MAX16046EVKIT+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX16046EVKIT+ Datasheet

MAX16046EVKIT+
Specifications of MAX16046EVKIT+
Related parts for MAX16046EVKIT+
MAX16046EVKIT+ Summary of contents
Page 1
... TQFP package and are fully specified from -40°C to +85°C. Pin Configurations appear at end of data sheet. ________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com. o Operates from 3V to 14V ...
Page 2
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers V SUPPLY IN DC-DC EN GND IN DC-DC EN GND IN DC-DC EN GND VOLTAGE-DETECTOR PART INPUTS MAX16046 12 MAX16048 8 2 _______________________________________________________________________________________ OUT MON1 DACOUT1 EN_OUT1 OUT MON2–MON11 ...
Page 3
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS V to GND ....................……………………………-0.3V to +15V CC EN, MON_, SCL, SDA, A0 ........................................-0.3V to +6V GPIO_, RESET (configured as open drain) to GND.....-0.3V to +6V EN_OUT1–EN_OUT6 (configured as open ...
Page 4
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued 14V -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified. Typical values are PARAMETER SYMBOL ADC LSB Step Size ADC V EN ...
Page 5
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued 14V -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified. Typical values are PARAMETER SYMBOL DAC Center Code Absolute DAC Accuracy Gain ...
Page 6
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued 14V -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified. Typical values are PARAMETER SYMBOL Input Leakage Current Output-Voltage Low Input Capacitance ...
Page 7
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers SDA t SU:DAT t LOW SCL t HIGH t HD:STA START CONDITION 2 Figure 1. I C/SMBus Timing Diagram TCK TDI, TMS TDO Figure ...
Page 8
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers (V = 3.3V +25°C, unless otherwise noted SUPPLY CURRENT CC vs. V SUPPLY VOLTAGE CC 4 +85°C A 3.5 3 +25°C A 2.5 ...
Page 9
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers (V = 3.3V +25°C, unless otherwise noted OUTPUT-VOLTAGE HIGH vs. SOURCE CURRENT (CHARGE-PUMP OUTPUT ...
Page 10
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers (V = 3.3V +25°C, unless otherwise noted MIXED MODE MAX16046 toc15 INS4 INS3 1V/div INS2 INS1 0V 20ms/div ADC INL 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 -0.4 ...
Page 11
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PIN THIN QFN NAME MAX16046 MAX16048 1–8 1–8 MON1–MON8 9–12 — MON9–MON12 9–12, 33–36, — N.C. 53–56 RESET SCL 16 16 SDA 17 17 TMS ...
Page 12
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PIN THIN QFN NAME MAX16046 MAX16048 37 37 ABP DBP 41 41 GPIO1 42 42 GPIO2 43 43 GPIO3 44 44 GPIO4 EN_OUT1– 45–50 45–50 EN_OUT6 ...
Page 13
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PIN TQFP NAME MAX16046 MAX16048 1–7, 10 1–7, 10 MON1–MON8 11–14 — MON9–MON12 8, 9, 11–15 15, 25, 25, 33, 33, 48, N.C. 38–41, 48, 49, 64 49, 60–64 RESET ...
Page 14
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PIN TQFP NAME MAX16046 MAX16048 42 42 ABP DBP 46 46 GPIO1 47 47 GPIO2 50 50 GPIO3 51 51 GPIO4 EN_OUT1– 52–57 52–57 EN_OUT6 EN_OUT7, ...
Page 15
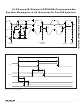
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers MAX16046 MAX16048 EN V TH_EN NONVOLATILE FAULT EVENT LOGGER MON1– VOLTAGE 10-BIT MON12 SCALING ADC (SAR) (MON1– AND MUX MON8) DACOUT1– TRACK AND DACOUT12 8-BIT DAC HOLD (DACOUT1– DACOUT8) EEPROM REGISTERS GND ...
Page 16
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Note: This data sheet uses a specific convention for referring to bits within a particular address location example, r0Fh[3:0] refers to bit 3 to bit 0 in register with address ...
