S71PL064J80BAW0K Advanced Micro Devices, S71PL064J80BAW0K Datasheet

S71PL064J80BAW0K
Related parts for S71PL064J80BAW0K
S71PL064J80BAW0K Summary of contents
Page 1
S71PL254/127/064/032J based MCPs Stacked Multi-Chip Product (MCP) Flash Memory and RAM 256M/128/64/32 Megabit (16/8/4/2M x 16-bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Simultaneous Operation Page Mode Flash Memory and 64/32/16/8/4 Megabit (4M/2M/1M/512K/256K x 16-bit) Static RAM/Pseudo Static RAM Distinctive Characteristics MCP Features Power ...
Page 2
Product Selector Guide 32Mb Flash Memory Device-Model# Flash Access time (ns) S71PL032J04-0B S71PL032J04-0F S71PL032J08-0B S71PL032J40-07 S71PL032J80-05 S71PL032J80-07 S71PL032JA0-0K S71PL032JA0-0F 64Mb Flash Memory Device-Model# Flash Access time (ns) S71PL064J08-0B S71PL064J08-0U S71PL064J80-0K S71PL064JA0-05 S71PL064JA0-0K S71PL064JA0-0P S71PL064JB0-07 S71PL064JB0-0U 128Mb Flash Memory Device-Model# Flash ...
Page 3
Flash Memory (2xS29PL127J) Device-Model# Flash Access time (ns) S71PL254JB0-T7 S71PL254JB0-TB S71PL254JB0-TU S71PL254JC0-TB S71PL254JC0-TU S71PL254JC0-TZ July 16, 2004 S71PL254/127/064/032J_00_A4 pSRAM density pSRAM Access time (ns) 65 32M pSRAM 65 ...
Page 4
S71PL254/127/064/032J based MCPs Distinctive Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 MCP Features ........................................................................................................ 1 General Description . . ...
Page 5
Table 18. Sector Protection Command Definitions .................. 72 Write Operation Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73 DQ7: Data# Polling ............................................................................................73 Figure 6. Data# Polling ...
Page 6
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . ...
Page 7
Data Retention Characteristics (4M Version G) .................................... 154 Data Retention Characteristics (8M Version C) .................................... 154 Data Retention Characteristics (8M Version D) .................................... 154 Timing Diagrams ................................................................................................ 154 Figure 73. Timing Waveform of Read Cycle(1) (Address Controlled, CS#1=OE#=V , CS2=WE#=V ...
Page 8
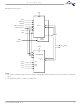
MCP Block Diagram CE#f1 WP#/ACC RESET# Flash-only Address Shared Address OE# WE# CE#f2 (Note 1) CE#s UB#s LB#s CE2 Notes: 1. For 1 Flash + pSRAM, CE#f1=CE#. For 2 Flash + pSRAM, CE#=CE#f1 and CE#f2 is the chip-enable for the ...
Page 9
Connection Diagram (S71PL032J VSS F1 F2 CE1#f OE CE1#s DQ0 H2 DQ8 Notes: 1. May be shared depending on density. — ...
Page 10
Connection Diagram (S71PL064J VSS F1 F2 CE1#f OE CE1#s DQ0 H2 DQ8 Notes: 1. May be shared depending on density. — ...
Page 11
Connection Diagram (S71PL127J) 64-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array VSS H2 H3 CE#f OE CE1#s DQ0 K3 DQ8 M1 NC ...
Page 12
Connection Diagram (S71PL254J RFU RFU C2 C3 RFU VSS H2 H3 CE#f1 OE CE1#s DQ0 K2 K3 RFU ...
Page 13
Pin Description A21–A0 DQ15–DQ0 CE1#f CE#f2 CE1#ps CE2ps OE# WE# RY/BY# UB# LB# RESET# WP#/ACC ...
Page 14
Ordering Information The order number is formed by a valid combinations of the following: S71PL 127 July 16, 2004 S71PL254/127/064/032J_00_A4 PACKING TYPE ...
Page 15
S71PL032J Valid Combinations Base Ordering Package & Part Number Temperature S71PL032J04 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J08 S71PL032J40 BAW S71PL032J80 S71PL032J80 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J08 S71PL032J40 BFW S71PL032J80 S71PL032J80 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J08 S71PL032J40 BAI S71PL032J80 S71PL032J80 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032JA0 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J04 S71PL032J08 ...
Page 16
S71PL064J Valid Combinations Package & Base Ordering Package Modifier/ Temperatur Part Number e S71PL064J08 S71PL064J08 S71PL064J80 S71PL064JA0 S71PL064JA0 BAW S71PL064JB0 S71PL064JB0 S71PL064J80 S71PL064JA0 S71PL064J08 S71PL064J08 S71PL064J80 S71PL064JA0 S71PL064JA0 BFW S71PL064JB0 S71PL064JB0 S71PL064J80 S71PL064JA0 S71PL064J08 S71PL064J08 S71PL064J80 S71PL064JA0 BAI S71PL064JA0 S71PL064JB0 ...
Page 17
S71PL127J Valid Combinations Base Ordering Package & Part Number Temperature S71PL127JA0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 BAW S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JA0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 BFW S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JA0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 BAI S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JC0 S71PL127JA0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 S71PL127JB0 BFI S71PL127JC0 ...
Page 18
S71PL254J Valid Combinations Base Ordering Package & Part Number Temperature S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 BAW S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 BFW S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 BAI S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 S71PL254JB0 BFI S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 S71PL254JC0 Notes: 1. ...
Page 19
Physical Dimensions TLC056—56-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA 7mm Package D 0.15 C (2X) INDEX MARK PIN A1 CORNER 10 TOP VIEW SIDE VIEW 6 b 56X 0. 0. ...
Page 20
TLA064—64-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA 11.6mm Package D 0.15 C (2X) INDEX MARK PIN A1 CORNER 10 TOP VIEW SIDE VIEW 6 b 64X 0. 0. PACKAGE TLA ...
Page 21
FTA084—84-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA 11.6mm D 0.15 C (2X) INDEX MARK PIN A1 CORNER 10 TOP VIEW SIDE VIEW 6 b 84X 0. 0. PACKAGE FTA 084 ...
