DS2196LN Maxim Integrated Products, DS2196LN Datasheet

DS2196LN
Available stocks
Related parts for DS2196LN
DS2196LN Summary of contents
Page 1
... IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan § 3.3V supply with 5V tolerant inputs and outputs § 100-pin LQFP ( mm) package ORDERING INFORMATION PART TEMP RANGE DS2196L 0ºC to +70ºC DS2196LN -40ºC to +85º 157 DS2196 PIN-PACKAGE 100 LQFP 100 LQFP 093002 ...
Page 2
INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................ 6 1.1 FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS.................................................................................................................. 6 1.2 TYPICAL APPLICATIONS............................................................................................................. 10 1.3 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................... 10 2 PIN DESCRIPTION .......................................................................................................................... 10 3 PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................... 13 4 REGISTER MAP............................................................................................................................... 21 5 PARALLEL PORT............................................................................................................................ 27 6 CONTROL, ID, AND TEST REGISTERS ..................................................................................... ...
Page 3
LEGACY FDL SUPPORT.......................................................................................................... 115 18.2.1 Overview............................................................................................................................... 115 18.2.2 Receive Section..................................................................................................................... 115 18.2.3 Transmit Section ................................................................................................................... 116 18.3 D4/SLC–96 OPERATION .......................................................................................................... 117 19 LINE INTERFACE FUNCTION................................................................................................ 118 19.1 RECEIVE CLOCK AND DATA RECOVERY ......................................................................... 118 19.2 TRANSMIT WAVESHAPING AND LINE ...
Page 4
Figure 1-1: T1 Dual Framer LIU .............................................................................................................. 9 Figure 15-1: BERT Mux Diagram .......................................................................................................... 87 Figure 19-1: External Analog Connections .......................................................................................... 121 Figure 19-2: Jitter Tolerance ................................................................................................................. 122 Figure 19-3: Transmit Waveform Template ........................................................................................ 122 Figure 19-4: Jitter Attenuation.............................................................................................................. 123 ...
Page 5
Table 2-1: Pin Description Sorted by Pin Number................................................................................ 10 Table 4-1: Register Map Sorted by Address .......................................................................................... 21 Table 6-1: Output Pin Test Modes .......................................................................................................... 36 Table 6-2: Receive Data Source Mux Modes......................................................................................... 37 Table 6-3: TPOSB/TNEGB Data Source Select..................................................................................... ...
Page 6
INTRODUCTION The DS2196 is a derivative of the DS21352 T1 SCT. The feature set has been optimized for transport applications commonly found in T1 transmission equipment. The DS2196 register map and register bit definitions are compatible with the DS21352/DS21552, ...
Page 7
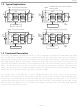
Typical Applications OFFICE REPEATER/NIU 1.544 MHz DS2196 Long / Interface Framer A Formatter B Short A Haul Rx HDLC Tx HDLC Line Tx HDLC Rx HDLC Interface Tx Rx Unit Formatter A Framer B (LIU) Microcontroller ...
Page 8
Reader’s Note: This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the T1 operating environment. In each 125ms frame, there are 24 8-bit channels plus a framing bit assumed that the framing bit is sent first followed by channel ...
Page 9
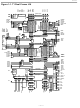
Figure 1-1. T1 Dual Framer LIU UOP0 POWER UOP1 UOP2 UOP3 TCHBLKB/ TLINKB TCHCLKB TLCLKB sync clock data clock data SSER TSERB SYSCLK TCLKB SFSYNC TSYNCB RMSYNCA RMSYNC RFSYNCA RCLK RCLKA RSER RSERA RBPVA RLOSA / LOTCA RCHCLKA/ RLCLKA RCHBLKA/ ...
Page 10
PIN DESCRIPTION Table 2-1. Pin Description Sorted by Pin Number PIN SYMBOL 1 PCLK 2 PNRZ 3 WCLK 4 WNRZ 5 JTMS 6 JTCLK 7 JTRST* 8 JTDI 9 JTDO 10 RCL 11 LNRZ 12 LCLK 13 LFSYNC 14 ...
Page 11
PIN SYMBOL TYPE 43 TCLKOB 44 DVSS 45 DVDD 46 TCLKOA 47 TNEGOA / TFSYNCA 48 TPOSOA / TNRZA 49 TSERA 50 TCLKA 51 TSYNCA I/O 52 TCHCLKA / TLCLKA 53 TCHBLKA / I/O TLINKA 54 MUX ...
Page 12
PIN SYMBOL TYPE 86 RBPVA 87 DVSS 88 DVDD 89 RBPVB 90 RLOSB/ LOTCB 91 RFSYNCB 92 RMSYNCB 93 RSERB 94 RCLKB 95 RNEGIB 96 RPOSIB 97 RCLKIB 98 RCHCLKB / RLCLKB 99 RCHBLKB / RLINKB 100 WPS O Receive ...
Page 13
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Transmit Side Pins Signal Name: TCLKA/B Signal Description: Transmit Clock Signal Type: Input A 1.544 MHz primary clock is applied here. Used to clock data through the transmit side formatters. TCLKA/B can be internally connected to ...
Page 14
Signal Name: TNEGA/B / TFSYNCA/B Signal Description: Transmit Negative Data & Frame Sync Pulse Output Signal Type: Output Updated on the rising edge of TCLKA or TCLKB with either bipolar data or a frame sync pulse out of the transmit ...
Page 15
Signal Name: RLOSA/B / LOTCA/B Signal Description: Receive Loss of Sync / Loss of Transmit Clock Signal Type: Output A dual function output that is controlled by the CCR3.5 control bit. This pin can be programmed to either toggle high ...
Page 16
Parallel Control Port Pins Signal Name: INT* Signal Description: Interrupt Signal Type: Output Flags host controller during conditions and change of states as defined in the Status Registers. Active low, open drain output. Signal Name: MUX Signal Description: Bus Operation ...
Page 17
Signal Name: JTCLK Signal Description: JTAG IEEE 1149.1 Test Serial Clock Signal Type: Input This signal is used to shift data into JTDI on the rising edge and out of JTDO on the falling edge. If not used, this pin ...