Page 17
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Detailed Description The MAX16046 is capable of managing up to twelve system voltages simultaneously, and the MAX16048 can manage up to eight system voltages. After boot- up high and ...
Page 18
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers To initiate sequencing/tracking and enable monitoring, the voltage at EN must be above 0.525V and the Software Enable bit in r4Dh[0] must be set to ‘0.’ To power down and disable monitoring, ...
Page 19
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 2. Input Monitor Ranges and Enables REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 0Fh [5:4] [7:6] [1:0] [3:2] 10h [5:4] [7:6] ______________________________________________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION MON1 Voltage Range Selection From 0 ...
Page 20
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 2. Input Monitor Ranges and Enables (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 11h [5:4] [7:6] * MAX16046 only 20 ______________________________________________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION MON9 Voltage Range Selection From 0 ...
Page 21
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers The extended memory page contains the ADC conver- sion result registers (see Table 3). These registers are also used internally for fault threshold comparison. Voltage-monitoring thresholds are compared with the 8 MSBs ...
Page 22
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers General-Purpose Inputs/Outputs GPIO1–GPIO6 are programmable general-purpose inputs/outputs. GPIO1–GPIO6 are configurable as a manual reset input, a margin disable input, margin- up/margin-down control inputs, a watchdog timer input Table 4. General-Purpose IO Configuration ...
Page 23
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Voltage Tracking Sense (INS_) Inputs GPIO1–GPIO4 are configurable as feedback sense return inputs (INS_) for closed-loop tracking. Connect the gate of an external n-channel MOSFET to each EN_OUT_ configured for closed-loop tracking. ...
Page 24
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers GPIO1–GPIO4 are configurable as active-low push-pull or open-drain fault-dependent outputs. These outputs assert when any monitored input exceeds an overvolt- age, undervoltage, or early warning threshold. FAULT1 and FAULT2 GPIO5 and GPIO6 ...
Page 25
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 7. FAULT1 and FAULT2 Output Configuration and Dependencies (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] 18h [5] [6] [7] * MAX16046 only Fault-On Power-Up (FAULTPU) GPIO6 indicates ...
Page 26
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers GPIO6 is configurable as an active-low MARGIN input. Drive MARGIN low before varying system voltages above or below the thresholds to avoid signaling an error. Drive MARGIN high for normal operation. When ...
Page 27
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 9. EN_OUT1–EN_OUT12 Configuration (continued) REGISTER/EEPROM BIT ADDRESS RANGE [0] [3:1] 20h [6:4] [7] [1:0] 21h [3:2] [5:4] [7:6] ______________________________________________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION EN_OUT3 Configuration (MSB)—see r1Fh[7:6] EN_OUT4 Configuration: 000 = EN_OUT4 is an ...
Page 28
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 9. EN_OUT1–EN_OUT12 Configuration (continued) REGISTER/EEPROM BIT ADDRESS RANGE [1:0] [3:2] 22h [5:4] [7:6] * MAX16046 only Charge-Pump Configuration EN_OUT1–EN_OUT6 can act as high-voltage charge- pump outputs to drive up to six ...
Page 29
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers MAX16046 fig03 20ms/div Figure 3. RESET and EN_OUT_ During Power-Up, EN_OUT_ Is in Open-Drain Active-Low Configuration Each EN_OUT_ has one or more associated MON_ inputs, facilitating the voltage monitoring of multiple power ...
Page 30
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers RESET Deassertion After any MON_ inputs assigned to Slot 12 exceed their undervoltage thresholds, the reset timeouts begin. When the reset timeout completes, RESET deasserts. The reset timeout period is set in ...
Page 31
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 11. MON_ Slot Assignment CONFIGURATION BITS 0000 MON_ is not assigned to a slot 0001 MON_ is assigned to Slot 1 0010 MON_ is assigned to Slot 2 0011 MON_ is ...
