24LC16B-I/SN Microchip Technology, 24LC16B-I/SN Datasheet - Page 8

24LC16B-I/SN
Manufacturer Part Number
24LC16B-I/SN
Description
IC EEPROM 16KBIT 400KHZ 8SOIC
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Specifications of 24LC16B-I/SN
Memory Size
16K (2K x 8)
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Format - Memory
EEPROMs - Serial
Memory Type
EEPROM
Speed
400kHz
Interface
I²C, 2-Wire Serial
Voltage - Supply
2.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Organization
8 Block x 256 x 8
Interface Type
I2C
Maximum Clock Frequency
0.4 MHz
Access Time
900 ns
Supply Voltage (max)
5.5 V
Supply Voltage (min)
2.5 V
Maximum Operating Current
5 mA
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Operating Supply Voltage
6.5 V
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
24LC16B-I/SN
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
32 000
Company:
Part Number:
24LC16B-I/SN
Manufacturer:
MCP
Quantity:
59 521
Part Number:
24LC16B-I/SN
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
24AA16/24LC16B
6.0
6.1
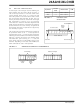
Following the Start condition from the master, the
device code (4 bits), the block address (3 bits) and the
R/W bit, which is a logic-low, is placed onto the bus by
the master transmitter. This indicates to the addressed
slave receiver that a byte with a word address will
follow once it has generated an Acknowledge bit during
the ninth clock cycle. Therefore, the next byte transmit-
ted by the master is the word address and will be
written into the Address Pointer of the 24XX16. After
receiving another Acknowledge signal from the
24XX16, the master device will transmit the data word
to be written into the addressed memory location. The
24XX16
generates a Stop condition. This initiates the internal
write cycle and, during this time, the 24XX16 will not
generate Acknowledge signals (Figure 6-1).
FIGURE 6-1:
DS21703J-page 8
SDA Line
Bus Activity
Master
Bus Activity
WRITE OPERATION
Byte Write
acknowledges
BYTE WRITE
S
S
T
A
R
T
1
0
again
1 0 B2 B1 B0 0
Control
Byte
Select
Block
Bits
and
the
master
A
C
K
Address
Word
6.2
The write control byte, word address and the first data
byte are transmitted to the 24XX16 in the same way as
in a byte write. However, instead of generating a Stop
condition, the master transmits up to 16 data bytes to
the 24XX16, which are temporarily stored in the on-
chip page buffer and will be written into memory once
the master has transmitted a Stop condition. Upon
receipt of each word, the four lower-order Address
Pointer bits are internally incremented by ‘
higher-order 7 bits of the word address remain
constant. If the master should transmit more than 16
bytes prior to generating the Stop condition, the
address counter will roll over and the previously
received data will be overwritten. As with the byte write
operation, once the Stop condition is received an
internal write cycle will begin (Figure 6-2).
6.3
The WP pin allows the user to write-protect the entire
array (000-7FF) when the pin is tied to V
V
SS
Note:
the write protection is disabled.
Page Write
Write Protection
Page write operations are limited to writing
bytes within a single physical page,
regardless of the number of bytes
actually being written. Physical page
boundaries start at addresses that are
integer multiples of the page buffer size (or
‘page-size’) and end at addresses that are
integer multiples of [page size – 1]. If a
page write command attempts to write
across a physical page boundary, the
result is that the data wraps around to the
beginning of the current page (overwriting
data previously stored there), instead of
being written to the next page, as might be
expected. It is therefore necessary for the
application software to prevent page write
operations that would attempt to cross a
page boundary.
A
C
K
© 2009 Microchip Technology Inc.
Data
CC
. If tied to
A
C
K
1
P
S
T
O
P
’. The