Page 22
MCP 128/128/64/32 Megabit (8/4 16-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only, Simultaneous Read/Write Flash Memory with Enhanced VersatileIO Distinctive Characteristics ARCHITECTURAL ADVANTAGES 128/64/32Mbit Page Mode devices — Page size of 8 words: Fast page read access from random locations within the ...
Page 23
HARDWARE FEATURES Ready/Busy# pin (RY/BY#) — Provides a hardware method of detecting program or erase cycle completion Hardware reset pin (RESET#) — Hardware method to reset the device to reading array data WP#/ ACC (Write Protect/Acceleration) input — ...
Page 24
General Description The PL127J/PL064J/PL032J is a 128/128/64/32Mbit, 3.0 volt-only Page Mode and Simultaneous Read/Write Flash memory device organized as 8/8/4/2 Mwords. The word-wide data (x16) appears on DQ15-DQ0. This device can be pro- grammed in-system or in standard EPROM programmers. ...
Page 25
Device programming occurs by executing the program command sequence. The Unlock Bypass mode facilitates faster programming times by requiring only two write cycles to program data instead of four. Device erasure occurs by executing the erase command sequence. The host ...
Page 26
Product Selector Guide Part Number 2.7–3 Speed Option V = 2.7–3 1.65–1.95 V (PL127J only) IO Max Access Time ACC Max CE# Access ...
Page 27
Block Diagram RY/BY# (See Note RESET# WE# State Control Command Register CE# OE# V Detector CC Amax–A3 A2–A0 Notes: 1. RY/BY open drain output. 2. Amax = A22 (PL127J), A21 (PL064J), A20 (PL032J) 26 ...
Page 28
Simultaneous Read/Write Block Diagram Mux Amax–A0 RY/BY# Amax–A0 RESET# STATE WE# CONTROL CE# & WP#/ACC COMMAND REGISTER DQ0–DQ15 Amax–A0 Mux Note: Amax = A22 (PL127J), A21 (PL064J), A20 (PL032J) Note: Pinout shown for PL127J. May 21, ...
Page 29
Pin Description Amax–A0 DQ15–DQ0 CE# OE# WE RY/BY# WP#/ACC RESET# CE#1 Notes: 1. Amax = A22 (PL127J), A21 (PL064J), A20 (PL032J) Logic Symbol ...
Page 30
Device Bus Operations This section describes the requirements and use of the device bus operations, which are initiated through the internal command register. The command register itself does not occupy any addressable memory location. The register is a latch used ...
Page 31
OE# to valid data at the out- put inputs (assuming the addresses have been stable for at least t Page Mode Read The device is capable of fast page ...
Page 32
Writing Commands/Command Sequences To write a command or command sequence (which includes programming data to the device and erasing sectors of memory), the system must drive WE# and CE and OE The device features ...
Page 33
If the device is deselected during erasure or programming, the device draws ac- tive current until the operation is completed “DC Characteristics” ...
Page 34
Bank Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 SA11 SA12 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA16 SA17 SA18 SA19 SA20 SA21 SA22 SA23 SA24 SA25 SA26 SA27 SA28 SA29 SA30 SA31 SA32 SA33 SA34 SA35 SA36 SA37 ...
Page 35
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA39 SA40 SA41 SA42 SA43 SA44 SA45 SA46 SA47 SA48 SA49 SA50 SA51 SA52 SA53 SA54 SA55 SA56 SA57 SA58 SA59 SA60 SA61 SA62 SA63 SA64 SA65 SA66 SA67 SA68 SA69 SA70 ...
Page 36
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA79 SA80 SA81 SA82 SA83 SA84 SA85 SA86 SA87 SA88 SA89 SA90 SA91 SA92 SA93 SA94 SA95 SA96 SA97 SA98 SA99 SA100 SA101 SA102 SA103 SA104 SA105 SA106 SA107 SA108 SA109 SA110 ...
Page 37
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA119 SA120 SA121 SA122 SA123 SA124 SA125 SA126 SA127 SA128 SA129 SA130 SA131 SA132 SA133 SA134 SA135 SA136 SA137 SA138 SA139 SA140 SA141 SA142 SA143 SA144 SA145 SA146 SA147 SA148 SA149 SA150 ...
Page 38
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA159 SA160 SA161 SA162 SA163 SA164 SA165 SA166 SA167 SA168 SA169 SA170 SA171 SA172 SA173 SA174 SA175 SA176 SA177 SA178 SA179 SA180 SA181 SA182 SA183 SA184 SA185 SA186 SA187 SA188 SA189 SA190 ...
Page 39
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA199 SA200 SA201 SA202 SA203 SA204 SA205 SA206 SA207 SA208 SA209 SA210 SA211 SA212 SA213 SA214 SA215 SA216 SA217 SA218 SA219 SA220 SA221 SA222 SA223 SA224 SA225 SA226 SA227 SA228 SA229 SA230 ...
Page 40
Table 4. PL127J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA231 SA232 SA233 SA234 SA235 SA236 SA237 SA238 SA239 SA240 SA241 SA242 SA243 SA244 SA245 SA246 SA247 SA248 SA249 SA250 SA251 SA252 SA253 SA254 SA255 SA256 SA257 SA258 SA259 SA260 SA261 SA262 ...
Page 41
Bank Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 SA11 SA12 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA16 SA17 SA18 SA19 SA20 SA21 SA22 SA23 SA24 SA25 SA26 SA27 SA28 SA29 SA30 SA31 SA32 SA33 SA34 SA35 SA36 SA37 ...
Page 42
Table 5. PL064J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA48 SA49 SA50 SA51 SA52 SA53 SA54 SA55 SA56 SA57 SA58 SA59 SA60 SA61 SA62 SA63 SA64 SA65 SA66 SA67 SA68 SA69 SA70 SA71 SA72 SA73 SA74 SA75 SA76 SA77 SA78 SA79 ...
Page 43
Table 5. PL064J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA96 SA97 SA98 SA99 SA100 SA101 SA102 SA103 SA104 SA105 SA106 SA107 SA108 SA109 SA110 SA111 SA112 SA113 SA114 SA115 SA116 SA117 SA118 SA119 SA120 SA121 SA122 SA123 SA124 SA125 SA126 SA127 ...
