RC28F256P33TF Numonyx, RC28F256P33TF Datasheet

RC28F256P33TF
Available stocks
Related parts for RC28F256P33TF
RC28F256P33TF Summary of contents
Page 1
... Password Access feature Software: — 20µs (Typ) program suspend — 20µs (Typ) erase suspend — Numonyx™ Flash Data Integrator optimized — Basic Command Set and Extended Function Interface Command Set compatible — Common Flash Interface capable Density and Packaging — ...
Page 2
... Contact your local Numonyx sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order. Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Numonyx literature may be obtained by visiting Numonyx's website at http://www.numonyx.com. ...
Page 3
P33-65nm Contents 1.0 Functional Description ............................................................................................... 5 1.1 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 5 1.2 Overview ........................................................................................................... 5 1.3 Virtual Chip Enable Description.............................................................................. 6 1.4 Memory Maps ..................................................................................................... 7 2.0 Package Information ................................................................................................. 8 2.1 56-Lead TSOP..................................................................................................... 8 2.2 64-Ball Easy BGA Package ...
Page 4
Power-Up and Power-Down .................................................................................43 12.2 Reset Specifications ...........................................................................................43 12.3 Power Supply Decoupling ....................................................................................44 13.0 Maximum Ratings and Operating Conditions ............................................................45 13.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .................................................................................45 13.2 Operating Conditions..........................................................................................45 14.0 Electrical Specifications ...........................................................................................46 14.1 DC Current Characteristics ..................................................................................46 14.2 DC ...
Page 5
... NOR device, and support for code and data storage. Features include high-performance synchronous-burst read mode, fast asynchronous access times, low power, flexible security options, and two industry-standard package choices. P33-65nm is manufactured using Numonyx™ 65nm ETOX™ X process technology. 1.2 Overview This family of devices provides high performance at low voltage on a 16-bit data bus. ...
Page 6
Virtual Chip Enable Description The 512 Mbit P33 Family Flash memory employs a Virtual Chip Enable which combines two 256-Mbit die with a common chip enable, CE# for Easy BGA packages. Address A25 is then used to select between ...
Page 7
P33-65nm 1.4 Memory Maps Figure 1: P33-65nm Memory Map FF 0000 - FFFFFF 7F 0000 - 7 FFFFF 3 F0000 - 3 FFFFF 020000 – 02 FFFF 010000 – 01 FFFF 00C000 – 00 FFFF 008000 – 00 BFFF 004000 ...
Page 8
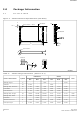
Package Information 2.1 56-Lead TSOP Figure 2: TSOP Mechanical Specifications (256-Mbit) Z Pin 1 See Detail A Detail A Table 2: TSOP Package Dimensions (Sheet Product Information Symbol Package Height A Standoff A 1 Package Body ...
Page 9
P33-65nm Table 2: TSOP Package Dimensions (Sheet Product Information Symbol Lead Count N Lead Tip Angle θ Seating Plane Coplanarity Y Lead to Package Offset Z Notes: 1. One dimple on package denotes Pin ...
Page 10
... Package Body Width Package Body Length Pitch Ball (Lead) Count Seating Plane Coplanarity Corner to Ball A1 Distance Along D Corner to Ball A1 Distance Along E Note: Daisy Chain Evaluation Unit information is at Numonyx™ Flash Memory Packaging Technology developer.numonyx.com/design/flash/packtech. Datasheet 10 Millimeters Symbol Min Nom Max ...
Page 11
... A1 is the least significant address bit. 2. A24 is valid for 256-Mbit densities; otherwise connect (NC Internal Connection on VCC Pin 13; it may be driven or floated. For legacy designs, pin can be tied to Vcc Datasheet 11 ™ Numonyx P33 Flash Memory 56-Lead TSOP Pinout Top View WAIT 56 A17 ...
Page 12
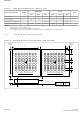
Figure 5: 64-Ball Easy BGA Ballout (256/512-Mbit VPP B A2 VSS A9 CE A10 A12 A11 RST# E DQ8 DQ1 DQ9 DQ3 F RFU DQ0 DQ10 ...