Page 18
Signal Type: Output This digital output will provide either a frame synchronization pulse or the negative half of a bipolar data stream. The signal is based on what is provided at the TNEGLI input. Signal Name: LNRZ Signal Description: LIU ...
Page 19
Signal Name: PNRZ Signal Description: Protect NRZ Data Signal Type: Input This digital input is used to pass a NRZ data stream via the Data Source Selection MUX and the jitter attenuator block to the RPOSLO and RNEGLO output pins. ...
Page 20
Supply Pins Signal Name: DVDD Signal Description: Digital Positive Supply Signal Type: Supply 3.3 volts ±5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD pins. Signal Name: RVDD Signal Description: Receive Analog Positive Supply Signal Type: Supply 3.3 volts ±5%. ...
Page 21
REGISTER MAP Table 4-1. Register Map Sorted By Address ADDRESS R/W 00 R/W HDLC Control for Framer A 01 R/W HDLC Status from Framer A 02 R/W HDLC Interrupt Mask for Framer A 03 R/W Receive HDLC Information for ...
Page 22
ADDRESS R/W 2C R/W Receive Control 2 for Framer A 2D R/W Receive Mark 1 for Framer A 2E R/W Receive Mark 2 for Framer A 2F R/W Receive Mark 3 for Framer A 30 R/W Common Control 3 for ...
Page 23
ADDRESS R/W 5D — Reserved (Set to 00h on power-up) 5E R/W LIU Test Register 1 (Set to 00h on power-up) 5F R/W LIU Test Register 2 (Set to 00h on power-up Receive Signaling 1 from Framer A ...
Page 24
ADDRESS R/W 8E — Reserved (Set to 00h on power-up) 8F — Reserved (Set to 00h on power-up) 90 R/W Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 for Framer A 91 R/W Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 2 for Framer A ...
Page 25
ADDRESS R/W B9 R/W Common Control 5 for Framer Transmit DS0 Monitor from Formatter B BB R/W Receive Spare Code Definition 1 for Framer B BC R/W Receive Spare Code Definition 2 for Framer B BD R/W ...
Page 26
ADDRESS R Receive Signaling 10 from Framer Receive Signaling 11 from Framer Receive Signaling 12 from Framer B EC R/W Receive Channel Blocking 1 for Framer B ED R/W Receive Channel Blocking ...
Page 27
PARALLEL PORT The DS2196 is controlled via either a nonmultiplexed (MUX = multiplexed (MUX = 1) bus by an external microcontroller or microprocessor. The DS2196 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timing configurations. If ...
Page 28
The factory in testing the DS2196 uses the two Test Registers at addresses 09 and 7D hex. On power–up, the Test Registers should be set to 00 hex in order for the DS2196 to operate properly. RCR1A: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER ...
Page 29
RCR1B: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = CB Hex) (MSB) LCVCRF ARC OOF1 SYMBOL POSITION LCVCRF RCR1B.7 ARC RCR1B.6 OOF1 RCR1B.5 OOF2 RCR1B.4 SYNCC RCR1B.3 SYNCT RCR1B.2 SYNCE RCR1B.1 RESYNC RCR1B.0 OOF2 SYNCC SYNCT NAME AND DESCRIPTION Line ...
Page 30
RCR2A: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 2C Hex) (MSB) RCS – SYMBOL POSITION RCS RCR2A.7 – RCR2A.6 – RCR2A.5 – RCR2A.4 – RCR2A.3 RD4YM RCR2A.2 FSBE RCR2A.1 MOSCRF RCR2A.0 – – – NAME AND DESCRIPTION Receive Code ...
Page 31
RCR2B: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = CC Hex) (MSB) RCS – SYMBOL POSITION RCS RCR2B.7 – RCR2B.6 – RCR2B.5 – RCR2B.4 – RCR2B.3 RD4YM RCR2B.2 FSBE RCR2B.1 MOSCRF RCR2B.0 – – – NAME AND DESCRIPTION Receive Code ...
Page 32
TCR1A: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 35 Hex) (MSB) LOTCMC TFPT TCPT SYMBOL POSITION LOTCMC TCR1A.7 TFPT TCR1A.6 TCPT TCR1A.5 RBSE TCR1A.4 GB7S TCR1A.3 TFDLS TCR1A.2 TBL TCR1A.1 TYEL TCR1A.0 NOTE: For a description of how the ...
Page 33
TCR1B: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = D5 Hex) (MSB) LOTCMC TFPT TCPT SYMBOL POSITION LOTCMC TCR1B.7 TFPT TCR1B.6 TCPT TCR1B.5 RBSE TCR1B.4 GB7S TCR1B.3 TFDLS TCR1B.2 TBL TCR1B.1 TYEL TCR1B.0 NOTE: For a description of how the ...
Page 34
TCR2A: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 36 Hex) (MSB) TEST1 TEST0 TAISM SYMBOL POSITION TEST1 TCR2A.7 TEST0 TCR2A.6 TAISM TCR2A.5 TSDW TCR2A.4 TSM TCR2A.3 TSIO TCR2A.2 TD4YM TCR2A.1 TB7ZS TCR2A.0 TSDW TSM TSIO NAME AND DESCRIPTION Test ...
Page 35
TCR2B: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = D6 Hex) (MSB) – – TAISM SYMBOL POSITION – TCR2B.7 – TCR2B.6 TAISM TCR2A.5 TSDW TCR2B.4 TSM TCR2B.3 TSIO TCR2B.2 TD4YM TCR2B.1 TB7ZS TCR2B.0 TSDW TSM TSIO NAME AND DESCRIPTION Not ...
Page 36
Table 6-1: OUTPUT PIN TEST MODES TEST 1 TEST 0 EFFECT ON OUTPUT PINS 0 0 operate normally 0 1 force all output pins into 3–state (including all I/O pins and parallel port pins force all output pins ...
Page 37
Table 6-2: Receive Data Source Mux Modes RDS2 RDS1 RDS0 CCR1B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = D7 Hex) (MSB) TRAIM ODF RSAO ...
Page 38
Table 6-3: TPOSB/TNEGB Data Source Select TTDSS1 TTDSS0 0 0 Pass tpos/tclk/tneg from the framer through to the TPOSOB/TCLKOB/TNEGOB pins Force TPOSOB to source data from the BERT circuit. TNEGOB is the frame sync pulse Force ...
