LT1011 Linear Technology, LT1011 Datasheet - Page 6

LT1011
Manufacturer Part Number
LT1011
Description
Voltage Comparator
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LT1011
Manufacturer:
AUTONICS
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
LT1011ACJ8
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
LT1011ACJ8
Manufacturer:
NXP
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
LT1011ACN8
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
LT1011ACN8#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LT1011AIS8
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LT1011AIS8#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LT1011AIS8#TRPBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
LT1011/LT1011A
TYPICAL PERFOR A CE CHARACTERISTICS
APPLICATIONS
6
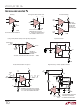
Preventing Oscillation Problems
Oscillation problems in comparators are nearly always
caused by stray capacitance between the output and
inputs or between the output and other sensitive pins on
the comparator. This is especially true with high gain
bandwidth comparators like the LT1011, which are
designed for fast switching with millivolt input signals.
The gain bandwidth product of the LT1011 is over 10GHz.
Oscillation problems tend to occur at frequencies around
5MHz, where the LT1011 has a gain of
implies that attenuation of output signals must be at
least 2000:1 at 5MHz as measured at the inputs. If the
source impedance is 1k , the effective stray capaci-
tance between output and input must have a reactance
of more than (2000)(1k ) = 2M , or less than 0.02pF.
The actual interlead capacitance between input and out-
put pins on the LT1011 is less than 0.002pF when cut to
printed circuit mount length. Additional stray capaci-
tance due to printed circuit traces must be minimized by
routing the output trace directly away from input lines
and, if possible, running ground traces next to input
traces to provide shielding. Additional steps to ensure
oscillation-free operation are:
1. Bypass the STROBE/BALANCE pins with a 0.01 F
capacitor connected from Pin 5 to Pin 6. This elimi-
nates stray capacitive feedback from the output to the
– 0.5
– 2.0
– 2.5
–1.0
–1.5
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
U
V
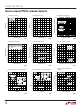
Input Offset Voltage
vs Common Mode Voltage
–
T
J
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
= 25 C
V
SINGLE SUPPLY)
INFORMATION
–
U
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE (V)
(OR GND WITH
W
U
LIMIT = V
COMMON MODE
W
+
– (1.5V)
UPPER
2000. This
U
1011 G19
V
+
2. Bypass the negative supply (Pin 4) with a 0.1 F
3. Bypass any slow moving or DC input with a capacitor
4. Keep resistive source impedance as low as possible. If
5. Use hysteresis. This consists of shifting the input
–150mV
–100mV
BALANCE pins, which are nearly as sensitive as the
inputs.
ceramic capacitor close to the comparator. 0.1 F can
also be used for the positive supply (Pin 8) if the pull-
up load is tied to a separate supply. When the pull-up
load is tied directly to Pin 8, use a 2 F solid tantalum
bypass capacitor.
( 0.01 F) close to the comparator to reduce high
frequency source impedance.
a resistor is added in series with one input to balance
source impedances for DC accuracy, bypass it with a
capacitor. The low input bias current of the LT1011
usually eliminates any need for source resistance bal-
ancing. A 5k imbalance, for instance, will create only
0.25mV DC offset.
offset voltage of the comparator when the output
changes state. Hysteresis forces the comparator to
move quickly through its linear region, eliminating
oscillations by “overdriving” the comparator under all
input conditions. Hysteresis may be either AC or DC.
AC techniques do not shift the apparent offset voltage
– 50mV
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
– 50 – 25
Offset Pin Characteristics
CHANGE IN V
VOLTAGE ON PINS 5 AND 6
0
WITH RESPECT TO V
TEMPERATURE ( C)
INTO PINS 5 OR 6
25
OS
50
FOR CURRENT
75
100 125 150
+
1011 G20