Page 13
P33-65nm 4.0 Signals Table 4: TSOP and Easy BGA Signal Descriptions (Sheet Symbol Type ADDRESS INPUTS: Device address inputs. 256-Mbit: A[24:1]; 512-Mbit: A[25:1]. Note: The A[MAX:1] Input virtual selection of the 256-Mbit “Top parameter” die in the ...
Page 14
... Table 4: TSOP and Easy BGA Signal Descriptions (Sheet Symbol Type RESERVED FOR FUTURE USE: Reserved by Numonyx for future device functionality and RFU — enhancement. These should be treated in the same way as a Don’t Use (DU) signal. DU — DON’T USE: Do not connect to any other signal, or power supply; must be left floating. ...
Page 15
P33-65nm 5.0 Bus Operations CE# low and RST# high enable device read operations. The device internally decodes upper address inputs to determine the accessed block. ADV# low opens the internal address latches. OE# low activates the outputs and gates selected ...
Page 16
... CPU initialization may occur because the flash memory may be providing status information rather than array data. Flash memory devices from Numonyx allow proper CPU initialization following a system reset through the use of the RST# input. RST# should be controlled by the same low-true reset signal that resets the system CPU ...
Page 17
P33-65nm 6.0 Command Set 6.1 Device Command Codes The system Central Processing Unit provides control of all in-system read, write, and erase operations of the device via the system bus. The on-chip WSM manages all block- erase and word-program algorithms. ...
Page 18
Table 6: Command Codes and Definitions (Sheet Mode Code Device Mode Program or Erase 0xB0 Suspend Suspend 0xD0 Suspend Resume 0x60 Block lock Setup 0x01 Block lock Protection 0xD0 Unlock Block 0x2F Lock-Down Block Protection program 0xC0 ...
Page 19
P33-65nm Table 7: Command Bus Cycles (Sheet Mode Command Read Array Read Device Identifier Read Read CFI Read Status Register Clear Status Register Word Program Buffered Program Program Buffered Enhanced Factory Program (4) (BEFP) Erase Block Erase ...
Page 20
Table 7: Command Bus Cycles (Sheet Mode Command Blank Check Extended Function Others Interface (5) command Notes: 1. First command cycle address should be the same as the operation’s target address. DBA = Device Base Address (NOTE: ...
Page 21
P33-65nm 7.0 Read Operation The device can be in any of four read states: Read Array, Read Identifier, Read Status or Read Query. Upon power-up, or after a reset, the device defaults to Read Array mode. To change the read ...
Page 22
... Lock Register 1 128-bit User-Programmable OTP registers Notes: 1. BBA = Block Base Address. 2. DBA = Device base Address, Numonyx reserves other configuration address locations 3. In P33-65nm, the GPR is used as read out register for Extended Functional interface command. Table 9: Device ID codes ID Code Type Device Code Note: The 512-Mbit devices do not have a Device ID associated with them ...
Page 23
P33-65nm 8.0 Program Operation The device supports three programming methods: Word Programming (40h), Buffered Programming (E8h, D0h), and Buffered Enhanced Factory Programming (80h, D0h). The following sections describe device programming in detail. Successful programming requires the addressed block to be ...
Page 24
On the next write, a word count is written to the device at the buffer address. This tells the device how many data words will be written to the buffer the maximum size of the buffer. On the ...
Page 25
P33-65nm 8.3.1 BEFP Requirements and Considerations BEFP requirements: • Case temperature: T • Nominal VCC • VPP driven to V • Target block must be unlocked before issuing the BEFP Setup and Confirm commands • The first-word address for the ...
Page 26
Caution: The buffer must be completely filled for programming to occur. Supplying an address outside of the current block's range during a buffer-fill sequence causes the algorithm to exit immediately. Any data previously loaded into the buffer during the fill ...
Page 27
P33-65nm 8.5 Program Resume The Resume command instructs the device to continue programming, and automatically clears Status Register bits SR[7,2]. This command can be written to any address. If error bits are set, the Status Register should be cleared before ...
Page 28
Erase Operation Flash erasing is performed on a block basis. An entire block is erased each time an erase command sequence is issued, and only one block is erased at a time. When a block is erased, all bits ...