Page 44
Bank Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 SA11 SA12 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA16 SA17 SA18 SA19 SA20 SA21 SA22 SA23 SA24 SA25 SA26 SA27 SA28 SA29 SA30 SA31 SA32 SA33 SA34 SA35 SA36 SA37 ...
Page 45
Table 6. PL032J Sector Architecture (Continued) Bank Sector SA39 SA40 SA41 SA42 SA43 SA44 SA45 SA46 SA47 SA48 SA49 SA50 SA51 SA52 SA53 SA54 SA55 SA56 SA57 SA58 SA59 SA60 SA61 SA62 SA63 SA64 SA65 SA66 SA67 SA68 SA69 SA70 ...
Page 46
Autoselect Mode The autoselect mode provides manufacturer and device identification, and sector protection verification, through identifier codes output on DQ7–DQ0. This mode is primarily intended for programming equipment to automatically match a device to be programmed with its corresponding programming ...
Page 47
Table 9. PL127J Boot Sector/Sector Block Addresses for Protection/Unprotection Sector A22-A12 SA0 00000000000 SA1 00000000001 SA2 00000000010 SA3 00000000011 SA4 00000000100 SA5 00000000101 SA6 00000000110 SA7 00000000111 SA8 00000001XXX SA9 00000010XXX SA10 00000011XXX SA11-SA14 000001XXXXX SA15-SA18 000010XXXXX SA19-SA22 000011XXXXX SA23-SA26 ...
Page 48
Table 10. PL064J Boot Sector/Sector Block Addresses for Protection/Unprotection Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 SA11-SA14 SA15-SA18 SA19-SA22 SA23-SA26 SA27-SA30 SA31-SA34 SA35-SA38 SA39-SA42 SA43-SA46 SA47-SA50 SA51-SA54 SA55-SA58 SA59-SA62 SA63-SA66 SA67-SA70 SA71-SA74 SA75-SA78 SA79-SA82 SA83-SA86 ...
Page 49
Table 10. PL064J Boot Sector/Sector Block Addresses for Protection/Unprotection Sector SA139 SA140 SA141 Table 11. PL032J Boot Sector/Sector Block Addresses for Protection/Unprotection Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 SA11-SA14 SA15-SA18 SA19-SA22 SA23-SA26 SA27-SA30 SA31-SA34 ...
Page 50
Password Mode Locking Bit permanently sets the device to the Password Sec- tor Protection mode not possible to switch between the two protection modes once a locking bit has been set. One of the two modes must be ...
Page 51
PPBs can potentially be over-erased. The Flash device does not have a built-in means of preventing sector PPBs over-erasure. Persistent Protection Bit Lock (PPB Lock) The Persistent Protection Bit Lock (PPB Lock global ...
Page 52
Non-Volatile PPBs. In effect, the PPB Lock “freezes” the PPBs into their cur- rent state. The only way to clear the PPB Lock through a power cycle possible to have sectors that have ...
Page 53
When the device is first powered on, or comes out of a reset cycle, the PPB Lock bit set to the locked state, rather than cleared to the unlocked state. The only means to clear the PPB Lock bit is ...
Page 54
Write Protect (WP#) The Write Protect feature provides a hardware method of protecting the upper two and lower two sectors(PL127J 268, and 269, PL064J 140, and 141, PL032J 76, and 77, PL129J: SA1-133, SA1-134,SA2-0 ...
Page 55
START PLSCNT = 1 RESET Wait 4 µs No First Write Temporary Sector Cycle = 60h? Unprotect Mode Yes Set up sector address Sector Protect: Write 60h to sector address with A7-A0 = 00000010 Wait 100 µs ...
Page 56
Temporary Sector Unprotect This feature allows temporary unprotection of previously protected sectors to change data in-system. The Sector Unprotect mode is activated by setting the RESET# pin grammed or erased by selecting the sector addresses. Once V ...
Page 57
SecSi Sector Factory-locked Indicator Bit (DQ7) is permanently set to a “1”. Op- tional Spansion programming services can program the factory-locked area with a random ESN, a customer-defined code, or any combination of the two. Because only FASL can program ...
Page 58
Hardware Data Protection The command sequence requirement of unlock cycles for programming or erasing provides data protection against inadvertent writes. In addition, the following hardware data protection measures prevent accidental erasure or programming, which might otherwise be caused by spurious ...
Page 59
Common Flash Memory Interface (CFI) The Common Flash Interface (CFI) specification outlines device and host system software interrogation handshake, which allows specific vendor-specified soft- ware algorithms to be used for entire families of devices. Software support can then be device-independent, ...
Page 60
Addresses Data 1Bh 0027h 1Ch 0036h 1Dh 0000h 1Eh 0000h 1Fh 0003h 20h 0000h 21h 0009h 22h 0000h 23h 0004h 24h 0000h 25h 0004h 26h 0000h Addresses Data 0018h (PL127J) 27h 0017h (PL064J) 0016h (PL032J) 28h 0001h 29h 0000h 2Ah ...
Page 61
Table 16. Primary Vendor-Specific Extended Query Addresses Data 40h 0050h 41h 0052h 42h 0049h 43h 0031h 44h 0033h 45h TBD 46h 0002h 47h 0001h 48h 0001h 49h 0007h (PLxxxJ) 00E7h (PL127J) 4Ah 0077h (PL064J) 003Fh (PL032J) 4Bh 0000h 4Ch 0002h ...
Page 62
Table 16. Primary Vendor-Specific Extended Query (Continued) Addresses Data 0027h (PL127J) 5Bh 0017h (PL064J) 000Fh (PL032J) May 21, 2004 S29PL127_064_032J_00_A1 Bank 4 Region Information X = Number of Sectors ...
Page 63
Command Definitions Writing specific address and data commands or sequences into the command register initiates device operations. Table sequences. Writing incorrect address and data values or writing them in the improper sequence may place the device in an unknown state. ...
