LH28F016SCR-L12 Sharp, LH28F016SCR-L12 Datasheet

LH28F016SCR-L12
Related parts for LH28F016SCR-L12
LH28F016SCR-L12 Summary of contents
Page 1
... In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that may occur in equipment using any SHARP devices shown in catalogs, data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest device specification sheets before using any SHARP device. ...
Page 2
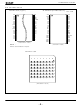
PIN CONNECTIONS 40-PIN TSOP (Type CE RP# 12 ...
Page 3
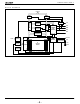
BLOCK DIAGRAM Y DECODER INPUT BUFFER ADDRESS LATCH X DECODER ADDRESS COUNTER DQ - OUTPUT INPUT BUFFER BUFFER IDENTIFIER REGISTER STATUS REGISTER DATA COMPARATOR Y GATING 32 64 k-BYTE BLOCKS - 3 - LH28F016SC-L/SCH-L ...
Page 4
PIN DESCRIPTION SYMBOL TYPE ADDRESS INPUTS : Inputs for addresses during read and write operations. Addresses A -A INPUT 0 20 are internally latched during a write cycle. DATA INPUT/OUTPUTS : Inputs data and commands during CUI write cycles; outputs ...
Page 5
INTRODUCTION This datasheet contains LH28F016SC-L/SCH-L specifications. Section 1 provides a flash memory overview. Sections and 5 describe the memory organization and functionality. Section 6 covers electrical specifications. LH28F016SC-L/ SCH-L flash memories documentation also includes ordering information ...
Page 6
independent of other blocks. Each block PP can be independently erased 100 000 times (3.2 million block erases per device). Block erase suspend mode allows system software to suspend block erase to read data from, or ...
Page 7
Block 1F0000 1EFFFF 64 k-Byte Block 1E0000 1DFFFF 64 k-Byte Block 1D0000 1CFFFF 64 k-Byte Block 1C0000 1BFFFF 64 k-Byte Block 1B0000 1AFFFF 64 k-Byte Block 1A0000 19FFFF 64 k-Byte Block 190000 18FFFF 64 k-Byte Block 180000 ...
Page 8
Byte write suspend allows system software to suspend a byte write to read data from any other flash memory array location. 2.1 Data ...
Page 9
... CPU initialization may not occur because the flash memory may be providing status information instead of array data. SHARP’s flash memories allow proper CPU initialization following a system reset through the use of the RP# input. In this application, RP# is controlled by the same RESET# signal that resets the system CPU ...
Page 10
Write Writing commands to the CUI enable reading of device data and identifier codes. They also control inspection and clearing of the status register. When the CUI additionally controls PP PPH1/2/3 block erasure, byte write, ...
Page 11
... The clear block lock-bits operation simultaneously clears all block lock-bits. If the master lock-bit is not set, the Clear Block Lock-Bits command can be done while RP Commands other than those shown above are reserved by SHARP for future device implementations and should not be used. to enable ...
Page 12
Read Array Command Upon initial device power-up and after exit from deep power-down mode, the device defaults to read array mode. This operation is also initiated by writing the Read Array command. The device remains enabled for reads until ...
Page 13
Fig. 3). The CPU can detect block erase completion by analyzing the output data of the RY/BY# pin or status register bit SR.7. When the block erase is complete, status ...
Page 14
Write Suspend command (see Section 4.8), a byte write operation can also be suspended. During a byte write operation with block erase suspended, status register bit SR.7 will return to “0” and the RY/BY# output will transition to V SR.6 ...
Page 15
When the set lock-bit operation is complete, status register bit SR.4 should be checked error is detected, the status register should be cleared. The CUI will remain in read status register mode until a new command is issued. ...
Page 16
MASTER BLOCK OPERATION LOCK-BIT LOCK-BIT 0 Block Erase X or Byte Write Set Block Lock-Bit 1 X Set Master X X Lock-Bit 0 X Clear Block Lock-Bits 1 X WSMS ESS ECLBS SR.7 = ...
Page 17
Start Write 20H, Block Address Write D0H, Block Address Read Status Register Suspend Block No Erase Loop 0 Suspend SR.7 = Block Erase Yes 1 Full Status Check if Desired Block Erase Complete FULL STATUS CHECK PROCEDURE Read Status Register ...
Page 18
Start Write 40H, Address Write Byte Data and Address Read Status Register Suspend Byte No Write Loop 0 Suspend SR.7 = Byte Write Yes 1 Full Status Check if Desired Byte Write Complete FULL STATUS CHECK PROCEDURE Read Status Register ...
Page 19
Start Write B0H Read Status Register 0 SR Block Erase SR.6 = Completed 1 Read Read Byte Write or Byte Write? Read Array Data Byte Write Loop No Done? Yes Write D0H Write FFH Block Erase Resumed ...
Page 20
Start Write B0H Read Status Register 0 SR Byte Write SR.2 = Completed 1 Write FFH Read Array Data No Done Reading Yes Write D0H Write FFH Read Byte Write Resumed Array Data Fig. 6 Byte Write ...
Page 21
Start Write 60H, Block/Device Address Write 01H/F1H, Block/Device Address Read Status Register 0 SR Full Status Check if Desired Set Lock-Bit Complete FULL STATUS CHECK PROCEDURE Read Status Register Data (See Above Range Error ...
