ZXLD1322DCTC ZETEX [Zetex Semiconductors], ZXLD1322DCTC Datasheet - Page 16

ZXLD1322DCTC
Manufacturer Part Number
ZXLD1322DCTC
Description
Buck/boost mode DC-DC converter for LED driving with 700mA output and current control
Manufacturer
ZETEX [Zetex Semiconductors]
Datasheet
1.ZXLD1322DCTC.pdf
(18 pages)
ZXLD1322
Additional notes
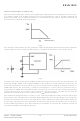
Note that the ON time is set by the time it takes the coil to reach the peak current. This peak value
is reduced by the control loop to give the desired LED power, so the ON time can vary over a wide
range. The minimum coil current can be zero (discontinuous operation) or finite (continuous
operation) depending on the supply voltage, LED current and the LED voltage. The OFF time is
set by an internal timer and is nominally 1.2µs at 100% LED power (VADJ = 500mV), increasing to
about 8µs at 10% LED power (VADJ = 50mV). The longer OFF time and variable peak current
enables the circuit to dim the LED whilst maintaining continuous switching, rather than "skipping"
or stalling and continuous running is better for reducing electrical noise and also for eliminating
audible noise from the coil core.
Layout considerations
As with all switching DC to DC converters, the currents can be large. Using small inductors with
a reasonable high supply voltage will cause currents to change quickly. High dI/dt can cause
inductively-coupled spikes into adjacent tracks. At the transition from of the ON phase to the OFF
phase and back, where the power transistor switches, the voltage at the collector rises and falls
quickly. High dV/dt can cause capacitively coupled spikes into adjacent tracks, especially if they
have a high impedance. For this reason, all tracks on the PCB should be thick, to minimise drops,
and short to keep all the components coupled tightly together.
A double-sided board should be used with a ground plane to screen the tracks and provide a good
ground return for the various functions and the rear exposed pad on the package should have an
appropriately-sized land with good ground connections, both to reduce electrical noise due to
ground drops and to improve thermal conductivity.
The input decoupling capacitor C1 should be very close to the chip pins and the LED sense
resistor R3 should have Kelvin tracks to M_VIN and VIN to achieve LED current measurement
accuracy, as the PCB tracks will have comparable resistance to the 100mΩ resistor, so taking
sense tracks to the current monitor which are not connected close to the ends of R3 will cause a
measurement error.
The peak current sense resistor R1 should have short tracks to the ground at the bottom end and
Kelvin tracks to ISENSE at the top end. This resistor might need to be only 25mΩ and PCB track
resistance becomes comparable if the tracks are not very short. ISENSE is a high impedance
input, so a thin track from this pin directly to the top of R
resistor R1 will still give an accurate
SENSE
measurement.
The ADJ pin should have short tracks, as this is a fairly low-level signal controlling the power of
the system. As it needs to be less than 28mV for shutdown, a close ground connection is needed
for the pull-down device, as any ground drops could raise the potential. In particular, if a bipolar
transistor is used as a pull-down device, this will have an appreciable V
, which could perhaps
SAT
be half the shutdown potential.
The bottom of the thermistor must be coupled very closely to ground, as the TADJ pin varies the
LED current from 100% to 0% for a voltage change of only 25mV, so any noise on the bottom of
the thermistor will seriously affect the accuracy of the Thermal Protection circuit.
Issue 1 - January 2008
16
www.zetex.com
© Zetex Semiconductors plc 2008