MAX1180ECM+TD Maxim Integrated, MAX1180ECM+TD Datasheet - Page 12

MAX1180ECM+TD
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX1180ECM+TD
Description
Analog to Digital Converters - ADC
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated
Datasheet
1.MAX1180ECMTD.pdf
(18 pages)
Specifications of MAX1180ECM+TD
Number Of Channels
2
Architecture
Pipeline
Conversion Rate
105 MSPs
Resolution
10 bit
Input Type
Single-Ended/Differential
Snr
59 dB
Interface Type
Parallel
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Package / Case
TQFP EP
Maximum Power Dissipation
511 mW
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Converters
2
Voltage Reference
Internal, External
Dual/Triple, Ultra-Low-Voltage, SOT23 µP
Supervisory Circuits
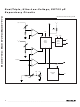
Most µPs with bidirectional reset pins can interface
directly to open-drain RST output options. Systems
simultaneously requiring a push-pull RST output and a
bidirectional reset interface can be in logic contention.
To prevent contention, connect a 4.7kΩ resistor
between RST and the µP’s reset I/O port as shown in
Figure 4.
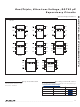
The power-fail comparator has a typical input hysteresis
of 3mV. This is sufficient for most applications where a
power-supply line is being monitored through an external
voltage-divider (see the Power-Fail Comparator section).
If additional noise margin is desired, connect a resistor
between PFO and PFI as shown in Figure 5. Select the
values of R1, R2, and R3 so PFI sees V
V
rises to its power-good trip point (V
window extends between the specified V
thresholds. R3 adds the additional hysteresis by sinking
current from the R1/R2 divider network when PFO is
logic-low and sourcing current into the network when PFO
is logic-high. R3 is typically an order of magnitude greater
than R1 or R2.
Figure 4. Interfacing to µPs with Bidirectional Reset I/O
12
EXT
V
CC
1 V
______________________________________________________________________________________
falls to its power-fail trip point (V
CC
2
Interfacing to µPs with Bidirectional
Adding Hysteresis to the Power-Fail
V
V
CC
CC
2
1
MAX6715A–
MAX6729A/
MAX6797A
GND
Applications Information
RST
RESET TO OTHER SYSTEM COMPONENTS
4.7kΩ
GOOD
FAIL
PFI
RESET
FAIL
). The hysteresis
Comparator
) and when V
(626mV) when
Reset Pins
GND
and V
µP
GOOD
IN
The current through R2 should be at least 2.5µA to ensure
that the 100nA (max) PFI input current does not signifi-
cantly shift the trip points. Therefore, R2 < V
62kΩ for most applications. R3 will provide additional hys-
teresis for PFO push-pull (V
(V
These µP supervisors can monitor either positive or
negative supplies using a resistor voltage-divider to
PFI. PFO can be used to generate an interrupt to the µP
or cause reset to assert (Figure 3).
The power-fail comparator can be used to monitor a
negative supply voltage using the circuit shown in
Figure 3. When the negative supply is valid, PFO is low.
When the negative supply voltage drops, PFO goes
high. The circuit’s accuracy is affected by the PFI
threshold tolerance, V
The MAX6715A–MAX6729A/MAX6797A supervisors are
relatively immune to short-duration negative-going V
transients (glitches). It is usually undesirable to reset
the µP when V
Typical Operating Characteristics show Maximum
Transient Duration vs. Reset Threshold Overdrive, for
which reset pulses are not generated. The graph was
produced using negative-going V
above V
Figure 5. Adding Hysteresis to Power-Fail for Push-Pull PFO
V
OH
EXT
A
R1
R2
= V
Monitoring an Additional Power Supply
TH
PULLUP
PFI
and ending below the reset threshold by the
MAX6729A
GND
CC
Negative-Going V
R3
) applications.
Monitoring a Negative Voltage
PFO
experiences only small glitches. The
CC
V
V
V
R2 = 50kΩ (FOR > 10µA R2 CURRENT)
R1 = R2 ((V
R3 = (R1 x V
GOOD
FAIL
OH
, R1, and R2.
PFO
V
= V
IN
= DESIRED V
= DESIRED V
CC
OH
1 (FOR PUSH-PULL PFO)
GOOD
OH
)/(V
- V
= V
EXT
GOOD
EXT
PFI
FAIL VOLTAGE THRESHOLD
) - (V
GOOD VOLTAGE THRESHOLD
CC
- V
CC
FAIL
CC
PFI
1) or open-drain
)(V
)
pulses, starting
GOOD
Transients
V
V
GOOD
FAIL
- V
PFI
FAIL
)/V
/10µA <
OH
)/V
PFI
CC