MP1482 MPS, MP1482 Datasheet - Page 9

MP1482
Manufacturer Part Number
MP1482
Description
2a, 18v Synchronous Rectified Step-down Converter
Manufacturer
MPS
Datasheet
1.MP1482.pdf
(13 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MP1482
Manufacturer:
台湾明智类比
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MP1482DN
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MP1482DN-LF
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
9 600
Part Number:
MP1482DN-LF-Z
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MP1482DS
Manufacturer:
MPS
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MP1482DS-C165-IF-Z
Manufacturer:
MPS/美国芯源
Quantity:
20 000
In this case (as shown in Figure 2), a third pole
set by the compensation capacitor (C6) and the
compensation
compensate the effect of the ESR zero on the
loop gain. This pole is located at:
The goal of compensation design is to shape
the converter transfer function to get a desired
loop gain. The system crossover frequency
where the feedback loop has the unity gain is
important. Lower crossover frequencies result
in slower line and load transient responses,
while higher crossover frequencies could cause
system instability. A good rule of thumb is to set
the crossover frequency below one-tenth of the
switching frequency.
To optimize the compensation components, the
following procedure can be used.
1. Choose the compensation resistor (R3) to set
the desired crossover frequency.
Determine the R3 value by the following
equation:
Where f
which is typically below one tenth of the
switching frequency.
2. Choose the compensation capacitor (C3) to
achieve
applications with typical inductor values, setting
the compensation zero, f
the crossover frequency provides sufficient
phase margin.
Determine the C3 value by the following equation:
Where R3 is the compensation resistor.
MP1482 Rev. 1.2
1/13/2010
R
3
=
2
G
π
EA
×
C
C
×
the
2
is the desired crossover frequency
G
×
CS
f
C
f
×
desired
C
P
resistor
3
3
V
V
OUT
=
>
FB
2
2
MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
π
π
<
MP1482 – 2A, 18V SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFIED, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
×
×
2
C
R
π
1
phase
Z1
4
6
3
(R3)
×
G
, below one-forth of
×
×
C
EA
R
f
2
C
3
×
×
G
0
1 .
is
CS
margin.
×
f
S
used
© 2010 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
×
V
V
www.MonolithicPower.com
OUT
FB
For
to
3. Determine if the second compensation
capacitor (C6) is required. It is required if the
ESR zero of the output capacitor is located at
less than half of the switching frequency, or the
following relationship is valid:
If this is the case, then add the second
compensation capacitor (C6) to set the pole f
at the location of the ESR zero. Determine the
C6 value by the equation:
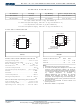
External Bootstrap Diode
An external bootstrap diode may enhance the
efficiency of the regulator, and it will be a must
if the applicable condition is:
In these cases, an external BST diode is
recommended from the output of the voltage
regulator to BST pin, as shown in Figure.2
The recommended external BST diode is
IN4148, and the BST cap is 0.1~1µF.
Figure 2—Add Optional External Bootstrap
V
D=
MP1482
OUT
Diode to Enhance Efficiency
V
V
OUT
is 5V or 3.3V, and duty cycle is high:
IN
BST
SW
2
>65%
π
C
×
6
C
=
2
1
C
×
C
2
R
External BST Diode
BST
×
ESR
R
L
R
3
IN4148
ESR
C
<
OUT
f
+
2
S
5V or 3.3V
P3
9