hit Read, Non-Interleaved ...
Page 103
CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 RAS0 RAS1 RAS2 RAS3 MWE Figure 40. DRAM CAS-Before-RAS Refresh t7a t27 CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 RAS MWE Notes: Because the sequence shown above is performed when the microcontroller is in Suspend mode, the ...
Page 104
CASH3–CASH0 CASL3–CASL0 RAS0 RAS1 RAS2 RAS3 MWE Notes: The diagram above shows RAS and CAS behavior for an ÉlanSC400 or ÉlanSC410 microcontroller running at a frequency of 16 MHz or less. In this case, the RAS signals are not staggered ...
Page 105
Symbol Parameter Description t1a Setup, SA, SBHE stable to command assertion, 16-bit I/O, 8-bit I/O, Mem t1b Setup, SA, SBHE stable to command assertion, 16-bit Mem t2a Delay, MCS16 stable from SA t2b Delay, IOCS16 stable from SA t3a Pulse ...
Page 106
Symbol Parameter Description t29 Hold, SA, SBHE from read command t30 Setup read command deassertion t31 Hold, TC from read command deassertion t32a Pulse width, I/O write command t32b Pulse width, I/O read command t33a Pulse width, memory ...
Page 107
SA25–SA0, SBHE IOW/MEMW IOR/MEMR IOCHRDY SD7–SD0 (Write) SD7–SD0 (Read) DBUFRDL DBUFOE Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t41 t4 t45 t6 t11a t12 t5a t46 t3a,b t42 t9 Figure 43. 8-Bit ISA Bus Cycles t1a t4 t13a t3c,d t6 ...
Page 108
SA25–SA0, SBHE BALE IOW/MEMW IOR/MEMR IOCS16/MCS16 IOCHRDY DBUFRDL DBUFRDH DBUFOE SD15–SD0 (Write) SD15–SD0 (Read) 108 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t2a,b t2a,b t1a,b t15 t16 t16 t41 t4 t11a,b t6 t45 t46 t5b t42 t3e,f t3e,f t9 Figure 44. ...
Page 109
PDRQx PDACKx SA25–SA0, SBHE AEN IOW MEMR SD15–SD0 IOCHRDY TC DBUFRDL DBUFRDH DBUFOE Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t20 t21 t19 t17 t22b t24 t39 t32a t32a t26 t23 t49 t51 t33a t34 Figure 45. ISA DMA Read Cycle ...
Page 110
PDRQx PDACKx SA23–SA0, SBHE AEN MEMW IOR SD15–SD0 IOCHRDY TC DBUFRDL DBUFRDH DBUFOE 110 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t20 t21 t19 t17 t22a t24 t38 t33b t26 t23 t30 t53 t54 t36 t32b Figure 46. ISA DMA Write ...
Page 111
Symbol Parameter Description t1 VL_LCLK period t2 VL_LCLK pulse High t3 VL_LCLK pulse Low t4 VL_ADS delay from VL_LCLK t5 SA25–SA2, VL_BE3–VL_BE0, VL_M/IO, VL_W/R, VL_D/C delay from VL_LCLK t6 VL_BLAST valid from VL_LCLK t7 VL_LDEV valid from SA25–SA2, VL_BE3–VL_BE0, VL_M/IO, ...
Page 112
VL_LCLK 1 CPUADS VL_ADS t5 SA25–SA2, VL_BE t7 VL_LDEV Read Data Write Data VL_LRDY VL_BRDY VL_BLAST Notes: 1. This signal is shown as a timing reference only not available as a pin on the ÉlanSC400 ...
Page 113
Symbol Parameter Description t1 PPDWE delay from IOW t2 PPOEN delay from IOW t3 STRB delay from IOW t4 SLCTIN, AFDT valid from IOW t5 SD setup to IOW t6 SD hold from IOW t7 BUSY asserted from IOW asserted ...
Page 114
IOW t1 PPDWE t2 PPOEN t3 STRB t4 SLCTIN t4 AFDT SD7–SD0 BUSY DBUFOE DBUFRDL Figure 48. EPP Parallel Port Write Cycle 114 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t9 Address Register Access Data Register Access t7 ...
Page 115
IOR t13 PPDWE PPOEN STRB t14 SLCTIN t14 AFDT SD7–SD0 BUSY t20 DBUFOE DBUFRDL Figure 49. EPP Parallel Port Read Cycle Table 41. General-Purpose Input/Output Cycles Symbol Parameter Description t1 SA stable to GPIO_CSx rising edge t2 SA stable to ...
Page 116
SA25–SA0 GPIO_CSx IOW IOR IOCHRDY SD7–SD0/SD15–SD0 (Write) D7–D0/D15–D0 (Read) Notes: See the ISA bus section on page 105 for detailed timings between these signals. Figure 50. I/O Decode (R/W), Address Decode Only SA25–SA0 GPIO_CSx IOW IOR IOCHRDY SD7–SD0/SD15–SD0 (Write) ...
