LTC2494 Linear Technology, LTC2494 Datasheet - Page 27

LTC2494
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC2494
Description
16-Bit 8-/16-Channel ADC
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC2494.pdf
(36 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC2494CUHF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC2494IUHF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
www.DataSheet4U.com
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
PRESERVING THE CONVERTER ACCURACY
The LTC2494 is designed to reduce as much as possible
sensitivity to device decoupling, PCB layout, anti-aliasing
circuits, line frequency perturbations, and temperature
sensitivity. In order to achieve maximum performance a
few simple precautions should be observed.
Digital Signal Levels
The LTC2494’s digital interface is easy to use. Its digital
inputs SDI, F
accept standard CMOS logic levels. Internal hysteresis
circuits can tolerate edge transition times as slow as
100μs.
The digital input signal range is 0.5V to V
transitions, the CMOS input circuits draw dynamic cur-
rent. For optimal performance, application of signals to
the serial data interface should be reserved for the sleep
and data output periods.
During the conversion period, overshoot and undershoot
of fast digital signals applied to both the serial digital in-
terface and the external oscillator pin (F
the converter performance. Undershoot and overshoot
occur due to impedance mismatch of the circuit board
trace at the converter pin when the transition time of an
external control signal is less than twice the propagation
delay from the driver to the input pin. For reference, on a
regular FR-4 board, the propagation delay is approximately
183ps/inch. In order to prevent overshoot, a driver with
a 1ns transition time must be connected to the converter
through a trace shorter than 2.5 inches. This becomes
diffi cult when shared control lines are used and multiple
refl ections occur.
Parallel termination near the input pin of the LTC2494 will
eliminate this problem, but will increase the driver power
dissipation. A series resistor from 27Ω to 54Ω (depend-
ing on the trace impedance and connection) placed near
the driver will also eliminate over/under shoot without
additional driver power dissipation.
For many applications, the serial interface pins (SCK, SDI,
CS, F
no degradation occurs. On the other hand, if an external
oscillator is used (F
O
) remain static during the conversion cycle and
O
, CS, and SCK (in external serial clock mode)
O
driven externally) it is active during
CC
O
) may degrade
– 0.5V. During
the conversion cycle. Moreover, the digital fi lter rejection
is minimal at the clock rate applied to F
taken to ensure external inputs and reference lines do not
cross this signal or run near it. These issues are avoided
when using the internal oscillator.
Driving the Input and Reference
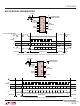
The input and reference pins of the LTC2494 are connected
directly to a switched capacitor network. Depending on
the relationship between the differential input voltage and
the differential reference voltage, these capacitors are
switched between these four pins. Each time a capacitor
is switched between two of these pins, a small amount
of charge is transferred. A simplifi ed equivalent circuit is
shown in Figure 12.
When using the LTC2494’s internal oscillator, the input
capacitor array is switched at 123kHz. The effect of the
charge transfer depends on the circuitry driving the in-
put/reference pins. If the total external RC time constant
is less then 580ns the errors introduced by the sampling
process are negligible since complete settling occurs.
Typically, the reference inputs are driven from a low imped-
ance source. In this case, complete settling occurs even
with large external bypass capacitors. The inputs (CH0 to
CH15, COM), on the other hand, are typically driven from
larger source resistances. Source resistances up to 10k
may interface directly to the LTC2494 and settle completely;
however, the addition of external capacitors at the input
terminals in order to fi lter unwanted noise (anti-aliasing)
results in incomplete settling.
The LTC2494 offers two methods of removing these errors.
The fi rst is automatic differential input current cancella-
tion (Easy Drive) and the second is the insertion of buffer
between the MUXOUT and ADCIN pins, thus isolating the
input switching from the source resistance.
Automatic Differential Input Current Cancellation
In applications where the sensor output impedance is
low (up to 10kΩ with no external bypass capacitor or up
to 500Ω with 0.001μF bypass), complete settling of the
input occurs. In this case, no errors are introduced and
direct digitization is possible.
LTC2494
O
. Care must be
27
2494fb