Page 29
P33-65nm The status register can be examined for Blank Check progress and errors by reading any address within the block being accessed. During a blank check operation, the Status Register indicates a busy status (SR7 = 0). Upon completion, the ...
Page 30
Security The device features security modes used to protect the information stored in the flash memory array. The following sections describe each security mode in detail. 10.1 Block Locking Individual instant block locking is used to protect user code ...
Page 31
P33-65nm 10.1.4 Block Lock Status The Read Device Identifier command is used to determine a block’s lock status (see Section 7.3, “Read Device Identifier” on page addressed block’s lock status; DQ0 is the addressed block’s lock bit, while DQ1 is ...
Page 32
... Password Access may be combined with Non-Volatile Protection and/or Volatile Protection to create a multi- tiered solution. Please contact your Numonyx Sales for further details concerning Password Access. Datasheet ...
Page 33
P33-65nm 11.0 Status Register To read the Status Register, issue the Read Status Register command at any address. Status Register information is available to which the Read Status Register, Word Program, or Block Erase command was issued. SRD is automatically ...
Page 34
Clear Status Register The Clear Status Register command clears the status register. It functions independent of VPP. The WSM sets and clears SR[7,6,2], but it sets bits SR[5:3,1] without clearing them. The Status Register should be cleared before starting ...
Page 35
P33-65nm Table 11: Read Configuration Register Description (Sheet Burst Wrap (BW) 3 2:0 Burst Length (BL[2:0]) 11.1.1 Read Mode The Read Mode (RM) bit selects synchronous burst-mode or asynchronous page-mode operation for the device. When the RM ...
Page 36
Figure 9: First-Access Latency Count CLK [C] Valid Address [A] Address ADV# [V] Code 0 (Reserved) DQ [D/Q] 15-0 Code 1 (Reserved DQ [D/Q] 15-0 Code 2 DQ [D/Q] 15-0 Code 3 DQ [D/Q] 15-0 Code 4 DQ [D/Q] 15-0 ...
Page 37
P33-65nm Figure 10: Example Latency Count Setting Using Code 3 CLK CE# ADV# A[MAX:0] A[MAX:1] D[15:0] 11.1.3 End of Word Line (EOWL) Considerations End of Wordline (EOWL) WAIT states can result when the starting address of the burst operation is ...
Page 38
Table 13: End of Wordline Data and WAIT state Comparison Latency Count Data States 1 Not Supported Not Supported 11.1.4 ...
Page 39
P33-65nm Table 14: WAIT Functionality Table Condition CE# = ‘1’, OE# = ‘X’ or CE# = ‘0’, OE# = ‘1’ CE# =’0’, OE# = ‘0’ Synchronous Array Reads Synchronous Non-Array Reads All Asynchronous Reads All Writes Notes: 1. Active: WAIT ...
Page 40
... The first 128-bit OTP Register is comprised of two 64-bit (8-word) segments. The lower 64-bit segment is pre-programmed at the Numonyx factory with a unique 64-bit number. The other 64-bit segment, as well as the other sixteen 128-bit OTP Registers, are blank. Users can program these registers as needed. Once programmed, users can then lock the OTP Register(s) to prevent additional bit programming (see “ ...
Page 41
P33-65nm The OTP Registers contain OTP bits; when programmed, PR bits cannot be erased. Each OTP Register can be accessed multiple times to program individual bits, as long as the register remains unlocked. Each OTP Register has an associated Lock ...
Page 42
Programming the OTP Registers To program any of the OTP Registers, first issue the Program OTP Register command at the parameter’s base address plus the offset to the desired OTP Register (see 6.2, “Device Command Bus Cycles” on page ...
Page 43
P33-65nm 12.0 Power and Reset Specifications 12.1 Power-Up and Power-Down Power supply sequencing is not required if VPP is connected to VCC or VCCQ. Otherwise VCC and VCCQ should attain their minimum operating voltage before applying VPP. Power supply transitions ...
Page 44
... Two-line control and correct de-coupling capacitor selection suppress transient voltage peaks. Because Numonyx MLC flash memory devices draw their power from VCC, VPP, and VCCQ, each power connection should have a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor to ground. High- frequency, inherently low-inductance capacitors should be placed as close as possible to package leads ...