Page 39
Framer Loopback A When CCR1A.0 is set the A Framer/Formatter will enter a Framer Loopback (FLB) mode. This loopback is useful in testing and debugging applications. In FLB, the DS2196 will loop data from the transmit side ...
Page 40
CCR2A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 38 Hex) (MSB) TFM TB8ZS TSLC96 SYMBOL POSITION TFM CCR2A.7 TB8ZS CCR2A.6 TSLC96 CCR2A.5 TZSE CCR2A.4 RFM CCR2A.3 RB8ZS CCR2A.2 RSLC96 CCR2A.1 RFDL CCR2A.0 TZSE RFM RB8ZS NAME AND DESCRIPTION Transmit ...
Page 41
CCR2B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = D8 Hex) (MSB) TFM TB8ZS TSLC96 SYMBOL POSITION TFM CCR2B.7 TB8ZS CCR2B.6 TSLC96 CCR2B.5 TZSE CCR2B.4 RFM CCR2B.3 RB8ZS CCR2B.2 RSLC96 CCR2B.1 RFDL CCR2B.0 TZSE RFM RB8ZS NAME AND DESCRIPTION Transmit ...
Page 42
CCR3A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 3 FRAMER A (Address = 30 Hex) (MSB) LIDST TCLKSRC RLOS SYMBOL POSITION LIDST CCR3A.7 TCLKSRC CCR3A.6 RLOSF CCR3A.5 RSMS CCR3A.4 FBCT2 CCR3A.3 ECUS CCR3A.2 TLOOP CCR3A.1 FBCT1 CCR3A.0 RSMS FBCT2 ECUS NAME AND DESCRIPTION Line ...
Page 43
CCR3B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 3 FRAMER B (Address = D0 Hex) (MSB) – TCLKSRC RLOS SYMBOL POSITION – CCR3B.7 TCLKSRC CCR3B.6 RLOSF CCR3B.5 RSMS CCR3B.4 FBCT2 CCR3B.3 ECUS CCR3B.2 TLOOP CCR3B.1 FBCT1 CCR3B.0 RSMS FBCT2 ECUS NAME AND DESCRIPTION Not ...
Page 44
CCR4A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 4 FRAMER A (Address = 11 Hex) (MSB) LCLKPOL PWCLKPOL SYMBOL POSITION LCLKPOL CCR4A.7 PWCLKPOL CCR4A.6 BERTMEN CCR4A.5 LNRZAIS CCR4A.4 – CCR4A.3 LFAMC CCR4A.2 RTDLPM CCR4A.1 TIRFS CCR4A.0 BERTMEN LNRZAIS NAME AND DESCRIPTION LCLK Polarity Select. ...
Page 45
CCR4B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 4 FRAMER B (Address = B1 Hex) (MSB) RCLKIPOL TCLKOPOL SYMBOL POSITION RCLKIPOL CCR4B.7 TCLKOPOL CCR4B.6 BERTMEN CCR4B.5 – CCR4B.4 – CCR4B.3 FAFBMC CCR4B.2 RTDLPM CCR4B.1 TIRFS CCR4B.0 BERTMEN – – NAME AND DESCRIPTION RCLKIB Polarity ...
Page 46
CCR5A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 FRAMER A (Address = 19 Hex) (MSB) TJC LLB LIAIS SYMBOL POSITION TJC CCR5A.7 LLB CCR5A.6 LIAIS CCR5A.5 TCM4 CCR5A.4 TCM3 CCR5A.3 TCM2 CCR5A.2 TCM1 CCR5A.1 TCM0 CCR5A.0 TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 NAME AND DESCRIPTION Transmit ...
Page 47
CCR5B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 FRAMER B (Address = B9 Hex) (MSB) TJC – SYMBOL POSITION TJC CCR5B.7 – CCR5B.6 – CCR5B.5 TCM4 CCR5B.4 TCM3 CCR5B.3 TCM2 CCR5B.2 TCM1 CCR5B.1 TCM0 CCR5B.0 CCR6A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 6 FRAMER A (Address ...
Page 48
RJC EAMS MECU SYMBOL POSITION RJC CCR6B.7 EAMS CCR6B.6 MECU CCR6B.5 RCM4 CCR6B.4 RCM3 CCR6B.3 RCM2 CCR6B.2 RCM1 CCR6B.1 RCM0 CCR6B.0 RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 NAME AND DESCRIPTION Receive Japanese CRC6 Enable use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation) ...
Page 49
CCR7A: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 7 FRAMER A (Address = 0A Hex) (MSB) LIRST RLB AIS13-24 SYMBOL POSITION LIRST CCR7A.7 RLB CCR7A.6 AIS13-24 CCR7A.5 AIS1-12 CCR7A.4 DISRCL CCR7A.3 – CCR7A.2 – CCR7A.1 LBOS3 CCR7A.0 AIS1-12 DISRCL NAME AND DESCRIPTION Line Interface ...
Page 50
CCR7B: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 7 FRAMER B (Address = AA Hex) (MSB) – BELB AIS13-24 SYMBOL POSITION – CCR7B.7 BELB CCR7B.6 AIS13-24 CCR7B.5 AIS1-12 CCR7B.4 UOP3 CCR7B.3 UOP2 CCR7B.2 UOP1 CCR7B.1 UOP0 CCR7B.0 Remote Loopback When CCR7A.6 is set to ...
Page 51
STATUS AND INFORMATION REGISTERS Found in each Framer/Formatter is a set of nine registers that contain information on the current real time status of the DS2196, Status Register 1 (SR1), Status Register 2 (SR2), Receive Information Registers 1 to ...
Page 52
BIRQ FDLSB SYMBOL POSITION – ISR.7 BIRQ ISR.6 FDLSB ISR.5 SR2B ISR.4 SR1B ISR.3 FDLSA ISR.2 SR2A ISR.1 SR1A ISR.0 SR2B SR1B FDLSA NAME AND DESCRIPTION Not Assigned. Could be any value when read. BERT INTERRUPT REQUEST. 0 ...
