1308AI Linear Technology Corporation, 1308AI Datasheet - Page 9

1308AI
Manufacturer Part Number
1308AI
Description
Lt1308b - Single Cell High Currentmicropower 600khz Boost Dc/dc Converter
Manufacturer
Linear Technology Corporation
Datasheet
1.1308AI.pdf
(20 pages)
APPLICATIONS
Waveforms for a LT1308B 5V to 12V boost converter
using a 10μF ceramic output capacitor are pictured in
Figures 4 and 5. In Figure 4, the converter is operating in
continuous mode, delivering a load current of approxi-
mately 500mA. The top trace is the output. The voltage
increases as inductor current is dumped into the output
capacitor during the switch off time, and the voltage
decreases when the switch is on. Ripple voltage is in this
case due to capacitance, as the ceramic capacitor has little
ESR. The middle trace is the switch voltage. This voltage
alternates between a V
The lower trace is the switch current. At the beginning of
the switch cycle, the current is 1.2A. At the end of the
switch on time, the current has increased to 2A, at which
point the switch turns off and the inductor current flows
into the output capacitor through the diode. Figure 5
depicts converter waveforms at a light load. Here the
converter operates in discontinuous mode. The inductor
current reaches zero during the switch off time, resulting
in some ringing at the switch node. The ring frequency is
set by switch capacitance, diode capacitance and induc-
tance. This ringing has little energy, and its sinusoidal
shape suggests it is free from harmonics. Minimizing the
copper area at the switch node will prevent this from
causing interference problems.
Figure 4. 5V to 12V Boost Converter Waveforms in
Continuous Mode. 10μF Ceramic Capacitor Used at Output
Figure 5. Converter Waveforms in Discontinuous Mode
100mV/DIV
500mA/DIV
20mV/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
1A/DIV
V
V
V
V
OUT
OUT
I
I
SW
SW
SW
SW
U
CESAT
INFORMATION
U
and V
500ns/DIV
500ns/DIV
OUT
W
plus the diode drop.
U
LAYOUT HINTS
The LT1308A/LT1308B switch current at high speed,
mandating careful attention to layout for proper perfor-
mance. You will not get advertised performance with
careless layout . Figure 6 shows recommended component
placement for an SO-8 package boost (step-up) converter.
Follow this closely in your PC layout. Note the direct path
of the switching loops. Input capacitor C1 must be placed
close (< 5mm) to the IC package. As little as 10mm of wire
or PC trace from C
inability to regulate or oscillation.
The negative terminal of output capacitor C2 should tie
close to the ground pin(s) of the LT1308A/LT1308B. Doing
this reduces dI/dt in the ground copper which keeps high
frequency spikes to a minimum. The DC/DC converter
ground should tie to the PC board ground plane at one
place only, to avoid introducing dI/dt in the ground plane.
Figure 7 shows recommended component placement for
a boost converter using the TSSOP package. Placement is
similar to the SO-8 package layout.
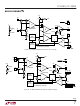
Figure 6. Recommended Component Placement for SO-8
Package Boost Converter. Note Direct High Current Paths
Using Wide PC Traces. Minimize Trace Area at Pin 1 (V
Pin 2 (FB). Use Multiple Vias to Tie Pin 4 Copper to Ground
Plane. Use Vias at One Location Only to Avoid Introducing
Switching Currents into the Ground Plane
GROUND PLANE
SHUTDOWN
MULTIPLE
R1
VIAs
R2
GND
1
2
3
4
IN
to V
LT1308A
LT1308B
C2
+
LT1308A/LT1308B
IN
LBI
will cause problems such as
LBO
8
7
6
5
V
C1
OUT
+
D1
V
L1
IN
C
) and
1308abfa
1308 F04
9