Page 45
P33-65nm 13.0 Maximum Ratings and Operating Conditions 13.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Warning: Stressing the device beyond the Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage. These are stress ratings only. Table 17: Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Temperature under bias Storage temperature ...
Page 46
Electrical Specifications 14.1 DC Current Characteristics Table 19: DC Current Characteristics (Sheet Sym Parameter I Input Load Current LI Output I Leakage DQ[15:0], WAIT LO Current 256-Mbit I , VCC Standby, CCS I Power-Down 512-Mbit CCD ...
Page 47
P33-65nm Table 19: DC Current Characteristics (Sheet Sym Parameter I VPP Blank Check PPBC Notes: 1. All currents are RMS unless noted. Typical values at typical VCC the average current measured over any ...
Page 48
AC Characteristics 15.1 AC Test Conditions Figure 14: AC Input/Output Reference Waveform V CCQ Input V /2 CCQ 0V Note: AC test inputs are driven at VCCQ for Logic "1" and 0 V for Logic "0." Input/output timing begins/ends ...
Page 49
P33-65nm 15.2 Capacitance Table 22: Capacitance Symbol Parameter C Input Capacitance IN C Output Capacitance OUT Notes: 1. Capacitance values are for a single die; for dual die, the capacitance values are doubled. 2. Sampled, not 100% tested. 3. Silicon ...
Page 50
Table 23: AC Read Specifications - (Sheet Num Symbol R101 t Address setup to ADV# high AVVH R102 t CE# low to ADV# high ELVH R103 t ADV# low to output valid VLQV R104 t ADV# pulse ...
Page 51
P33-65nm Table 23: AC Read Specifications - (Sheet Num Symbol (5) Synchronous Specifications R301 t Address setup to CLK AVCH/L R302 t ADV# low setup to CLK VLCH/L R303 t CE# low setup to CLK ELCH/L R304 ...
Page 52
Figure 18: Asynchronous Single-Word Read (ADV# Latch) Address [A] A[1:0][A] R101 R105 R105 R106 ADV# CE# [E} OE# [G] WAIT [T] Data [D/Q] Note: WAIT shown deasserted during asynchronous read mode (RCR.10=0, WAIT asserted low) Figure 19: Asynchronous Page-Mode Read ...
Page 53
P33-65nm . Figure 20: Synchronous Single-Word Array or Non-array Read Timing R301 CLK [C] Address [A] R101 R105 R105 R104 R104 ADV# [V] R303 R102 CE# [E] OE# [G] WAIT [T] Data [D/Q] Notes: 1. WAIT is driven per OE# ...
Page 54
Figure 22: Synchronous Burst-Mode Four-Word Read Timing R302 R301 R306 CLK [C] R101 Address [A] A R105 R105 R106 R102 ADV# [V] R303 CE# [E] OE# [G] R15 WAIT [T] Data [D/Q] Note: WAIT is driven per OE# assertion during ...
Page 55
P33-65nm Table 24: AC Write Specifications (Sheet Num Symbol Write to Synchronous Read Specifications W19 t WE# high to Clock valid WHCH/L W20 t WE# high to ADV# high WHVH W28 t WE# high to ADV# low ...
Page 56
Figure 24: Asynchronous Read-to-Write Timing R2 Address [A] R3 CE# [E} OE# [G] WE# [W] WAIT [T] R6 Data [D/Q] R5 RST# [P] Note: WAIT deasserted during asynchronous read and during write. WAIT High-Z during write per OE# deasserted. Figure ...
Page 57
P33-65nm Figure 26: Synchronous Read-to-Write Timing R301 R302 R306 CLK [C] R2 R101 Address [A] R105 R105 R106 R102 ADV# [V] R303 R3 CE# [E] OE# [G] WE# WAIT [T] Data [D/Q] Note: WAIT shown deasserted and High-Z per OE# ...
Page 58
Program and Erase Characteristics 15.5 Table 25: Program and Erase Specifications Num Symbol Program W200 t PROG/W Time Program W250 t PROG Time W451 t BEFP/B Program W452 t BEFP/Setup W500 t ERS/PB Erase Time W501 t ERS/MB W600 t ...