Page 53
RIR1A: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 22 Hex) (MSB) COFA 8ZD 16ZD SYMBOL POSITION COFA RIR1A.7 8ZD RIR1A.6 16ZD RIR1A.5 – RIR1A.4 – RIR1A.3 SEFE RIR1A.2 B8ZS RIR1A.1 FBE RIR1A.0 – – SEFE NAME AND DESCRIPTION Change ...
Page 54
RIR1B: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = C2 Hex) (MSB) COFA 8ZD 16ZD SYMBOL POSITION COFA RIR1B.7 8ZD RIR1B.6 16ZD RIR1B.5 – RIR1B.4 – RIR1B.3 SEFE RIR1B.2 B8ZS RIR1B.1 FBE RIR1B.0 – – SEFE NAME AND DESCRIPTION Change ...
Page 55
RIR2A: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 31 Hex) (MSB) RLOSC LRCLC FRCLC SYMBOL POSITION RLOSC RIR2A.7 LRCLC RIR2A.6 FRCLC RIR2A.5 – RIR2A.4 – RIR2A.3 RBLC RIR2A.2 – RIR2A.1 – RIR2A.0 RIR2B: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 2 FRAMER B ...
Page 56
RIR3A: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 3 FRAMER A (Address = 10 Hex) (MSB) RL1 RL0 JALT SYMBOL POSITION RL1 RIR3A.7 RL0 RIR3A.6 JALT RIR3A.5 LORC RIR3A.4 LRCL RIR3A.3 – RIR3A.2 – RIR3A.1 RAIS-CI RIR3A.0 RIR3B: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 3 FRAMER B ...
Page 57
Table 7-1: RECEIVE T1 LEVEL INDICATION RL1 NOTE: The RAIS-CI bit is qualified with the RBL status bit (SR1A.3 and SR1B.3). Hence the RAIS-CI status bit will not be set unless the RBL status bit is ...
Page 58
SR1B: STATUS REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = C0 Hex) (MSB) LUP LDN LOTC SYMBOL POSITION LUP SR1B.7 LDN SR1B.6 LOTC SR1B.5 LSPARE SR1B.4 RBL SR1B.3 RYEL SR1B.2 FRCL SR1B.1 RLOS SR1B.0 LSPARE RBL RYEL NAME AND DESCRIPTION Loop Up ...
Page 59
Table 7-2: ALARM CRITERIA ALARM Blue Alarm (AIS) (see note 1 below) Yellow Alarm (RAI bit 2 mode(RCR2.2= 12th F–bit mode (RCR2.2=1; this mode is also referred to as the “Japanese Yellow Alarm”) 3. ESF mode ...
Page 60
SR2A: STATUS REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 21 Hex) (MSB) RMF TMF SYMBOL POSITION RMF SR2A.7 TMF SR2A.6 SEC SR2A.5 RFDL SR2A.4 TFDL SR2A.3 RMTCH SR2A.2 RAF SR2A.1 – SR2A.0 SR2B: STATUS REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = C1 ...
Page 61
IMR1A: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 7F Hex) (MSB) LUP LDN LOTC SYMBOL POSITION LUP IMR1A.7 LDN IMR1A.6 LOTC IMR1A.5 LSPARE IMR1A.4 RBL IMR1A.3 RYE IMR1A.2 FRCL IMR1A.1 RLOS IMR1A.0 LSPARE RBL RYEL NAME AND DESCRIPTION Loop ...
Page 62
IMR1B: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = FF Hex) (MSB) LUP LDN LOTC SYMBOL POSITION LUP IMR1B.7 LDN IMR1B.6 LOTC IMR1B.5 LSPARE IMR1A.4 RBL IMR1B.3 RYE IMR1B.2 FRCL IMR1B.1 RLOS IMR1B.0 LSPARE RBL RYEL NAME AND DESCRIPTION Loop ...
Page 63
IMR2A: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 6F Hex) (MSB) RMF TMF SYMBOL POSITION RMF IMR2A.7 TMF IMR2A.6 SEC IMR2A.5 RFDL IMR2A.4 TFDL IMR2A.3 RMTCH IMR2A.2 RAF IMR2A.1 – IMR2A.0 SEC RFDL TFDL NAME AND DESCRIPTION Receive Multiframe. ...
Page 64
IMR2B: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = EF Hex) (MSB) RMF TMF SYMBOL POSITION RMF IMR2B.7 TMF IMR2B.6 SEC IMR2B.5 RFDL IMR2B.4 TFDL IMR2B.3 RMTCH IMR2B.2 RAF IMR2B.1 – IMR2B.0 8. ERROR COUNT REGISTERS There is a set ...
Page 65
Line Code Violation Count Register (LCVCR) Line Code Violation Count Register 1 (LCVCR1) is the most significant word and LCVCR2 is the least significant word of a 16–bit counter that records code violations (CVs). CVs are defined as Bipolar Violations ...
Page 66
Table 8-1: LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS COUNT EXCESSIVE ZEROS (RCR1.7) no yes no yes Path Code Violation Count Register (PCVCR) When the receive side of a framer is set to operate in the ESF framing mode (CCR2.3=1), PCVCR will ...
Page 67
Table 8-2: PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS FRAMING MODE (CCR2. ESF MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNT REGISTER (MOSCR) Normally the MOSCR is used to count the number of multiframes that the receive synchronizer is out of sync (RCR2.0=1). ...
Page 68
FRAMING MODE COUNT MOS OR F–BIT (CCR2. ESF ESF 9. SIGNALING OPERATION The robbed–bit signaling bits embedded in the T1 stream can be extracted from the receive stream and inserted into the transmit stream by each framer. There ...
Page 69
Each Receive Signaling Register (RS1 to RS12) reports the incoming robbed bit signaling from eight DS0 channels. In the ESF framing mode, there can four signaling bits per channel ( and D). In the D4 ...
Page 70
DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION Each framer in the DS2196 has the ability to monitor one DS0 64 kbps channel in the transmit direction and one DS0 channel in the receive direction at the same time. In the transmit direction the ...
Page 71
TDS0MA: TRANSMIT DS0 MONITOR REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 1A Hex) TDS0MB: TRANSMIT DS0 MONITOR REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = BA Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION B1 TDS0M.7 B2 TDS0M.6 B3 TDS0M.5 B4 TDS0M.4 B5 TDS0M.3 B6 TDS0M.2 B7 ...
