SC4502H Semtech Corporation, SC4502H Datasheet - Page 10

SC4502H
Manufacturer Part Number
SC4502H
Description
1.4 Amp, 2 Mhz Step-up Switching Regulator With Soft-start | Semtech
Manufacturer
Semtech Corporation
Datasheet
1.SC4502H.pdf
(19 pages)
temperature and voltage characteristics. One may be
tempted to use Z5U and Y5V ceramic capacitors for
output filtering because of their high capacitance and
small sizes. However these types of capacitors have high
temperature and high voltage coefficients. For example,
the capacitance of a Z5U capacitor can drop below 60%
of its room temperature value at –25 C and 90 C. X5R
ceramic capacitors, which have stable temperature and
voltage coefficients, are the preferred type.
The diode current waveform in Figure 4 is discontinuous
with high ripple-content. In a buck converter, the inductor
ripple current
The output ripple voltage of a boost regulator is however
much higher and is determined by the absolute value of
the inductor current. Decreasing the inductor ripple
current does not appreciably reduce the output ripple
voltage. The current flowing in the output filter capacitor
is the difference between the diode current and the
output current. This capacitor current has a RMS value
of:
If a tantalum capacitor is used, then its ripple current rating
in addition to its ESR will need to be considered.
When the switch is turned on, the output capacitor supplies
the load current I
due to charging and discharging of the output capacitor is
therefore:
For most applications, a 10µF - 22µF ceramic capacitor
is sufficient for output filtering. It is worth noting that the
output ripple voltage due to discharging of a 10µF ceramic
capacitor (9) is higher than that due to its ESR.
Rectifying Diode
For high efficiency, Schottky barrier diodes should be used
as rectifying diodes for the SC4502/SC4502H. These
diodes should have a RMS current rating between 0.5A
and 1A with a reverse blocking voltage of at least a few
Applications Information
POWER MANAGEMENT
2005 Semtech Corp.
I
OUT
V
OUT
V
V
OUT
IN
I
OUT
C
OUT
1
D
I
L
OUT
determines the output ripple voltage.
T
(Figure 4). The output ripple voltage
(8)
(9)
10
Volts higher than the output voltage. For switching
regulators operating at low duty cycles (i.e. low output
voltage to input voltage conversion ratios), it is beneficial
to use rectifying diodes with somewhat higher RMS
current ratings (thus lower forward voltages). This is
because the diode conduction interval is much longer
than that of the transistor. Converter efficiency will be
improved if the voltage drop across the diode is lower.
The rectifying diodes should be placed close to the SW
pins of the SC4502/SC4502H to minimize ringing due
to trace inductance. Surface-mount equivalents of
1N5817, 1N5819, MBRM120, MBR0520 (ON Semi) and
10BQ015, 10BQ040 (IRF) are all suitable.
Soft-Start
Soft-start prevents a DC-DC converter from drawing
excessive current (equal to the switch current limit) from
the power source during start up. If the soft-start time is
made sufficiently long, then the output will enter regulation
without overshoot. An external capacitor from the SS pin
to the ground and an internal 1.5µA charging current
source set the soft-start time. The soft-start voltage ramp
at the SS pin clamps the error amplifier output. During
regulator start-up, COMP voltage follows the SS voltage.
The converter starts to switch when its COMP voltage
exceeds 0.7V. The peak inductor current is gradually
increased until the converter output comes into regulation.
If the shutdown pin is forced below 1.1V or if a fault
situation is detected, then the soft-start capacitor will
be discharged to ground immediately.
The SS pin can be left open if soft-start is not required.
Shutdown
The input voltage and shutdown pin voltage must be greater
than 1.4V and 1.1V respectively to enable the SC4502/
SC4502H. Forcing the shutdown pin below 1.1V stops
the SC4502/SC4502H from switching. Pulling this pin
below 0.1V completely shuts off the SC4502/SC4502H.
The total V
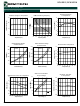
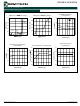
Figure 5 shows several ways of interfacing the control
logic to the shutdown pin. Beware that the shutdown pin
is a high impedance pin. It should always be driven from
a low-impedance source or tied to a resistive divider.
Floating the shutdown pin will result in undefined voltage.
In Figure 5(c) the shutdown pin is driven from a logic
IN
shutdown current decreases to 10µA at 2V.
SC4502/SC4502H
www.semtech.com