Page 22
Start Write 60H Write D0H Read Status Register 0 SR Full Status Check if Desired Clear Block Lock-Bits Complete FULL STATUS CHECK PROCEDURE Read Status Register Data (See Above Range Error ...
Page 23
... DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS 5.1 Three-Line Output Control The device will often be used in large memory arrays. SHARP provides three control inputs to accommodate multiple memory connections. Three-line control provides for : a. Lowest possible memory power consumption. b. Complete assurance that data bus contention will not occur. To use these control inputs efficiently, an address decoder should enable CE# while OE# should be connected to all memory devices and the system’ ...
Page 24
Device power-off or RP# transitions to V clear the status register. IL The CUI latches commands issued by system software and is not altered by V transitions or WSM actions. Its state is read array mode upon ...
Page 25
... Test condition : Ambient temperature 2. Block erase, byte write and lock-bit configuration operations with V NOTICE : The specifications are subject to change without notice. Verify with your local SHARP sales office that you have the latest datasheet before finalizing a design. WARNING : Stressing the device beyond the Absolute ...
Page 26
CAPACITANCE SYMBOL PARAMETER C Input Capacitance IN C Output Capacitance OUT NOTE : 1. Sampled, not 100% tested. 6.2.2 AC INPUT/OUTPUT TEST CONDITIONS 2.7 INPUT 0.0 AC test inputs are driven at 2.7 V for a Logic ...
Page 27
V 1N914 DEVICE UNDER TEST Includes Jig L Capacitance Fig. 12 Transient Equivalent Testing Load Circuit Test Configuration Capacitance Loading Value TEST CONFIGURATION V = 3.3±0.3 V, 2.7 to 3.6 V ...
Page 28
DC CHARACTERISTICS SYMBOL PARAMETER NOTE I Input Load Current LI I Output Leakage Current Standby Current CCS CC LH28F016 V Deep Power- SC CCD Down Current LH28F016 SCH Read ...
Page 29
DC CHARACTERISTICS (contd.) SYMBOL PARAMETER NOTE Input Low Voltage Input High Voltage IH V Output Low Voltage Output High Voltage OH1 (TTL) Output High Voltage OH2 (CMOS) ...
Page 30
AC CHARACTERISTICS - READ-ONLY OPERATIONS V = 2 +70 • VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Read Cycle Time AVAV t Address to Output Delay AVQV t CE# to Output Delay ELQV ...
Page 31
AC CHARACTERISTICS - READ-ONLY OPERATIONS (contd.) • 5.0±0.25 V, 5.0±0 VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Read Cycle Time AVAV t Address to Output Delay AVQV t CE# to Output Delay ELQV t RP# High ...
Page 32
Standby V IH ADDRESSES ( CE# ( OE# ( WE# ( High Z DATA (D/Q) ( ...
Page 33
AC CHARACTERISTICS - WRITE OPERATION V = 2 +70 • VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Write Cycle Time AVAV t RP# High Recovery to WE# Going Low PHWL t CE# Setup ...
Page 34
AC CHARACTERISTICS - WRITE OPERATION (contd.) • 5.0±0.25 V, 5.0±0 VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Write Cycle Time AVAV RP# High Recovery to WE# t PHWL Going Low t CE# Setup to WE# Going ...
Page 35
V IH ADDRESSES ( CE# ( ELWL V IH OE# ( WE# ( High DATA (D/Q) t PHWL V IL ...
Page 36
ALTERNATIVE CE#-CONTROLLED WRITES • 2 +70˚C or – VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Write Cycle Time AVAV t RP# High Recovery to CE# Going Low PHEL t ...
Page 37
ALTERNATIVE CE#-CONTROLLED WRITES (contd.) • 5.0±0.25 V, 5.0±0 VERSIONS SYMBOL PARAMETER t Write Cycle Time AVAV RP# High Recovery to CE# t PHEL Going Low t WE# Setup to CE# Going Low WLEL ...
Page 38
V IH ADDRESSES ( AVAV V IH WE# ( WLEL V IH OE# ( CE# ( High DATA (D/Q) t ...
Page 39
RESET OPERATIONS V OH RY/BY# ( RP# ( RY/BY# ( RP# ( 2.7 V/3.3 V RP# (P) V ...
Page 40
BLOCK ERASE, BYTE WRITE AND LOCK-BIT CONFIGURATION PERFORMANCE • 3.3±0 +70˚C or – SYMBOL PARAMETER NOTE t WHQV1 Byte Write Time t EHQV1 Block Write Time t WHQV2 ...
Page 41
... ORDERING INFORMATION Product line designator for all SHARP Flash products ( Device Density 016 = 16 M-bit Architecture S = Symmetrical Block Power Supply Type C = SmartVoltage Technology Operating Temperature Blank = – + OPTION ORDER CODE 1 ...
Page 42
TSOP (TSOP040-P-1020 0.3 20.0 0.2 18.4 0.3 19.0 PACKAGING Package base plane ...
Page 43
SOP (SOP044-P-0600 0.4 0 0.1 0.15 M 1.27 TYP 0.2 28.2 PACKAGING 0.15 0.05 Package base plane ...
Page 44
CSP (FBGA048-P-0810 0.1 S 3.0 0.8 0 0.1 S TYP. 0.4 + 0.2 10 TYP. TYP. TYP 0.03 0. PACKAGING Land ...