Page 72
RDS0MA: RECEIVE DS0 MONITOR REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 1F Hex) RDS0MB: RECEIVE DS0 MONITOR REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = BF Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION B1 RDS0M.7 B2 RDS0M.6 B3 RDS0M.5 B4 RDS0M.4 B5 RDS0M.3 B6 RDS0M.2 B7 ...
Page 73
TIR1A/TIR2A/TIR3A: TRANSMIT IDLE REGISTERS FRAMER A (Address = Hex) TIR1B/TIR2B/TIR3B: TRANSMIT IDLE REGISTERS FRAMER B (Address = Hex) [Also used for Per–Channel Loopback] (MSB) CH8 CH7 CH6 CH16 CH15 CH14 CH24 CH23 CH22 SYMBOLS ...
Page 74
RMR1A/RMR2A/RMR3A: RECEIVE MARK REGISTERS FRAMER A (Address = Hex) RMR1B/RMR2B/RMR3B: RECEIVE MARK REGISTERS FRAMER B (Address = Hex) (MSB) CH8 CH7 CH6 CH16 CH15 CH14 CH24 CH23 CH22 SYMBOLS POSITIONS CH1-24 RMR1.0-3.7 12. PROGRAMMABLE ...
Page 75
IBCCB: IN–BAND CODE CONTROL REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = B2 Hex) (MSB) TC1 TC0 RUP2 SYMBOL POSITION TC1 IBCC.7 TC0 IBCC.6 RUP2 IBCC.5 RUP1 IBCC.4 RUP0 IBCC.3 RDN2 IBCC.2 RDN1 IBCC.1 RDN0 IBCC.0 Table 12-1: TRANSMIT CODE LENGTH TC1 TC0 ...
Page 76
TCD1A: TRANSMIT CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 13 Hex) TCD1B: TRANSMIT CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = B3 Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION C7 TCD1.7 Transmit Code Definition Bit 7. First ...
Page 77
TCD2A: TRANSMIT CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 16 Hex) TCD2B: TRANSMIT CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = B6 Hex) Least significant byte of 16 bit codes (MSB SYMBOL POSITION C7 TCD2.7 C6 TCD2.6 ...
Page 78
RUPCD1A: RECEIVE UP CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 14 Hex) RUPCD1B: RECEIVE UP CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = B4 Hex) NOTE: Writing this register resets the detector’s integration period. (MSB SYMBOL POSITION ...
Page 79
RUPCD2A: RECEIVE UP CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 17 Hex) RUPCD2B: RECEIVE UP CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = B7 Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION C7 RUPCD2.7 C6 RUPCD2.6 C5 RUPCD2.5 C4 RUPCD2.4 C3 ...
Page 80
RDNCD1A: RECEIVE DOWN CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 15 Hex) RDNCD1B: RECEIVE DOWN CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = B5 Hex) NOTE: Writing this register resets the detector’s integration period. (MSB SYMBOL POSITION ...
Page 81
RDNCD2A: RECEIVE DOWN CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 18 Hex) RDNCD2B: RECEIVE DOWN CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = B8 Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION C7 RDNCD2.7 C6 RDNCD2.6 C5 RDNCD2.5 C4 RDNCD2.4 C3 ...
Page 82
RSCD1A: RECEIVE SPARE CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 1B Hex) RSCD1B: RECEIVE SPARE CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = BB Hex) NOTE: Writing this register resets the detector’s integration period. (MSB SYMBOL POSITION ...
Page 83
RSCD2A: RECEIVE SPARE CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 1C Hex) RSCD2B: RECEIVE SPARE CODE DEFINITION REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = BC Hex) (MSB SYMBOL POSITION C7 RSCD2.7 C6 RSCD2.6 C5 RSCD2.5 C4 RSCD2.4 C3 ...
Page 84
RCBR1A/RCBR2A/RCBR3A: RECEIVE CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS FRAMER A (Address = Hex) RCBR1B/RCBR2B/RCBR3B: RECEIVE CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS FRAMER B (Address = Hex) (MSB) CH8 CH7 CH6 CH16 CH15 CH14 CH24 CH23 CH22 SYMBOLS POSITIONS CH1-24 RCBR1.0-3.7 ...
Page 85
TRANSMIT TRANSPARENCY Each of the 24 T1 channels in the transmit direction of the framer can be either forced to be transparent or in other words, can be forced to stop Bit 7 Stuffing from overwriting the data in ...
Page 86
BERT FUNCTION The BERT Block can generate and detect both pseudorandom and repeating bit patterns and it is used to test and stress data communication links. The BERT Block is capable of generating and detected the following patterns: · ...
Page 87
Figure 15-1: BERT Mux Diagram RECEIVE SIDE Framed / Unframed Select (BIC.6) Use RCHBLK Select (BIC.5) Framer A/B Framer A/B Select mux Select (BIC.4) Framer A Framer B enable (CCR4A.5) normal transmit data Note 1: Always includes a clock pulse ...
Page 88
BERT REGISTER DESCRIPTION BC0: BERT CONTROL REGISTER 0 (Address = 40 Hex) (MSB) – TINV RINV SYMBOL POSITION – BC0.7 TINV BC0.6 RINV BC0.5 PS2 BC0.4 PS1 BC0.3 PS0 BC0.2 LC BC0.1 RESYNC BC0.0 PS2 PS1 PS0 NAME AND ...
Page 89
Table 15-1: BERT PATTERN SELECT OPTIONS PS2 PS1 PS0 Pseudorandom 2E7 – Pseudorandom 2E11 – Pseudorandom 2E15 – Pseudorandom Pattern QRSS consecutive zero ...
Page 90
Repetitive Pattern Length Configuration RPL0 is the LSB and RPL3 is the MSB of a nibble that describes the how long the repetitive pattern is. The valid range is 17 (0000 (1111). These bits are ignored if the ...
Page 91
BC2: BERT Control Register 2 (Address = 42 Hex) (MSB) EIB2 EIB1 EIB0 SYMBOL POSITION EIB2 BC2.7 EIB1 BC2.6 EIB0 BC2.5 SBE BC2.4 – BC2.3 – BC2.2 – BC2.1 TC BC2.0 Table 15-3: BERT RATE INSERTION SELECT EIB2 EIB1 EIB0 ...