Page 117
SA25–SA0 GPIO_CSx IOW IOR IOCHRDY SD7–SD0 (Write) SD7–SD0 (Read) Notes: See the ISA bus section on page 105 for detailed timings between these signals. Figure 52. I/O Decode (R/W), GPIO_CSx as 8042CS Timing t9 SA25–SA0 GPIO_CSx MEMW MEMR IOCHRDY ...
Page 118
SA25–SA0 GPIO_CSx MEMW MEMR IOCHRDY SD7–SD0/SD15–SD0 (Write) SD7–SD0/SD15–SD0 (Read) Notes: See the ISA bus section on page 105 for detailed timings between these signals. Figure 54. Memory CS Decode (R/W), Command Qualified 118 Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t14 ...
Page 119
Table 42. PC Card Cycles—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only Symbol Parameter Description t1 REG_x, SA setup to command active t2 Command pulse width t3 SA hold and write data valid from command inactive t4 WAIT_AB Active from command active t5 Command hold ...
Page 120
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B MCEL_A MCEL_B MCEH_A MCEH_B t1 OE WAIT_AB Three-state or Not Valid for Attribute Memory Read Cycles SD15–SD8 SD7–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 55. PC Card Attribute Memory Read Cycle (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Table 43. PC Card Attribute ...
Page 121
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B MCEL_A MCEL_B MCEH_A MCEH_B WAIT_AB Not Valid for Attribute Memory Write Cycles SD15–SD8 SD7–SD0 Write Cycle Data DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 56. PC Card Attribute Memory Write Cycle (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Table 44. PC ...
Page 122
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B MCEL_A MCEL_B MCEH_A MCEH_B WAIT_AB SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 57. PC Card Common Memory Read Cycle (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Table 45. PC Card Common Memory Read Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Mode REG_x Byte ...
Page 123
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B MCEL_A MCEL_B MCEH_A MCEH_B WAIT_AB Write Cycle Data SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 58. PC Card Common Memory Write Cycle (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Table 46. PC Card Common Memory Write Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) ...
Page 124
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B t1 IOR WAIT_AB MCEL_A MCEL_B MCEH_A MCEH_B WP_x (IOCS16_x) SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Table 47. PC Card I/O Read Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Mode REG_x MCEH_x Byte Access Word Access L L ...
Page 125
SA25–SA0 REG_A REG_B t1 IOW WAIT_AB MCEL_A MCEL_B t10 MCEH_A MCEH_B WP_x (IOCS16_x) Write Cycle Data SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Table 48. PC Card I/O Write Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Mode REG_x MCEH_x MCEL_x Byte Access L L Word ...
Page 126
REG_A, REG_B, (DACK) MCEL_A, MCEL_B, MCEH_A, MCEH_B OE, IOR IOW WE (TC) SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DUBFRDH Figure 61. PC Card DMA Read Cycle (Memory Read to I/O Write) Table 49. PC Card DMA Read Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Mode DACK ...
Page 127
REG_A, REG_B, (DACK) MCEL_A, MCEL_B, MCEH_A, MCEH_B WE, IOW IOR OE (TC) SD15–SD0 DBUFOE DBUFRDL DBUFRDH Figure 62. PC Card DMA Write Cycle (I/O Read to Memory Write) Table 50. PC Card DMA Write Function (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Mode DACK ...
Page 128
Table 51. LCD Graphics Controller Cycles—ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only Symbol Parameter Description t1a SCK period, monochrome panel t1b SCK period, color STN panel t2 SCK High time t3 SCK Low time t4 Setup, data to SCK falling edge t5 Hold, LCD_data ...
Page 129
LVDD Graphics Panel Interface Signals (Figure 63) LVEE BL2 Normal Operation Figure 64. Graphics Panel Power Sequencing (ÉlanSC400 Microcontroller Only) Élan™SC400 and ÉlanSC410 Microcontrollers Data Sheet t12b t11a t11b t11b t12a Battery Failure t15 t14 t13 129 ...
Page 130
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS The thermal specifications for the ÉlanSC400 and ÉlanSC410 microcontrollers are given case temperature) specification. The 33-MHz and 66-MHz devices are specified for operation when T is with the range of 0°C–+95°C. The 100-MHz CASE device ...
Page 131
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS—BGA 292—PLASTIC BALL GRID ARRAY A1 CORNER A1 CORNER I.D. ENCAPSULATION 4X .20 0.50 0.70 0.51 0.61 C 2.11 2.61 DETAIL A SCALE:NONE . . 0. ...
Page 132
Trademarks 1998 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. AMD, the AMD logo and combinations thereof, Am186, Am188, E86, K86, Élan, Comm86, and Systems in Silicon are trademarks, and Am386 and Am486 are registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. ...