Page 59
... JS = 56- Lead TSOP, lead-free RC = 64-Ball Easy BGA, leaded -Ball Easy BGA, lead-free Product Line Designator 28F = Numonyx™ Flash Memory Device Density 256 = 256-Mbit Table 26: Valid Combinations for Discrete Products 256-Mbit RC28F256P33TF RC28F256P33BF PC28F256P33TF PC28F256P33BF TE28F256P33TF TE28F256P33BF JS28F256P33TF JS28F256P33BF Datasheet ...
Page 60
... Figure 29: Decoder for SCSP Devices Package Designator RC = 64- Ball Easy BGA , leaded PC = 64- Ball Easy BGA , lead- free Product Designator 48F = Numonyx™ Flash Memory Only Device Density die 4 = 256-Mbit Product Family ® Numonyx™ StrataFlash Embedded Memory (P33) ...
Page 61
P33-65nm Appendix A Supplemental Reference Information A.1 Common Flash Interface The Common Flash Interface (CFI) is part of an overall specification for multiple command-set and control-interface descriptions. This appendix describes the database structure containing the data returned by a read ...
Page 62
... BA = Block Address beginning location (i.e., 08000h is block 1’s beginning location when the block size is 32-KWord). 3. Offset 15 defines “P” which points to the Primary Numonyx-specific Extended Query Table. A.1.3 Read CFI Identification String The Identification String provides verification that the component supports the Common Flash Interface specification ...
Page 63
P33-65nm Table 31: CFI Identification Offset Length 10h 3 Query-unique ASCII string “QRY“ 13h 2 Primary vendor command set and control interface ID code. 16-bit ID code for vendor-specified algorithms 15h 2 Extended Query Table primary algorithm address 17h 2 ...
Page 64
A.1.4 Device Geometry Definition Figure 31: Device Geometry Definition Offset Length 27h 1 “n” such that device size = 2 Flash device interface code assignment: "n" such that n+1 specifies the bit field that represents the flash device w idth ...
Page 65
... P33-65nm A.1.5 Numonyx-Specific Extended Query Table Table 32: Primary Vendor-Specific Extended Query Offset (1) Length P = 10Ah (P+0)h 3 Primary extended query table (P+1)h Unique ASCII string “PRI“ (P+2)h (P+3)h 1 Major version number, ASCII (P+4)h 1 Minor version number, ASCII (P+5)h 4 Optional feature and command support (1=yes, 0=no) (P+6)h bits 10–31 are reserved; undefined bits are “0.” If bit 31 is (P+7)h “ ...
Page 66
Table 33: OTP Register Information Offset (1) Length P = 10Ah (P+E)h 1 Number of Protection register fields in JEDEC ID space. “00h,” indicates that 256 protection fields are available (P+F)h 4 Protection Field 1: Protection Description (P+10)h This field ...
Page 67
P33-65nm Figure 32: Burst Read Information Offset (1) Length P = 10Ah (P+1D)h 1 Page Mode Read capability bits 0–7 = “n” such that 2 read-page bytes. See offset 28h for device w ord w idth to determine page-mode data ...
Page 68
Table 35: Partition Region 1 Information (Sheet Offset ( 10Ah Bottom Top (P+24)h (P+24)h Data size of this Parition Region Information field (P+25)h (P+25)h (# addressable locations, including this field) (P+26)h (P+26)h Number of identical ...
Page 69
P33-65nm Table 36: Partition Region 1 Information (Sheet Offset ( 10Ah Bottom Top (P+2C)h (P+2C)h Partition Region 1 Erase Block Type 1 Information (P+2D)h (P+2D)h bits 0– y identical-size erase blks ...
Page 70
Table 37: Partition and Erase Block Region Information Datasheet 70 Address 256-Mbit –B –T 12D: --01 --01 12E: --24 --24 12F: --00 --00 130: --01 --01 131: --00 --00 132: --11 --11 133: --00 --00 134: --00 --00 135: --02 ...
Page 71
P33-65nm Table 38: CFI Link Information Length (Optional flash features and commands) 4 CFI Link Field bit definitions Bits 0–9 = Address offset (w ithin 32Mbit segment) of referenced CFI table Bits 10–27 = nth 32Mbit segment of referenced CFI ...
