LTC4150IMS#PBF Linear Technology, LTC4150IMS#PBF Datasheet - Page 7
LTC4150IMS#PBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC4150IMS#PBF
Description
IC COUNTER/GAUGE GAS/BATT 10MSOP
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC4150CMS.pdf
(14 pages)
Specifications of LTC4150IMS#PBF
Function
Fuel, Gas Gauge/Monitor
Battery Type
Li-Ion, NiCd, NiMH
Voltage - Supply
2.7 V ~ 8.5 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
10-TFSOP, 10-MSOP (0.118", 3.00mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
OPERATION
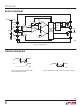
Charge is the time integral of current. The LTC4150 mea-
sures battery current by monitoring the voltage developed
across a sense resistor and then integrates this information
in several stages to infer charge. The Block Diagram shows
the stages described below. As each unit of charge passes
into or out of the battery, the LTC4150 INT pin interrupts
an external microcontroller and the POL pin reports the
polarity of the charge unit. The external microcontroller
then resets INT with the CLR input in preparation for the
next interrupt issued by the LTC4150. The value of each
charge unit is determined by the sense resistor value and
the sense voltage to interrupt frequency gain G
LTC4150.
Power-On and Start-Up Initialization
When power is fi rst applied to the LTC4150, all internal
circuitry is reset. After an initialization interval, the LTC4150
begins counting charge. This interval depends on V
the voltage across the sense resistor but will be at least
5ms. It may take an additional 80ms for the LTC4150 to
accurately track the sense voltage. An internal undervoltage
lockout circuit monitors V
V
Asserting SHDN low also resets the LTC4150’s internal
circuitry and reduces the supply current to 1.5μA. In this
condition, POL and INT outputs are high impedance. The
LTC4150 resumes counting after another initialization
interval. Shutdown minimizes battery drain when both
the charger and load are off.
DD
falls below 2.5V.
DD
and resets all circuitry when
VF
DD
of the
and
CHARGE COUNTING
First, the current measurement is fi ltered by capacitor C
connected across pins C
changes in current arising from ripple, noise and spikes
in the load or charging current.
Second, the fi lter’s output is applied to an integrator with
the amplifi er and 100pF capacitor at its core. When the
integrator output ramps to REFHI or REFLO levels, switches
S1 and S2 reverse the ramp direction. By observing the
condition of S1 and S2 and the ramp direction, polarity is
determined. The integrating interval is trimmed to 600μs
at 50mV full-scale sense voltage.
Third, a counter is incremented or decremented every
time the integrator changes ramp direction. The counter
effectively increases integration time by a factor of 1024,
greatly reducing microcontroller overhead required to
service interrupts from the LTC4150.
At each counter under or overfl ow, the INT output latches
low, fl agging a microcontroller. Simultaneously, the POL
output is latched to indicate the polarity of the observed
charge. With this information, the microcontroller can
total the charge over long periods of time, developing
an accurate estimate of the battery’s condition. Once the
interrupt is recognized, the microcontroller resets INT with
a low going pulse on CLR and awaits the next interrupt.
Alternatively, INT can drive CLR.
F
+
and C
F
–
. This averages fast
LTC4150
4150fc
7
F