Page 92
BIR: BERT INFORMATION REGISTER (Address = 43 Hex) (Refer to Section 7 for explanation of reading latched register bits) (MSB) – RA1 SYMBOL POSITION – BIR.7 RA1 BIR.6 RA0 BIR.5 RLOS BIR.4 BED BIR.3 BBCO BIR.2 BECO BIR.1 SYNC BIR.0 ...
Page 93
BAWC: BERT Alternating Word Count Rate. (Address = 44 Hex) (MSB) ALTCNT7 ALTCNT6 ALTCNT5 ALTCNT4 ALTCNT3 ALTCNT2 ALTCNT1 ALTCNT0 SYMBOL POSITION ALTCNT7 BAWC.7 ALTCNT6 BAWC.6 ALTCNT5 BAWC.5 ALTCNT4 BAWC.4 ALTCNT3 BAWC.3 ALTCNT2 BAWC.2 ALTCNT1 BAWC.1 ALTCNT0 BAWC.0 When the BERT ...
Page 94
BBC0: BERT Bit Count Register 0 (Address = 49 Hex) BBC1: BERT Bit Count Register 1 (Address = 4A Hex) BBC2: BERT Bit Count Register 2 (Address = 4B Hex) BBC3: BERT Bit Count Register 3 (Address = 4C Hex) ...
Page 95
BIC: BERT INTERFACE CONTROL REGISTER (Address = 50 Hex) (MSB) – RFUS RRCB SYMBOL POSITION – BIC.7 RFUS BIC.6 RRCB BIC.5 RABS BIC.4 TBAT BIC.3 TFUS BIC.2 TTCB BIC.1 TABS BIC.0 RABS TBAT TFUS NAME AND DESCRIPTION Not Assigned. Should ...
Page 96
ERROR INSERTION FUNCTION An Error insertion function is available in each formatter of the DS2196 and is used to create errors in the payload portion of the T1 frame in the transmit path. See Figure 21-7 for location. Errors ...
Page 97
ERCA: ERROR RATE CONTROL REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 80 Hex) ERCB: ERROR RATE CONTROL REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 85 Hex) (MSB) WNOE RNOE TCBE SYMBOL POSITION WNOE ERC.7 RNOE ERC.6 TCBE ERC.5 CE ERC.4 ER3 ERC.3 ER2 ERC.2 ...
Page 98
Table 16-1: Error Rate Options ER3 ER2 ER1 ER0 ...
Page 99
Table 16-2: Error Insertion examples Value Write 000h do not create any errors 001h create a single error 002h create 2 errors 3FFh create 1023 errors NOEL1A: NUMBER of ERRORS LEFT 1 FRAMER A (Address = 83 Hex) NOEL1B: NUMBER ...
Page 100
Four new registers were added for the enhanced functionality of the HDLC controller; RDC1, RDC2, TDC1, and TDC2. Note that the BOC controller is functional when the HDLC controller is used for DS0s. Section 18 contains all of the HDLC ...
Page 101
FDL/Fs EXTRACTION AND INSERTION Each Framer/Formatter has the ability to extract/insert data from/ into the Facility Data Link (FDL) in the ESF framing mode and from/into Fs–bit position in the D4 framing mode. Since SLC–96 utilizes the Fs-bit position, ...
Page 102
Table 18-1: HDLC/BOC CONTROLLER REGISTER LIST NAME HDLC Control Register (HCR) HDLC Status Register (HSR) HDLC Interrupt Mask Register (HIMR) Receive HDLC Information Register (RHIR) Receive BOC Register (RBOC) Receive HDLC FIFO Register (RHFR) Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 ...
Page 103
STATUS REGISTER FOR THE HDLC Four of the HDLC/BOC controller registers (HSR, RHIR, RBOC, and THIR) provide status information. When a particular event has occurred (or is occurring), the appropriate bit in one of these four registers will be ...
Page 104
Receive a HDLC Message or a BOC 1. Enable RBOC and RPS interrupts 2. Wait for interrupt to occur 3. If RBOC=1, then follow steps 5 and RPS=1, then follow steps 7 through LBD=1, ...
Page 105
HDLC/BOC Register Description HCRA: HDLC CONTROL REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 00 Hex) HCRB: HDLC CONTROL REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = A0 Hex) (MSB) RBR RHR TFS SYMBOL POSITION RBR HCR.7 RHR HCR.6 TFS HCR.5 THR HCR.4 TABT HCR.3 ...
Page 106
HSRA: HDLC STATUS REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 01 Hex) HSRB: HDLC STATUS REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = A1 Hex) (MSB) RBOC RPE RPS SYMBOL POSITION RBOC HSR.7 RPE HSR.6 RPS HSR.5 RHALF HSR.4 RNE HSR.3 THALF HSR.2 TNF HSR.1 ...
Page 107
HIMRA: HDLC INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 02 Hex) HIMRB: HDLC INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = A2 Hex) (MSB) RBOC RPE RPS SYMBOL POSITION RBOC HIMR.7 RPE HIMR.6 RPS HIMR.5 RHALF HIMR.4 RNE HIMR.3 THALF HIMR.2 ...
Page 108
RHIRA: RECEIVE HDLC INFORMATION REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 03 Hex) RHIRB: RECEIVE HDLC INFORMATION REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = A3 Hex) (MSB) RABT RCRCE ROVR SYMBOL POSITION RABT RHIR.7 RCRCE RHIR.6 ROVR RHIR.5 RVM RHIR.4 REMPTY RHIR.3 POK RHIR.2 ...
Page 109
RBOCA: RECEIVE BIT ORIENTED CODE REGISTER FRAMER A (Address = 04 Hex) RBOCB: RECEIVE BIT ORIENTED CODE REGISTER FRAMER B (Address = A4 Hex) (MSB) LBD BD BOC5 SYMBOL POSITION LBD RBOC.7 BD RBOC.6 BOC5 RBOC.5 BOC4 RBOC.4 BOC3 RBOC.3 ...