Page 32
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 13. Sequence Delays and Fault Recovery REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 4Eh [4] [5] [6] [7] [2:0] [3] 4Fh [5:4] [7:6] 32 ______________________________________________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION Power-Up Fault Timeout 00 = ...
Page 33
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 13. Sequence Delays and Fault Recovery (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [2:0] 50h [5:3] [7:6] [0] [3:1] 51h [6:4] [7] [1:0] 52h [4:2] [7:5] [2:0] 53h [5:3] [7:6] [0] [3:1] ...
Page 34
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Closed-Loop Tracking The MAX16046/MAX16048 track up to four voltages during any time slot except Slot 0 and Slot 12. Configure GPIO1–GPIO4 as sense line inputs (INS_) to monitor tracking voltages. Configure GPIO6 ...
Page 35
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 15. Power-Good (PG) Thresholds REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 64h [5:4] [7:6] The MAX16046/MAX16048 feature an 8-bit DAC with 12 outputs (MAX16046 outputs (MAX16048) for volt- age ...
Page 36
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 16. DACOUT Ranges REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 12h [5:4] [7:6] [1:0] [3:2] 13h [5:4] [7:6] 36 ______________________________________________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION DACOUT1 Range Selection DACOUT1 is OFF 01 = ...
Page 37
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 16. DACOUT Ranges (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [1:0] [3:2] 14h [5:4] [7:6] * MAX16046 only Table 17. DACOUT Enables EXTENDED PAGE DACOUT ENABLES ADDRESS [ DACOUT1 is ...
Page 38
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Voltage Margining Margining is commonly performed while a system is under development, but margining can also be per- formed during the manufacturing process. The supply voltages of external DC-DC regulators can be ...
Page 39
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers The MAX16046/MAX16048 monitor the input (MON_) channels and compare the results with an overvoltage threshold, an undervoltage threshold, and a selectable overvoltage or undervoltage early warning threshold. Based on these conditions, the ...
Page 40
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Fault conditions are detected at the end of each con- version. If the voltage on an input falls outside a moni- tored threshold for one acquisition, the input multiplexer remains on that ...
Page 41
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 23. Critical Fault Configuration and Enable Bits REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS Critical Fault Log Control 00 = Failed lines and ADC conversion values save to EEPROM upon critical fault [1:0] ...
Page 42
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 23. Critical Fault Configuration and Enable Bits (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [ Fault log triggered when MON9 is above/below its early warning threshold* [ Fault ...
Page 43
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Power-Up/Power-Down Faults All EN_OUTs are deasserted if an overvoltage or under- voltage fault is detected during power-up/power-down (regardless of the critical fault enable bits). Under these conditions, information of the failing slot ...
Page 44
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 26. EEPROM Fault Log Operation Period FAULT CONTROL REGISTER r47h[1:0] 00 Failed lines and ADC values saved The reset output, RESET, is asserted during power- up/power-down and deasserts ...
Page 45
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 27. RESET Configuration and Dependencies (continued) REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS RESET DEPENDENCIES [ RESET is dependent on MON1 1 = RESET is dependent on MON2 [ ...
Page 46
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers LAST MON_ WDI RESET Figure 6. Normal Watchdog Startup Sequence V CC < t WDI WDI < t < t WDI WDI WDO 0V Figure 7. Watchdog Timer Operation ...
Page 47
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 28. Watchdog Mode Selection REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS 0 1 4Dh 2 3 [7:4] Table 29. Watchdog Enables and Configuration REGISTER/ EEPROM BIT RANGE ADDRESS [2:0] [4:3] 55h [5] [6] ...
Page 48
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Independent Watchdog Timer Operation When r4Dh[3] is ‘1’ the watchdog timer operates in the independent mode. In the independent mode, the watchdog timer operates were a separate chip. The ...
Page 49
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers 2 I C/SMBus-Compatible The MAX16046/MAX16048 feature an I patible 2-wire serial interface consisting of a serial data line (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL). SDA and SCL facilitate bidirectional communication between ...