Page 64
If DQ5 goes high during a program or erase operation, writing the reset command returns the banks to the read mode (or erase-suspend-read mode if that bank was in Erase Suspend). Autoselect Command Sequence The autoselect command sequence allows the ...
Page 65
The program command sequence should be reinitiated once that bank has returned to the read mode, to ensure data integrity. Note that the SecSi Sec- tor, autoselect and CFI functions are unavailable when the SecSi Sector is enabled. Programming ...
Page 66
Increment Address Note: See Table 17 Chip Erase Command Sequence Chip erase is a six bus cycle operation. The chip erase command sequence is ini- tiated by writing two unlock cycles, followed by a set-up command. Two additional unlock write ...
Page 67
Refer to the Erase/Program Operations tables in the AC Characteristics section for parameters, and section for timing diagrams. Sector Erase Command Sequence Sector erase is a six bus cycle operation. The sector ...
Page 68
Notes: 1. See Table 17 for erase command sequence. 2. See the section on DQ3 for information on the sector erase timer. Erase Suspend/Erase Resume Commands The Erase Suspend command, B0h, allows the system to interrupt a sector erase operation ...
Page 69
DQ7 or DQ6 status bits, just as in the standard Word Program operation. Refer to the Write Operation Status section for more information. In the erase-suspend-read mode, the system can also issue the autoselect com- mand sequence. ...
Page 70
Protection Mode Locking Bit is programmed, the Persistent Sector Protection Locking Bit program circuitry is disabled, thereby forcing the device to remain in the Password Protection mode. Exiting the Mode Locking Bit Program command is accomplished by writing the Read/Reset ...
Page 71
Once the Password Unlock command is entered, the RY/BY# indicates that the device is busy. Approximately 1 µs is required for each portion of the unlock. Once the first portion of the password unlock completes (RY/BY# is not low or ...
Page 72
DYBs. The bank address is latched when the command is written. Command The programming of either the PPB or DYB for a given sector or sector group can be verified ...
Page 73
Legend Address of bank switching to autoselect mode, bypass mode, or erase operation. Determined by PL127J: Amax:A20, PL064J: Amax:A19, PL032J: Amax:A18 Program Address (Amax:A0). Addresses latch on falling edge of WE# or CE# pulse, whichever happens ...
Page 74
Legend: DYB = Dynamic Protection Bit OW = Address (A7:A0) is (00011010) PD[3:0] = Password Data ( portions) PPB = Persistent Protection Bit PWA = Password Address. A1:A0 selects portion of password. PWD = Password Data being verified. ...
Page 75
If not all selected sectors are protected, the Em- bedded Erase algorithm erases the unprotected sectors, and ignores the selected sectors that are protected. However, if the system reads DQ7 at an address within ...
Page 76
RY/BY#: Ready/Busy# The RY/BY dedicated, open-drain output pin which indicates whether an Embedded Algorithm is in progress or complete. The RY/BY# status is valid after the rising edge of the final WE# pulse in the command sequence. Since ...
Page 77
Note: The system should recheck the toggle bit even if DQ5 = “1” because the toggle bit may stop toggling as DQ5 changes to “1.” See the DQ6: Toggle Bit I and DQ2: Toggle Bit II for more information. DQ2: ...
Page 78
After the second read, the system would compare the new value of the toggle bit with the first. If the toggle bit is not toggling, the device has completed ...
Page 79
Status Embedded Program Algorithm Standard Mode Embedded Erase Algorithm Erase Suspended Sector Erase-Suspend- Erase Read Suspend Non-Erase Mode Suspended Sector Erase-Suspend-Program Notes: 1. DQ5 switches to ‘1’ when an Embedded Program or Embedded Erase operation has exceeded the maximum timing ...
Page 80
Absolute Maximum Ratings Storage Temperature Plastic Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C Ambient Temperature with Power Applied . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 81
Operating Ranges Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the de- vice is guaranteed. Industrial (I) Devices Ambient Temperature (T Extended (E) Devices Ambient Temperature (T Supply Voltages ...
Page 82
DC Characteristics Parameter Parameter Description Symbol I Input Load Current LI I A9, OE#, RESET# Input Load Current LIT I Reset Leakage Current LR I Output Leakage Current Active Read Current (Notes 1, 2) CC1 CC I ...
Page 83
AC Characteristic Test Conditions Device Under Test 3 Note: Diodes are IN3064 or equivalent Output Load Output Load Capacitance, C (including jig capacitance) L Input Rise and Fall Times Input Pulse Levels Input timing ...
Page 84
SWITCHING WAVEFORMS Table 22. KEY TO SWITCHING WAVEFORMS WAVEFORM Don’t Care, Any Change Permitted VIO VIO/2 In 0.0 V Figure 10. Input Waveforms and Measurement Levels VCC RampRate All DC characteristics are specified for a V >=V - 100 mV. ...
Page 85
Read Operations Parameter JEDEC Std. Description t t Read Cycle Time (Note 1) AVAV Address to Output Delay AVQV ACC t t Chip Enable to Output Delay ELQV CE t Page Access Time PACC t t Output ...
Page 86
Amax-A3 A2-A0 Data CE# OE# Reset Parameter JEDEC Std RESET# Pin Low (During Embedded Algorithms) t Ready to Read Mode (See Note) RESET# Pin Low (NOT During Embedded t Ready Algorithms) to Read Mode (See Note) t RESET# Pulse Width ...
Page 87
RY/BY# CE#, OE# RESET# RY/BY# CE#, OE# RESET Ready Reset Timings NOT during Embedded Algorithms Reset Timings during Embedded Algorithms t Ready t ...
Page 88
Erase/Program Operations Parameter JEDEC Std Description t t Write Cycle Time (Note 1) AVAV Address Setup Time AVWL AS Address Setup Time to OE# low during toggle bit t ASO polling t t Address Hold Time WLAX ...
Page 89
Timing Diagrams Program Command Sequence (last two cycles Addresses 555h CE# OE# WE Data RY/BY VCS Notes program address program data ...
Page 90
Erase Command Sequence (last two cycles Addresses 2AAh CE# OE# WE Data RY/BY# t VCS V CC Notes sector address (for Sector Erase Valid Address for reading status data (see “Write ...
