ADR430 Analog Devices, Inc., ADR430 Datasheet - Page 15

ADR430
Manufacturer Part Number
ADR430
Description
Ultralow Noise Xfet Voltage References With Current Sink And Source Capability
Manufacturer
Analog Devices, Inc.
Datasheet
1.ADR430.pdf
(24 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ADR430AR
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ADR430ARMZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADR430ARMZ-REEL
Manufacturer:
MDT
Quantity:
1 000
Part Number:
ADR430ARZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADR430ARZ-REEL7
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
101
Part Number:
ADR430B
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ADR430BRZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
THEORY OF OPERATION
The ADR43x series of references uses a new reference generation
technique known as XFET (eXtra implanted junction FET).
This technique yields a reference with low supply current, good
thermal hysteresis, and exceptionally low noise. The core of the
XFET reference consists of two junction field-effect transistors
(JFETs), one of which has an extra channel implant to raise its
pinch-off voltage. By running the two JFETs at the same drain
current, the difference in pinch-off voltage can be amplified and
used to form a highly stable voltage reference.
The intrinsic reference voltage is around 0.5 V with a negative
temperature coefficient of about –120 ppm/°C. This slope is
essentially constant to the dielectric constant of silicon and can
be closely compensated by adding a correction term generated
in the same fashion as the proportional-to-temperature (PTAT)
term used to compensate band gap references. The primary
advantage of an XFET reference is its correction term, which is
~30 times lower and requires less correction than that of a band
gap reference. Because most of the noise of a band gap reference
comes from the temperature compensation circuitry, the XFET
results in much lower noise.
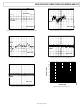
Figure 29 shows the basic topology of the ADR43x series. The
temperature correction term is provided by a current source
with a value designed to be proportional to absolute temperature.
The general equation is
where:
G is the gain of the reciprocal of the divider ratio.
Δ V
I
ADR43x devices are created by on-chip adjustment of R2
and R3 to achieve 2.048 V or 2.500 V, respectively, at the
reference output.
PTAT
P
is the difference in pinch-off voltage between the two JFETs.
is the positive temperature coefficient correction current.
V
I
PTAT
OUT
=
*EXTRA CHANNEL IMPLANT
V
OUT
G
* *
I
1
(
= G(ΔV
Figure 29. Simplified Schematic Device
Δ
V
Power Dissipation Considerations
P
−
P
I
1
– R1 × I
R1
ΔV
×
I
P
PTAT
PTAT
)
R1
)
ADR43x
R3
R2
GND
V
V
IN
OUT
ADR430/ADR431/ADR433/ADR434/ADR435/ADR439
Rev. D | Page 15 of 24
(1)
The ADR43x family of references is guaranteed to deliver load
currents to 10 mA with an input voltage that ranges from 4.1 V
to 18 V. When these devices are used in applications at higher
currents, users should use the following equation to account for
the temperature effects due to the power dissipation increases:
where:
T
P
θ
BASIC VOLTAGE REFERENCE CONNECTIONS
Voltage references, in general, require a bypass capacitor
connected from V
illustrates the basic configuration for the ADR43x family of
references. Other than a 0.1 μF capacitor at the output to help
improve noise suppression, a large output capacitor at the
output is not required for circuit stability.
NOISE PERFORMANCE
The noise generated by the ADR43x family of references is
typically less than 3.75 μV p-p over the 0.1 Hz to 10.0 Hz band
for ADR430, ADR431, and ADR433. Figure 22 shows the
0.1 Hz to 10.0 Hz noise of the ADR431, which is only 3.5 μV p-p.
The noise measurement is made with a band-pass filter made
of a 2-pole high-pass filter with a corner frequency at 0.1 Hz
and a 2-pole low-pass filter with a corner frequency at 10.0 Hz.
TURN-ON TIME
Upon application of power (cold start), the time required for
the output voltage to reach its final value within a specified
error band is defined as the turn-on settling time. Two compo-
nents normally associated with this are the time for the active
circuits to settle and the time for the thermal gradients on the
chip to stabilize. Figure 17 and Figure 18 show the turn-on
settling time for the ADR431.
JA
D
J
and T
is the device power dissipation.
is the device package thermal resistance.
T
V
IN
J
=
10µF
A
P
are the junction and ambient temperatures, respectively.
D
+
Figure 30. Basic Voltage Reference Configuration
×
θ
0.1µF
JA
+
OUT
T
A
NOTES:
1. NC = NO CONNECT
2. TP = TEST PIN (DO NOT CONNECT)
to GND. The circuit in Figure 30
GND
NC
TP
1
2
3
4
(Not to Scale)
ADR43x
TOP VIEW
8
7
6
5
TRIM
TP
NC
V
OUT
0.1µF
(2)