mpc9351 Integrated Device Technology, mpc9351 Datasheet - Page 7

mpc9351
Manufacturer Part Number
mpc9351
Description
Low Voltage Pll Clock Driver
Manufacturer
Integrated Device Technology
Datasheet
1.MPC9351.pdf
(12 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mpc9351AC
Manufacturer:
Micrel
Quantity:
180
Company:
Part Number:
mpc9351AC
Manufacturer:
IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mpc9351ACR2
Manufacturer:
IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mpc9351FA
Manufacturer:
IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mpc9351FAR2
Manufacturer:
IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc
Quantity:
10 000
IDT™ Low Voltage PLL Clock Driver
Freescale Timing Solutions Organization has been acquired by Integrated Device Technology, Inc
MPC9351
Low Voltage PLL Clock Driver
Advanced Clock Drivers Devices
Freescale Semiconductor
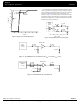
Calculation of Part-to-Part Skew
where critical clock signal timing can be maintained across
several devices. If the reference clock inputs (TCLK or PCLK)
of two or more MPC9351 are connected together, the
maximum overall timing uncertainty from the common TCLK
input to any output is:
static phase offset, output skew, feedback board trace delay
and I/O (phase) jitter:
is specified. I/O jitter numbers for other confidence factors
(CF) can be derived from
Table 10. Confidence Factor CF
layout and can be used to fine-tune the effective delay
through each device. In the following example calculation, an
I/O jitter confidence factor of 99.7% (± 3σ) is assumed,
resulting in a worst case timing uncertainty from input to any
output of –251 ps to 351 ps relative to TCLK (V
f
VCO
Figure 4. MPC9351 Maximum Device-to-Device Skew
The MPC9351 zero-delay buffer supports applications
This maximum timing uncertainty consist of 4 components:
Due to the statistical nature of I/O jitter, a RMS value (1 σ)
The feedback trace delay is determined by the board
± 1σ
± 2σ
± 3σ
± 4σ
± 5σ
± 6σ
CF
Any Q
Any Q
TCLK
QFB
= 400 MHz):
QFB
t
Max. skew
SK(PP)
t
t
SK(PP)
SK(PP)
Common
Device 1
Device 1
Device 2
Device2
[(17ps · –3)...(17ps ·3)] + t
Probability of Clock Edge within the Distribution
= t
=[–50 ps...150 ps] + [–150 ps...150 ps] +
=[–251 ps...351 ps] + t
(∅)
+ t
SK(O)
t
JIT(∅)
—t(ý)
Table
+t
+ t
SK(O)
PD, LINE(FB)
0.68268948
0.95449988
0.99730007
0.99993663
0.99999943
0.99999999
10.
+t
(∅)
t
PD, LINE(FB)
JIT(∅)
PD, LINE(FB)
t
SK(PP)
+ t
t
PD,LINE(FB)
+t
JIT(∅)
SK(O)
CC
= 3.3 V and
· CF
7
shown in the AC characteristic table for V
RMS). I/O jitter is frequency dependant with a maximum at
the lowest VCO frequency (200 MHz for the MPC9351).
Applications using a higher VCO frequency exhibit less I/O
jitter than the AC characteristic limit. The I/O jitter
characteristics in
a smaller I/O jitter number at the specific VCO frequency,
resulting in tighter timing limits in zero-delay mode and for
part-to-part skew (t
Power Supply Filtering
circuitry is naturally susceptible to random noise, especially if
this noise is seen on the power supply pins. Noise on the
V
for instance, I/O jitter. The MPC9351 provides separate
power supplies for the output buffers (V
phase-locked loop (V
design technique is to isolate the high switching noise digital
outputs from the relatively sensitive internal analog
phase-locked loop. In a digital system environment, where it
is more difficult to minimize noise on the power supplies, a
second level of isolation may be required. The simple but
effective form of isolation is a power supply filter on the V
pin for the MPC9351.
supply filter scheme. The MPC9351 frequency and phase
stability is most susceptible to noise with spectral content in
the 100 kHz to 20 MHz range; therefore, the filter should be
CCA
Above equation uses the maximum I/O jitter number
The MPC9351 is a mixed analog/digital product. Its analog
30
25
20
15
10
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
5
0
(PLL) power supply impacts the device characteristics,
75
75
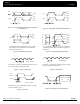
Figure 5. Maximum I/O Jitter (RMS)
Figure 6. Maximum I/O Jitter (RMS)
225
versus Frequency for V
225
versus Frequency for V
Max. I/O Jitter versus Frequency
Max. I/O Jitter versus Frequency
Figure 5
250
250
SK(PP)
CCA
Figure 7
275
275
).
) of the device. The purpose of this
and
Figure 6
300
300
illustrates a typical power
325
325
CC
CC
can be used to derive
CC
VCO Frequency [MHz]
VCO Frequency [MHz]
= 2.5 V
= 3.3 V
CC
) and the
350
350
= 3.3 V (17 ps
375
375
MPC9351
400
400
NETCOM
CCA
MPC9351
7