Page 110
THIRA: TRANSMIT HDLC INFORMATION for FORMATTER A (Address = 06 Hex) THIRB: TRANSMIT HDLC INFORMATION for FORMATTER B (Address = A6 Hex) (MSB) – – SYMBOL POSITION – THIR.7 – THIR.6 – THIR.5 – THIR.4 – THIR.3 TEMPTY THIR.2 TFULL ...
Page 111
TBOCA: TRANSMIT BIT ORIENTED CODE for FORMATTER A (Address = 07 Hex) TBOCB: TRANSMIT BIT ORIENTED CODE for FORMATTER B (Address = A7 Hex) (MSB) SBOC HBEN BOC5 SYMBOL POSITION SBOC TBOC.7 HBEN TBOC.6 BOC5 TBOC.5 BOC4 TBOC.4 BOC3 TBOC.3 ...
Page 112
RDC1A: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 90 Hex) RDC1B: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = 94 Hex) (MSB) RDS0E - RDS0M SYMBOL POSITION RDS0E RDC1.7 - RDC1.6 RDS0M RDC1.5 RD4 RDC1.4 ...
Page 113
RDC2A: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 91 Hex) RDC2B: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = 95 Hex) (MSB) RDB8 RDB7 RDB6 SYMBOL POSITION RDB8 RDC2.7 RDB7 RDC2.6 RDB6 RDC2.5 RDB5 RDC2.4 ...
Page 114
TDC1A: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER A (Address = 92 Hex) TDC1B: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 FRAMER B (Address = 96 Hex) (MSB) TDS0E - TDS0M SYMBOL POSITION TDS0E TDC1.7 - TDC1.6 TDS0M TDC1.5 TD4 TDC1.4 ...
Page 115
TDC2A: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER A (Address = 93 Hex) TDC2B: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 FRAMER B (Address = 97 Hex) (MSB) TDB8 TDB7 TDB6 SYMBOL POSITION TDB8 TDC2.7 TDB7 TDC2.6 TDB6 TDC2.5 TDB5 TDC2.4 ...
Page 116
If enabled via CCR2.0, the DS2196 will automatically look for five 1’ row, followed finds such a pattern, it will automatically remove the ...
Page 117
TFDL, it will be multiplexed serially (LSB first) into the proper position in the outgoing T1 data stream. After the full 8 bits has been shifted out, the framer will signal the host microcontroller that the ...
Page 118
LINE INTERFACE FUNCTION The line interface function in the DS2196 contains three sections; (1) the receiver which handles clock and data recovery, (2) the transmitter which wave shapes and drives the T1 line, and (3) the jitter attenuator. Each ...
Page 119
Normally, the clock that is output at the RCLKLO pin is the recovered clock from the T1 AMI/B8ZS waveform presented at the RTIP and RRING inputs. When no AMI signal is present at RTIP and RRING, a Receive Carrier Loss ...
Page 120
Table 19-2: TRANSFORMER SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATION Turns Ratio Primary Inductance Leakage Inductance Intertwining Capacitance Transmit Transformer DC Resistance Primary (Device side) Secondary Receive Transformer DC Resistance Primary (Device side) Secondary 19.3 JITTER ATTENUATOR The DS2196 contains an onboard jitter attenuator that ...
Page 121
Figure 19-1: EXTERNAL ANALOG CONNECTIONS Fuse Rp T1 Transmit Line Fuse Rp (larger winding toward Fuse Rp T1 Receive Line Fuse Rp Fuse Rp T1 Receive 100 Line Fuse Rp NOTES: 1. Resistor values are 1%. 2. Circuit requires use ...
Page 122
Figure 19-2: JITTER TOLERANCE 1K 100 10 Mimimum Tolerance Level as per TR 62411 (Dec. 90 Figure 19-3: TRANSMIT WAVEFORM TEMPLATE 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9 0 0 ...
Page 123
Figure 19-4: JITTER ATTENUATION 0dB -20dB -40dB -60dB 62411 (Dec. 90) Prohibited Area 100 1K 10K FREQUENCY (Hz) 123 of 157 100K ...
Page 124
JTAG-BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT 20.1 DESCRIPTION The DS2196 IEEE 1149.1 design supports the standard instruction codes SAMPLE/PRELOAD, BYPASS, and EXTEST. Optional public instructions included with this design are HIGHZ, CLAMP, and IDCODE. See Figure 20-1 for ...
Page 125
TAP CONTROLLER STATE MACHINE This section covers the details on the operation of the Test Access Port (TAP) Controller State Machine. Please see Figure 20.2 for details on each of the states described below. TAP Controller The TAP controller ...
Page 126
Exit2-DR While in this state, a rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS high will put the controller in the Update-DR state and terminate the scanning process. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS low will enter the Shift- DR state. ...
Page 127
Update-IR The instruction code shifted into the instruction shift register is latched into the parallel output on the falling edge of JTCLK as the controller enters this state. Once latched, this instruction becomes the current instruction. A rising edge on ...
Page 128
Table 20-1: Instruction Codes For The DS21352/552 IEEE 1149.1 Architecture Instruction SAMPLE/PRELOAD Boundary Scan BYPASS Bypass EXTEST Boundary Scan CLAMP Boundary Scan HIGHZ Boundary Scan IDCODE Device Identification SAMPLE/PRELOAD A mandatory instruction for the IEEE 1149.1 specification. This instruction supports ...
Page 129
Table 20-3: DEVICE ID CODES DEVICE DS2196 HIGHZ All digital outputs of the DS2196 will be placed in a high impedance state. The BYPASS register will be connected between JTDI and JTDO. CLAMP All digital outputs of the DS2196 will ...
Page 130
Table 20-4: BOUNDARY SCAN REGISTER DESCRIPTION PIN SCAN REGISTER BIT ...
Page 131
PIN SCAN REGISTER BIT ...
Page 132
PIN SCAN REGISTER BIT ...
Page 133
TIMING DIAGRAMS Figure 21-1: RECEIVE SIDE D4 TIMING FRAME RFSYNC 2 RFSYNC RMSYNC RLCLK 3 RLINK Notes: 1. RFSYNC double-wide frame sync is not enabled (RCR2 RFSYNC double-wide frame sync is ...