Page 91
Addresses t ACC OE# t OEH WE# DQ7 DQ6–DQ0 t BUSY RY/BY# Note Valid address. Illustration shows first status cycle after command sequence, last status read cycle, and array data read cycle Figure ...
Page 92
Enter Erase Embedded Suspend Erasing Erase Erase Suspend WE# DQ6 DQ2 Note:Note: DQ2 toggles only when read at an address within an erase-suspended sector. The system may use OE# or CE# to toggle DQ2 and DQ6. Protect/Unprotect Parameter JEDEC Std ...
Page 93
RESET# SA, A6, A1, A0 Sector Group Protect/Unprotect Data 60h 1 µs CE# WE# OE# Notes: 1. For sector protect For sector unprotect ...
Page 94
Controlled Erase Operations Table 27. Alternate CE# Controlled Erase and Program Operations Parameter JEDEC Std Description t t Write Cycle Time (Note 1) AVAV Address Setup Time AVWL Address Hold Time ELAX AH t ...
Page 95
Addresses WE# OE# CE Data t RH RESET# RY/BY# Notes: 1. Figure indicates last two bus cycles of a program or erase operation program address, ...
Page 96
Table 29. Erase And Programming Performance Parameter Sector Erase Time PL127J Chip Erase Time PL064J PL032J Word Program Time Accelerated Word Program Time PL127J Chip Program Time PL064J (Note 3) PL032J Notes: 1. Typical program and erase times assume the ...
Page 97
Type 2 pSRAM 16Mb (1Mb Word x 16-bit) 32Mb (2Mb Word x 16-bit) 64Mb (4Mb Word x 16-bit) Features Process Technology: CMOS Organization: x16 bit Power Supply Voltage: 2.7~3.1V Three State Outputs Compatible with Low Power SRAM Product Information Density ...
Page 98
Power Up Sequence 1. Apply power. 2. Maintain stable power (V CS1#=high or CS2=low min.=2.7V) for a minimum 200 µs with CC Type 2 pSRAM pSRAM_Type02_15A0 May 3, ...
Page 99
Timing Diagrams Power Up V CC(Min CS2 Notes: 1. After V reaches V (Min.), wait 200 µs with CS1# high. Then the device gets into the normal operation CC(Min CS1# CS2 Notes: ...
Page 100
Absolute Maximum Ratings Item Voltage on any pin relative to V Voltage on V supply relative Power Dissipation Operating Temperature Notes: 1. Stresses greater than those listed under Functional operation should be restricted to be used under ...
Page 101
Item Symbol Average Operating Current I CC2 Standby Current (CMOS) I SB1 Notes: 1. Standby mode is supposed to be set up after at least one active operation after power up. ISB1 is measure after 60ms from the ...
Page 102
Item Symbol I Average Operating Current I CC2 Standby Current (CMOS) I SB1 Notes: 1. Standby mode is supposed to be set up after at least one active operation after power up. ISB1 is measure after 60ms from ...
Page 103
ACC Characteristics (Ta = -40°C to 85°C, V Symbol t Read Cycle Time RC t Address Access Time AA t Chip Select to Output CO t Output Enable to Valid Output OE t UB#, LB# Access Time BA t Chip ...
Page 104
Timing Diagrams Read Timings Address Data Out Previous Data Valid Figure 26. Timing Waveform of Read Cycle(1) Notes: 1. Address Controlled, CS1#=OE#=V Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# OE# Data out High-Z Figure 27. Timing Waveform of Read Cycle(2) Notes: 1. ...
Page 105
A2 ~ A19, 32Mb A20, 64Mb A21. t and t are defined as the time at which the outputs achieve the open circuit conditions and are not referenced to HZ OHZ output voltage levels. ...
Page 106
Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# WE# Data in Data out Figure 31. Timing Waveform of Write Cycle(3) (CS2 Controlled) Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# WE# Data in Data out Figure 32. Timing Waveform of Write Cycle(4) (UB#, LB# Controlled) Notes: ...
Page 107
Type 3 16 Megabit (1M x 16) CMOS Pseudo SRAM Features Organized as 1M words by 16 bits Fast Cycle Time Standby Current: 100 µA Deep power-down Current: 10 µA (Memory cell data invalid) Byte data control: ...
Page 108
Operation Mode MODE CE1# CE2 Deselect H Deselect X Deselect L Output Disabled L Output Disabled L Lower Byte Read L Upper Byte Read L Word Read L Lower Byte Write L Upper Byte Write L Word Write L Note: ...
Page 109
Table 31. DC Characteristics (T SYMBOL PARAMETER I Input Leakage Current IL I Output Leakage Current LO I Operating Current @ Min Cycle Time CC1 I Operating Current @ Max Cycle Time CC2 I Standby Current (CMOS) SB1 I Deep ...
Page 110
Table 32. AC Characteristics and Operating Conditions (T Cycle Symbol Data Byte Control to End of Write WZH ...
Page 111
CE2=VIH Powe r Initial State on (Wait 200 µs) Powe r Up Sequence Table 34. Standby Mode Characteristics Power Mode Memory Cell Data Standby Deep Power Down Timing Diagrams Address Data Out Previous Data Valid Note: CE1# = OE# = ...
Page 112
Address CE1# UB#, LB# OE# High-Z Data Out Note: CE2 = WE Figure 36. Read Cycle 2—CS1# Controlled Address CE1# UB#, LB# WE# High-Z Data In Data Out Data Undefined Notes: 1. CE2 = ...
Page 113
Address CE1# UB#, LB# WE# Data In High-Z Data Out Notes: 1. CE2 = CE2 = WE Figure 38. Write Cycle 2—CS1# Controlled Address CE1# UB#, LB# WE# Data In High-Z Data Out Notes: ...
Page 114
CE2 Normal Operation Mode CE1 CE2 CE1# CE1# WE# Address Note: has a timing that is not supported at read operation. Data will be lost if your system The S71JL064HA0 Model 61 has multiple invalid address signal shorter ...
Page 115
Type 6 2M Word by 16-bit Cmos Pseudo Static RAM (32M Density) 4M Word by 16-bit Cmos Pseudo Static RAM (64M Density) Features Single power supply voltage of 2.6 to 3.3 V Direct TTL compatibility for all inputs and ...
