cs5301 ON Semiconductor, cs5301 Datasheet - Page 12
cs5301
Manufacturer Part Number
cs5301
Description
Three-phase Buck Controller With Integrated Gate Drivers And Power Good
Manufacturer
ON Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.CS5301.pdf
(19 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
CS5301
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA
Quantity:
28
Part Number:
CS5301
Manufacturer:
ON/安森美
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
cs5301GDW32
Manufacturer:
PROLIFIC
Quantity:
13
Part Number:
cs5301GDW32
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
cs5301GDW32G
Manufacturer:
ON/安森美
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
cs5301GDWR32G
Manufacturer:
ON/安森美
Quantity:
20 000
connected in parallel and are switched on at different times.
This reduces output current from the individual converters
and increases the apparent ripple frequency. Because several
converters are connected in parallel, output current can ramp
up or down faster than a single converter (with the same
value output inductor) and heat is spread among multiple
components.
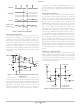
Enhanced V
the previous phase. Normally GATE(H) transitions high at
the beginning of each oscillator cycle. Inductor current
ramps up until the combination of the current sense signal
and the output ripple trip the PWM comparator and bring
GATE(H) low. Once GATE(H) goes low, it will remain low
until the beginning of the next oscillator cycle. While
GATE(H) is high, the enhanced V
and load transients. Once GATE(H) is low, the loop will not
respond again until the beginning of the next cycle.
Therefore, constant frequency Enhanced V
respond within 1/3 of the off−time for a three−phase
converter.
current in each phase. An additional input (CS
current information has been added to the V
phase as shown in Figure 9.
CSA and summed with the OFFSET and Output Voltage at
the non−inverting input of the PWM comparator. The
inductor current provides the PWM ramp and as inductor
SWNODE
FIXED FREQUENCY MULTI−PHASE CONTROL
In a multi−phase converter, multiple converters are
The CS5301 uses a three−phase, fixed frequency,
The Enhanced V
The inductor current is measured across R
Figure 9. Enhanced V
V
OUT
2
architecture. Each phase is delayed 120° from
L
+
R
2
R
L
+
Sense Scheme
S
architecture measures and adjusts
COMP
CS
DAC
V
CS
FB
2
REF
X
Feedback and Current
OUT
2
OFFSET
+
loop will respond to line
CSA
E.A.
+
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
2
+
+
+
S
2
x
, amplified by
will typically
loop for each
) for inductor
+
COMP
http://onsemi.com
PWM
CS5301
12
current increases the voltage on the positive pin of the PWM
comparator rises and terminates the PWM cycle. If the
inductor starts the cycle with a higher current, the PWM
cycle will terminate earlier providing negative feedback.
The CS5301 provides a CS
CS
Current sharing is accomplished by referencing all phases to
the same V
current signal will turn off earlier than phases with a smaller
current signal.
feedback signal allows the open loop output impedance of
the power stage to be controlled. If the COMP pin is held
steady and the inductor current changes, there must also be
a change in the output voltage. Or, in a closed loop
configuration when the output current changes, the COMP
pin must move to keep the same output voltage. The required
change in the output voltage or COMP pin depends on the
scaling of the current feedback signal and is calculated as
single−phase output impedance divided by the number of
phases. The output impedance of the power stage determines
how the converter will respond during the first few ms of a
transient before the feedback loop has repositioned the
COMP pin.
calculated from;
COMP pin at a fixed level. Before T1 the converter is in
normal steady state operation. The inductor current provides
the PWM ramp through the Current Share Amplifier. The
PWM cycle ends when the sum of the current signal, voltage
signal and OFFSET exceed the level of the COMP pin. At T1
the output current increases and the output voltage sags. The
next PWM cycle begins and the cycle continues longer than
previously while the current signal increases enough to make
up for the lower voltage at the V
T2. After T2 the output voltage remains lower than at light
load and the current signal level is raised so that the sum of
the current and voltage signal is the same as with the original
load. In a closed loop system the COMP pin would move
higher to restore the output voltage to the original level.
Single Stage Impedance + DV DI + R S
Including both current and voltage information in the
The single−phase power stage output impedance is:
The multi−phase power stage output impedance is the
The peak output current of each phase can also be
Figure 10 shows the step response of a single phase with the
REF
I pkout (per phase) +
, V
FB
FB
and COMP inputs are common to all phases.
and COMP pins, so that a phase with a larger
DV + R S
V COMP * V FB * V OFFSET
x
CSA Gain
input for each phase, but the
FB
R S
pin and the cycle ends at
CSA Gain
DI
CSA Gain.