TC7116 Microchip, TC7116 Datasheet - Page 13

TC7116
Manufacturer Part Number
TC7116
Description
3-1/2 Digit Analog-to-Digital Converters with Hold
Manufacturer
Microchip
Datasheet
1.TC7116.pdf
(22 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACKW
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACLW
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
12 000
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACLW
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACLW713
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACPL
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116ACPL
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
3 960
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116CKW
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
TC7116CKW
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
TC7116CKW713
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
TC7116CPL
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
6.0
The TC7117/TC7117A sink the LED display current,
causing heat to build up in the IC package. If the inter-
nal voltage reference is used, the changing chip tem-
perature can cause the display to change reading. By
reducing the LED common anode voltage, the TC7117/
TC7117A package power dissipation is reduced.
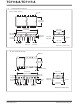
Figure 6-1 is a curve tracer display showing the rela-
tionship between output current and output voltage for
typical TC7117CPL/TC7117ACPL devices. Since a
typical LED has 1.8V across it at 8mA and its common
anode is connected to +5V, the TC7117/TC7117A out-
put is at 3.2V (Point A, Figure 6-1). Maximum power
dissipation is 8.1mA x 3.2V x 24 segments = 622mW.
However, notice that once the TC7117/TC7117A's out-
put voltage is above 2V, the LED current is essentially
constant as output voltage increases. Reducing the
output voltage by 0.7V (Point B Figure 6-1) results in
7.7mA of LED current, only a 5% reduction. Maximum
power dissipation is now only 7.7mA x 2.5V x 24 =
462mW, a reduction of 26%. An output voltage reduc-
tion of 1V (Point C) reduces LED current by 10%
(7.3mA), but power dissipation by 38% (7.3mA x 2.2V
x 24 = 385mW).
FIGURE 6-1:
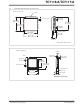
Reduced power dissipation is very easy to obtain.
Figure 6-2 shows two ways: either a 5.1Ω, 1/4W resis-
tor, or a 1A diode placed in series with the display (but
not in series with the TC7117/TC7117A). The resistor
reduces the TC7117/TC7117A's output voltage (when
all 24 segments are ON) to Point C of Figure 6-1. When
segments turn off, the output voltage will increase. The
diode, however, will result in a relatively steady output
voltage, around Point B.
©
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
10.000
9.000
8.000
7.000
6.000
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
2.00
C
2.50
B
Output Voltage (V)
TC7117/TC7117A OUTPUT
VS. OUTPUT VOLTAGE
3.00
A
3.50
4.00
In addition to limiting maximum power dissipation, the
resistor reduces change in power dissipation as the
display changes. The effect is caused by the fact that,
as fewer segments are ON, each ON output drops
more voltage and current. For the best case of six seg-
ments (a “111” display) to worst case (a “1888” display),
the resistor circuit will change about 230mW, while a
circuit without the resistor will change about 470mW.
Therefore, the resistor will reduce the effect of display
dissipation on reference voltage drift by about 50%.
The change in LED brightness caused by the resistor is
almost unnoticeable as more segments turn off. If dis-
play brightness remaining steady is very important to
the designer, a diode may be used instead of the
resistor.
FIGURE 6-2:
TC7116/A/TC7117/A
TP5
40
100
kΩ
1
1.5W, 1/4Ω
100
1N4001
pF
24kΩ
TP2
TP1
1kΩ
+5V
35
0.1
µF
1MΩ
TP3
TC7117A
DIODE OR RESISTOR
LIMITS PACKAGE POWER
DISSIPATION
TC7117
+
10
Display
0.01
µF
In
30
–
kΩ
0.47
47
µF
0.22
TP
4
DS21457B-page 13
µF
-5V
Display
150kΩ
20
21