Page 116
Functional Description Mode CE1# CE2 Read (Word) L Read (Lower Byte) L Read (Upper Byte) L Write (Word) L Write (Lower Byte) L Write (Upper Byte) L Outputs Disabled L Standby H Deep Power-down Standby H Legend:L = Low-level Input ...
Page 117
Symbol Parameter V Output Low Voltage CE1 Operating Current DDO1 mA, t Page Access CE1 DDO2 Operating Current Page add. cycling, t Standby CE1 DDS Current(MOS) CE2 = V Deep ...
Page 118
Symbol t Write Pulse Width WP t Chip Enable to End of Write CW t Data Byte Control to End of Write BW t Address Valid to End of Write AW t Address Set-up Time AS t Write Recovery Time ...
Page 119
Timing Diagrams Read Timings Address A0 to A20(32M A21(64M) CE1# CE2 OE# WE# UB# , LB# D OUT Hi-Z I/O1 to I/O16 April 26, 2004 pSRAM_Type06_14_A0 ...
Page 120
Address Address A3 to A20(32M A21(64M) CE1# CE2 OE# WE# UB#, LB# D OUT Hi-Z I/O1 to I/O16 Figure 44. Page Read Cycle (8 Words Access) 120 ...
Page 121
Write Timings Address A0 to A20 (32M A21(64M) WE# CE1 CE2 UB# , LB# D OUT I/O1 to I/O16 D IN I/O1 to I/O16 Figure 45. Write Cycle #1 (WE# Controlled) (See Note 8) April 26, ...
Page 122
Address A0 to A20 (32M A21(64M) WE# CE1 CE2 UB#, LB# D OUT I/O1 to I/O16 D IN I/O1 to I/O16 Figure 46. Write Cycle #2 (CE# Controlled) (See Note 8) Deep Power-down Timing CE1# CE2 ...
Page 123
Provisions of Address Skew Read In case multiple invalid address cycles shorter than t an active status, at least one valid address cycle over t 10µs. CE1# WE# Address Write In case multiple invalid address cycles shorter than t an ...
Page 124
Type 7 16Mb (1M word x 16-bit) 32Mb (2M word x 16-bit) 64Mb (4M word x 16-bit) CMOS 1M/2M/4M-Word x 16 bit Fast Cycle Random Access Memory with Low Power SRAM Interface Features Asynchronous SRAM Interface Fast Access Time ...
Page 125
Pin Name V Ground SS Functional Description Mode CE2# Standby (Deselect) H Output Disable (Note 1) Output Disable (No Read) Read (Upper Byte) Read (Lower Byte) Read (Word Write Write (Upper Byte) Write (Lower Byte) Write (Word) Power ...
Page 126
The default state is Sleep and it is the lowest power consumption but all data will be lost once CE2 is brought to Low for Power Down not required to program to Sleep mode after power-up. Power Down ...
Page 127
Absolute Maximum Ratings Item Voltage of V Supply Relative Voltage at Any Pin Relative Short Circuit Output Current Storage temperature WARNING: Semiconductor devices can be permanently damaged by application of stress (voltage, current, temperature, ...
Page 128
DC Characteristics (Under Recommended Conditions Unless Otherwise Noted) Parameter Symbol Input Leakage Current Output Leakage OUT I LO Current Disable Output High Voltage Level 0.5mA ...
Page 129
AC Characteristics (Under Recommended Operating Conditions Unless Otherwise Noted) Read Operation Parameter Symbol Read Cycle Time t RC CE1# Access Time t CE OE# Access Time t OE Address Access Time t AA LB# / UB# Access Time t BA ...
Page 130
Applicable A21 (32M and 64M) when CE1# is kept at Low. 6. Applicable only to A0, A1 and A2 (32M and 64M) when CE1# is kept at Low for the page address access case ...
Page 131
AC Characteristics Write Operation Parameter Symbol Write Cycle Time t WC Address Setup Time t AS CE1# Write Pulse Width t CW WE# Write Pulse Width t WP LB#/UB# Write Pulse Width t BW LB#/UB# Byte Mask Setup t BS ...
Page 132
AC Characteristics Power Down Parameters Parameter CE2 Low Setup Time for Power Down Entry CE2 Low Hold Time after Power Down Entry CE1# High Hold Time following CE2 High after Power Down Exit [SLEEP mode only] CE1# High Hold Time ...
Page 133
AC Characteristics AC Test Conditions Symbol Description V Input High Level IH V Input Low Level IL V Input Timing Measurement Level REF t Input Transition Time T AC Measurement Output Load Circuit V DD 0.1µ 134 P ...
Page 134
Timing Diagrams Read Timings ADDRESS t ASC CE1# OE# LB#/ UB# DQ (Output) Note: This timing diagram assumes CE2=H and WE#=H. ADDRESS ADDRESS VALID CE1# Low t ASO OE# LB#/UB# DQ (Output) Figure 53. Read Timing #2 (OE# Address Access ...
Page 135
AX ADDRESS t AA Low CE1#, OE# t LB# UB# DQ1-8 (Output) DQ9-16 (Output) Figure 54. Read Timing #3 (LB#/UB# Byte Access) Note: This timing diagram assumes CE2=H and WE#=H. ADDRESS (A21-A3 ADDRESS ADDRESS VALID (A2-A0) t ...
Page 136
ADDRESS ADDRESS VALID (A21-A3 ADDRESS ADDRESS VALID (A2-A0 CE1# Low t t ASO OE OE LB#/UB# t OLZ t BLZ DQ (Output) Figure 56. Read Timing #5 (Random and Page Address Access for 32M ...
Page 137
ADDRESS t OHAH CE1# Low t AS WE# LB#, UB# t OES OE# t OHZ DQ (Input) Figure 58. Write Timing #2 (WE# Control) Note:This timing diagram assumes CE2=H. ADDRESS CE1# Low t AS WE# LB UB# DQ1-8 ...