Page 72
A.2 Flowcharts Figure 33: Word Program Flowchart Start Command Cycle - Issue Program Command - Address = location to program - Data = 0x40 Data Cycle - Address = location to program - Data = Data to program Check Ready ...
Page 73
P33-65nm Figure 34: Program/Erase Suspend/Resume Flowchart Start Command Cycle - Issue Suspend Command - Address = any device address - Data = 0xB0 Wait t SUSP Read Status Register See Status Register Flowchart Erase Suspended ? (SR.6 = '1') No ...
Page 74
Figure 35: Buffer Program Flowchart Start Device Supports Buffer No Writes? Yes Set Timeout or Loop Counter Get Next Target Address Issue Write to Buffer Command E8h and Block Address Read Status Register (at Block Address) Is WSM Ready? SR.7 ...
Page 75
P33-65nm Figure 36: BEFP Flowchart Setup Phase Start Issue BEFP Setup Cmd (Data = 0x80) Issue BEFP Confirm Cmd (Data = 00D0h) BEFP Setup Delay Read Status Register Yes (SR.7=0) BEFP Setup Done ? No (SR.7=1) SR Error Handler (User-Defined) ...
Page 76
Figure 37: Block Erase Flowchart Start Command Cycle - Issue Erase command - Address = Block to be erased - Data = 0x20 Confirm Cycle - Issue Confirm command - Address = Block to be erased - Data = Erase ...
Page 77
P33-65nm Figure 38: Block Lock Operations Flowchart - Issue Block Lock Setup Command - Address = block address - Data = 0x60 - Issue Lock/Unlock Command - Address = block address - Data = 0x01 (Lock Block) -or- Error Handler ...
Page 78
Figure 39: OTP Register Programming Flowchart Datasheet 78 Start OTP Program Setup - Write 0xC0 - OTP Address Confirm Data - Write OTP Address and Data Check Ready Status - Read Status Register Command not required - Perform read operation ...
Page 79
P33-65nm Figure 40: Status Register Flowchart - Issue Status Register Command - Address = any device address - Data = 0x70 - Set/Reset by WSM - Set by WSM - Reset by user - See Clear Status Register Command Datasheet ...
Page 80
A.3 Write State Machine Show here are the command state transitions (Next State Table) based on incoming commands. Only one partition can be actively programming or erasing at a time. Each partition stays in its last read state (Read Array, ...
Page 81
P33-65nm Table 39: Next State Table for P3x-65nm (Sheet Current Chip State (FFh) (40h) (E8h) (EBh) (20h) (80h) (D0h) (B0) (70h) (50h) (90h, Setup (8) BP Load 1 (8) BP Load 2 Buffer BP Confirm Ready (Error ...
Page 82
Table 39: Next State Table for P3x-65nm (Sheet Current Chip State (FFh) (40h) (E8h) (EBh) (20h) (80h) (D0h) (B0) (70h) (50h) (90h, EFI Setup Sub-function Setup Sub-op-code Load 1 Sub-function Sub-function Confirm in Erase Suspend if data ...
Page 83
P33-65nm Table 40: Output Next State Table for P3x-65nm Current Chip State (FFh) (40h) (E8h) (EBh) (20h) (80h) (D0h) (B0) (70h) (50h) (90h, BEFP Setup, BEFP Pgm & Verify Busy, Erase Setup, OTP Setup, BP Setup, Load 1, Load 2 ...
Page 84
Appendix B Conventions - Additional Documentation B.1 Acronyms BEFP: CUI : MLC : OTP : PLR : PR : RCR : RFU : SR : SRD WSM B.2 Definitions and Terms VCC : ...
Page 85
P33-65nm Main block : Parameter block : Top parameter device : Bottom parameter device : Datasheet 85 An array block that is usually used to store code and/or data. Main blocks are larger than parameter blocks. An array block that ...
Page 86
... Return to StrataFlash; Nov 2008 05 Update the buffer program comments for cross 512-Word boundary; Remove 128M related contents from this document; Correct A24 to A25 for virtual CE description in section 1.3; Remove Numonyx Confidential; Datasheet 86 TM trademark; P33-65nm Nov 2008 Order Number: 320003-05 ...