Page 134
Figure 21-2: RECEIVE SIDE ESF TIMING FRAME RFSYNC 2 RFSYNC RMSYNC 3 RLCLK 4 RLINK 5 RLCLK 6 RLINK Notes: 1. RFSYNC double-wide frame sync is not enabled (RCR2 RFSYNC ...
Page 135
Figure 21-3: RECEIVE SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING RCLK CHANNEL 23 LSB MSB RSER RFSYNC RMSYNC 1 RLOS 2 RBPV RCHCLK 3 RCHBLK RLCLK 4 RLINK Notes: 1. RLOS transitions high during the F-bit time that caused an OOF event or when ...
Page 136
Figure 21-4: TRANSMIT SIDE D4 TIMING FRAME TSYNC / TFSYNC 2 TSYNC 3 TSYNC TLCLK 4 TLINK Notes: 1. TSYNC in the frame mode (TCR2 and double-wide frame sync is not enabled (TCR2.4 ...
Page 137
Figure 21-5: TRANSMIT SIDE ESF TIMING FRAME TSYNC 2 TSYNC 3 TSYNC 4 TLCLK TLINK 6 TLCLK 7 TLINK Notes: 1. TSYNC in the frame mode (TCR2 and double-wide frame sync ...
Page 138
Figure 21-6: TRANSMIT SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING TCLK CHANNEL 1 LSB F MSB TSER 1 TSYNC 2 TSYNC TCHCLK 3 TCHBLK TLCLK 4 TLINK Notes: 1. TSYNC is in the output mode (TCR2 TSYNC is in the input ...
Page 139
Figure 21-7: TRANSMIT DATA FLOW DS0 insertion enable (TDC1.7) DS2152 TRANSMIT DATA FLOW Figure 15.11 TDC2 0 TCD1 (4:0) TCHBLK 1 TDC1.5 TIR Function Select (CCR4.0) 0 TID R RSER (note#1) 1 Software Signaling Enable (TCR1.4) CH 1-12 AIS Enable ...
Page 140
Figure 21-8: RECEIVE DATA FLOW RNEGI B8ZS Decoder Channel Enables RMR1 to RMR3 RPOSI RCR2 Receive Mark Code Insertion SIGNALING EXTRACTION RSER 140 of 157 Receive Code Select Signaling All Ones CCR1.5 RS1 to RS12 Receive Signaling ...
Page 141
... See J-STD-020A specification (0ºC to +70ºC for DS2196L) (-40ºC to +85ºC for DS2196LN) MAX UNITS 5.5 V +0.8 V 3.465 V MAX UNITS 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196L 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196LN) MAX UNITS mA +1.0 µA 10 µ DS2196 NOTES 1 (t =25ºC) A NOTES NOTES ...
Page 142
... DHR t 0 DHW t 15 ASL t 10 AHL t 20 ASD 30 ASH 10 ASED t 20 DDR t 50 DSW 142 of 157 = 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196L 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196LN) MAX UNITS 150 ns ns DS2196 NOTES ...
Page 143
... V DD (-40ºC to +85º MIN TYP 143 of 157 = 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196L) = 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196LN) MAX UNITS ns ns 150 DS2196 NOTES ...
Page 144
... CL t 648 144 of 157 = 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196L 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196LN) MAX UNITS DS2196 NOTES ...
Page 145
... Falling TCLK, TCLKI Rise and Fall Times Delay TCLKO to TPOSO, TNEGO Valid Delay TCLK to TCHBLK, TCHBLK, TSYNC, TLCLK See Figures 22–10 to 22–11 for details. (0ºC to +70º (-40ºC to +85º 3.135 to 3.465V for DS2196LN) DD SYMBOL MIN TYP ...
Page 146
Figure 22-1: INTEL BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX = 1) ALE PW t ASD WR* t ASD RD CS* t ASL AD0-AD7 t CYC ASH t ASED DDR t AHL 146 of ...
Page 147
Figure 22-2: INTEL BUS WRITE TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=1) ALE PW t ASD RD* t ASD WR CS* t ASL AD0-AD7 t CYC ASH t ASED AHL 147 of 157 ...
Page 148
Figure 22-3: MOTOROLA BUS AC TIMING (BTS = 1 / MUX = ASD R/W* t ASL AD0-AD7 (read) CS* t ASL AD0-AD7 (write) t ASH t ASED t CYC t RWS t DDR ...
Page 149
Figure 22-4: INTEL BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=0) ADDRESS VALID WR* t1 CS* RD* DATA VALID t2 t3 149 of 157 t5 t4 ...
Page 150
Figure 22-5: INTEL BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=0) ADDRESS VALID RD* t1 CS* WR 150 of 157 t8 t4 ...
Page 151
Figure 22-6: MOTOROLA BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=1 / MUX=0) ADDRESS VALID R/W* t1 CS* DS* DATA VALID t2 t3 151 of 157 t5 t4 ...
Page 152
Figure 22-7: MOTOROLA BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=1 / MUX=0) ADDRESS VALID R/W* t1 CS* DS 152 of 157 t8 t4 ...
Page 153
Figure 22-8: RECEIVE SIDE AC TIMING RCLK t D1 RSER t D2 RCHCLK RCHBLK t D2 RSYNC RLCLK t D1 RLINK Notes: 1. Shown is RLINK/RLCLK in the ESF framing mode relationship between RCHCLK and ...
Page 154
Figure 22-9: RECEIVE LINE INTERFACE AC TIMING t R WCLK, PCLKI WNRZ, PNRZ RCLKLO t DD RPOSLO, RNEGLO t R RCLKI RPOSI, RNEGI 154 of 157 ...
Page 155
Figure 22-10: TRANSMIT SIDE AC TIMING TCLK TSER t D2 TCHCLK TCHBLK TSYNC TSYNC TLCLK TLINK t SU Notes: 1. TSYNC is in the output mode (TCR2.2 ...
Page 156
Figure 22-11: TRANSMIT LINE INTERFACE SIDE AC TIMING TCLKO TPOSO, TNEGO TFSYNC TCLKLI TPOSLI, TNEGLI 156 of 157 ...
Page 157
LQFP PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS 157 of 157 ...