Page 138
ADDRESS CE1# Low WE LB UB# DQ1-8 (Input) DQ9-16 (Input) Figure 60. Write Timing #3-2 (WE#/LB#/UB# Byte Write Control) Note: This timing diagram assumes CE2=H and OE#=H. ADDRESS CE1# Low WE LB ...
Page 139
ADDRESS CE1# Low WE LB# DQ1-8 (Input UB# DQ9-16 (Input) Figure 62. Write Timing #3-4 (WE#/LB#/UB# Byte Write Control) Note: This timing diagram assumes CE2=H and OE#=H. Read/Write Timings ADDRESS t t CHAH AS CE1# t ...
Page 140
ADDRESS t t CHAH AS CE1 WE# UB#, LB# t OHCL OE# t CHZ READ DATA OUTPUT Figure 64. Read / Write Timing #1-2 (CE1#/WE#/OE# Control) Notes: 1. This timing diagram assumes CE2=H. 2. OE# ...
Page 141
ADDRESS t CE1# OHAH Low WE OES AS UB#, LB# t BHZ OE READ DATA OUTPUT Figure 66. Read / Write Timing #3 (OE#, WE#, LB#, UB# Control) Notes: 1. This timing diagram assumes CE2=H. ...
Page 142
CE1# CE2 Note: The t specifies after V reaches specified minimum level and applicable to both CE1# and CE2. CHH DD CE1# CE2 t CSP DQ Power Down Entry Figure 69. Power Down Entry and Exit Timing ...
Page 143
RC MSB* 1 ADDRESS t CP CE1# OE# WE# LB#, UB# DQ* RDa 3 Cycle #1 Figure 71. Power Down Program Timing (for 32M/64M Only) Notes: 1. The all address inputs must be High from Cycle #1 to #5. ...
Page 144
SRAM 4/8 Megabit CMOS SRAM Common Features Process Technology: Full CMOS Power Supply Voltage: 2.7~3.3V Three state outputs Version Density F 4Mb G 4Mb C 8Mb D 8Mb Notes: 1. UB#, LB# swapping is available only at x16 ...
Page 145
Functional Description 4M Version F, 4M version G, 8M version C CS1# CS2 OE# WE# BYTE ...
Page 146
Functional Description 8M Version D CS1# CS2 OE# WE ...
Page 147
DC Characteristics Recommended DC Operating Conditions (Note 1) Item Symbol Supply voltage V CC Ground V SS Input high voltage V IH Input low voltage V IL Notes - ° C, unless otherwise specified. A ...
Page 148
DC Operating Characteristics 4M Version F Item Symbol I CC1 Average operating current I CC2 I SB1 Standby Current (CMOS) (Note) Note: Typical values are not 100% tested. DC Operating Characteristics 4M Version G Item Symbol I CC1 Average operating ...
Page 149
DC Operating Characteristics 8M Version C Item Symbol I CC1 Average operating current I CC2 I SB1 Standby Current (CMOS) (Note) Note: Typical values are not 100% tested. DC Operating Characteristics 8M Version D Item Symbol I CC1 Average operating ...
Page 150
AC Operating Conditions Test Conditions Test Load and Test Input/Output Reference Input pulse level: 0.4 to 2.2V Input rising and falling time: 5ns Input and output reference voltage: 1.5V Output load (See Figure 72): CL= 30pF+1TTL Notes: 1. Including scope ...
Page 151
Parameter List Write cycle time Chip select to end of write Address set-up time Address valid to end of write LB#, UB# valid to end of write Write pulse width Write recovery time Write to output high-Z Data to write ...
Page 152
Data Retention Characteristics (4M Version G) Item Symbol V for data retention Data retention current I DR Data retention set-up time t SDR Recovery time t RDR Notes: 1. CS1 controlled:CS1# ≥ V -0.2V. CS2 controlled: CS2 ...
Page 153
Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# OE# Data out High-Z Notes and t are defined as the time at which the outputs achieve the open circuit conditions and are not referenced to HZ OHZ output voltage levels ...
Page 154
Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# WE# Data in Data out Figure 76. Timing Waveform of Write Cycle(2) (CS# controlled, if BYTE# is Low, Ignore UB#/LB# Timing) Address CS1# CS2 UB#, LB# WE# Data in Data out Notes write ...
Page 155
CS1# Controlled V CC 2.7V 2. CS1# GND CS2 Controlled V CC 2.7V CS2 V DR 0.4V GND June 15, 2004 SRAM_Type01_02A0 Data Retention Mode t SDR ...
Page 156
Type 1 4Mbit (256K Word x 16-bit) 8Mbit (512K Word x 16-bit) 16Mbit (1M Word x 16-bit) 32Mbit (2M Word x 16-bit) 64Mbit (4M Word x 16-bit) Features Fast Cycle Times — T < ACC — T ...
Page 157
DC Characteristics (4Mb pSRAM Asynchronous) Symbol Parameter V Power Supply CC V Input High Level IH V Input Low Level IL Input Leakage I IL Current Output Leakage I LO Current Output High V OH Voltage Output Low V OL ...
Page 158
DC Characteristics (8Mb pSRAM Asynchronous) Version Performance Grade Density Symbol Parameter Conditions V Power Supply CC V Input High Level IH V Input Low Level IL Input Leakage I Vin = Current Output Leakage OE = ...
Page 159
DC Characteristics (16Mb pSRAM Asynchronous) Symbol Parameter V Power Supply CC V Input High Level IH V Input Low Level IL I Input Leakage Current IL I Output Leakage Current LO V Output High Voltage OH V Output Low Voltage ...
Page 160
DC Characteristics (16Mb pSRAM Page Mode) Performance Grade Density Symbol Parameter Conditions V Power Supply CC Input High V IH Level Input Low V IL Level Input Leakage I Vin = Current Output OE = ...
Page 161
DC Characteristics (32Mb pSRAM Page Mode) Version Performance Grade Density Symbol Parameter Conditions Power V CC Supply Input High V IH Level Input Low V IL Level Input I Leakage Vin = Current Output OE ...
Page 162
DC Characteristics (64Mb pSRAM Page Mode) Symbol Parameter V Power Supply CC V Input High Level IH V Input Low Level IL Input Leakage I IL Current Output Leakage I LO Current Output High V OH Voltage Output Low V ...
Page 163
Output Load Circuit Power Up Sequence After applying power, maintain a stable power supply for a minimum of 200 µs after CE# > 103 ...
Page 164
AC Characteristics (4Mb pSRAM Page Mode) 3 Volt June 8, 2004 pSRAM_Type01_12_A0 Asynchronous Performance Grade Density 4Mb pSRAM Symbol Parameter Min trc Read cycle time 70 Address Access taa ...
Page 165
Volt 105 Asynchronous Performance Grade -70 Density 4Mb pSRAM Symbol Parameter Min Max twc Write cycle time 70 Chipselect to end tcw 70 of write Address set up ...
Page 166
AC Characteristics (8Mb pSRAM Asynchronous) Version Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter trc Read cycle time Address Access taa Time Chip select to tco output Output enable to toe valid output UB#, LB# Access tba time Chip select to ...
Page 167
Version Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter twc Write cycle time Chip select to tcw end of write Address set up tas Time Address valid to taw end of write UB#, LB# valid tbw to end of write twp ...
Page 168
AC Characteristics (16Mb pSRAM Asynchronous) Performance Grade 3 Volt Symbol trc taa tco toe tba tlz tblz tolz thz tbhz tohz toh June 8, 2004 pSRAM_Type01_12_A0 Asynchronous -55 Density ...
Page 169
Performance Grade 3 Volt Symbol twc tcw tas taw tbw twp twr twhz tdw tdh tow tow tpc tpa twpc tcp 109 Asynchronous -55 Density 16Mb pSRAM Parameter Min ...
Page 170
AC Characteristics (16Mb pSRAM Page Mode) Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter trc Read cycle time Address Access taa Time Chip select to tco output Output enable to toe valid output UB#, LB# Access tba time Chip select to ...
Page 171
Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter twc Write cycle time Chipselect to end tcw of write Address set up tas Time Address valid to taw end of write UB#, LB# valid tbw to end of write twp Write pulse ...
Page 172
AC Characteristics (32Mb pSRAM Page Mode) Version Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter trc Read cycle time Address Access taa Time Chip select to tco output Output enable to toe valid output UB#, LB# Access tba time Chip select ...
Page 173
Version Performance Grade Density 3 Volt Symbol Parameter twc Write cycle time Chipselect to end tcw of write Address set up tas Time Address valid to taw end of write UB#, LB# valid tbw to end of write twp Write ...
Page 174
AC Characteristics (64Mb pSRAM Page Mode) 3 Volt June 8, 2004 pSRAM_Type01_12_A0 Page Mode Performance Grade Density 64Mb pSRAM Symbol Parameter Min trc Read cycle time 70 Address Access ...
Page 175
Volt Timing Diagrams Read Cycle Address Previous Data Valid Data Out Figure 80. Timing of Read Cycle (CE 115 Page Mode Performance Grade -70 ...
Page 176
Address CE# OE# LB#, UB# High-Z Data Out Figure 81. Timing Waveform of Read Cycle (WE June 8, 2004 pSRAM_Type01_12_A0 ...
Page 177
Page Address (A4 - A20) Word Address (A0 - A3) CE# OE# LB#, UB# High-Z Data Out Figure 82. Timing Waveform of Page Mode Read Cycle (WE 117 ...
Page 178
Write Cycle Addr es s CE# LB#, UB# WE# High-Z Dat Out Figure 83. Timing Waveform of Write Cycle (WE# Control, ZZ dres s CE# LB#, UB# WE# Dat ...
Page 179
Page A ddr 20) Wor d A ddr CE# WE# LB#, UB# High-Z Dat a Out Figure 85. Timing Waveform of Page Mode Write Cycle (ZZ# = ...
Page 180
The data in the remainder of the array will be lost. The PASR operation mode is only available during standby time (ZZ# low) and once ZZ# is returned high, the device resumes full array refresh. All future PASR cycles ...
Page 181
A21 - A8 A7 Reserved Must set to all 0 Page Mode 0 = Page Mode Disabled (default Page Mode Enabled Address CE# WE# t CDZZ ZZ# Figure 87. Mode Register Update Timings (UB#, LB#, OE# are Don’t ...
Page 182
ZZ# t CDZZ CE# Figure 88. Deep Sleep Mode - Entry/Exit Timings June 8, 2004 pSRAM_Type01_12_A0 ZZMIN pSRAM Type 122 ...
Page 183
Mode Register Update and Deep Sleep Timings Item Chip deselect to ZZ# low ZZ# low to WE# low Write register cycle time Chip enable to end of write Address valid to end of write Write recovery time Address setup time ...
Page 184
Deep ICC Characteristics (for 64Mb) Item Symbol PASR Mode Standby Current I PASR Item Temperature Compensated Refresh Current Item Symbol Deep Sleep Current I ZZ Address Patterns for PAR (A3= 0, A4=1) (32M Active Section 0 1 ...
Page 185
Low Power ICC Characteristics (32M) Item Symbol PAR Mode Standby Current I PAR RMS Mode Standby Current I RMSSB Deep Sleep Current I ZZ Address Patterns for PAR (A3= 0, A4=1) (16M Active Section ...
Page 186
Revision Summary Revision A (May 3, 2004) Initial release. Revision (May 6, 2004) MCP Features Corrected the high performance access times. Connection Diagrams Added reference points on all diagrams. Ordering ...
Page 187
Added row with the following content:S71PL064JB0-07; 65; 32M pSRAM; 70; Psram 1; TLC056. “32Mb Flash Memory” on page 2 Replaced “S71PL032JA0-08” with “S71PL032JA0-0F”. “64Mb Flash Memory” on page 2 Replaced “S71PL032JA0-07” with “S71PL032JA0-0K”. “128Mb Flash Memory” on page 2 Added ...
Page 188
“S71PL254J Valid Combinations” on page 17 Added 4 rows with the following content: S71PL254JC0; TB; pSRAM2/70. Added 4 rows with the following content: S71PL254JB0; TB; pSRAM2/70. “S71PL254/127/064/032J based MCPs” on page 1 Added ...