Page 50
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers The acknowledge bit (ACK) is the 9th bit attached to any 8-bit data word. The receiving device always gen- erates an ACK. The MAX16046/MAX16048 generate an ACK when receiving an address or ...
Page 51
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers The send byte protocol allows the master device to send one byte of data to the slave device (see Figure 12). The send byte presets a register pointer address for a subsequent ...
Page 52
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers The MAX16046/MAX16048 use eight command codes for block read, block write, and other commands. See Table 32 for a list of command codes. To initiate a software reboot, send 96h using the ...
Page 53
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers 8) The slave asserts an ACK on SDA. 9) The slave sends the 8-bit byte count (16). 10) The master asserts an ACK on SDA. 11) The slave sends 8 bits of ...
Page 54
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers JTAG Serial Interface The MAX16046/MAX16048 contain a JTAG port that complies with a subset of the IEEE 1149.1 specifica- 2 tion. Either the the JTAG interface may be used ...
Page 55
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Test Access Port (TAP) Controller State Machine The TAP controller is a finite state machine that responds to the logic level at TMS on the rising edge of TCK. See Figure 14 ...
Page 56
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Shift-DR: The test data register selected by the current instruction connects between TDI and TDO and shifts data one stage toward its serial output on each rising edge of TCK while TMS ...
Page 57
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Table 33. JTAG Instruction Set INSTRUCTION HEX CODE BYPASS 1Fh IDCODE 00h USERCODE 03h LOAD ADDRESS 04h READ DATA 05h WRITE DATA 06h REBOOT 07h SAVE 08h SETEXTRAM 09h RSTEXTRAM 0Ah SETEEPADD ...
Page 58
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers LOAD ADDRESS: This is an extension to the standard IEEE 1149.1 instruction set to support access to the memory in the MAX16046/MAX16048. When the LOAD ADDRESS instruction latches into the instruction regis- ...
Page 59
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers DC-DC OR LDO OUT REF Figure 15. Connections for Margining Using Feedback Method Filtering the DAC Outputs Some applications require filtering of the DAC ...
Page 60
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Set the DACOUT_ range bits (see the DAC Outputs section) such that V falls approximately halfway REF within the DACOUT range. Set R 5 control the DAC has on the output voltage ...
Page 61
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers MAX16046 MAX16048 GND Figure 18. Power Circuit for Shutdown During Fault Conditions Driving High-Side MOSFET Switches The MAX16046/MAX16048 use external n-channel MOSFET switches for voltage tracking applications. ...
Page 62
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers Simple slew-rate control is accomplished by adding a capacitor from the gate to ground. The slew rate is approximated by the RC charge curve of the pullup resistor acting with the capacitor ...
Page 63
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PAGE ADDRESS Ext 00h Ext 01h Ext 02h Ext 03h Ext 04h Ext 05h Ext 06h Ext 07h Ext 08h Ext 09h Ext 0Ah Ext 0Bh Ext 0Ch Ext 0Dh Ext 0Eh ...
Page 64
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PAGE ADDRESS Default 0Ah Default 0Bh EEPROM 00h EEPROM 01h EEPROM 02h EEPROM 03h EEPROM 04h EEPROM 05h EEPROM 06h EEPROM 07h EEPROM 08h EEPROM 09h EEPROM 0Ah EEPROM 0Bh EEPROM 0Ch ...
Page 65
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PAGE ADDRESS READ/WRITE Def/EE 26h Def/EE 27h Def/EE 28h Def/EE 29h Def/EE 2Ah Def/EE 2Bh Def/EE 2Ch Def/EE 2Dh Def/EE 2Eh Def/EE 2Fh Def/EE 30h Def/EE 31h Def/EE 32h Def/EE 33h Def/EE ...
Page 66
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PAGE ADDRESS Def/EE 4Eh Def/EE 4Fh Def/EE 50h Def/EE 51h Def/EE 52h Def/EE 53h Def/EE 54h Def/EE 55h Def/EE 56h Def/EE 57h Def/EE 58h Def/EE 59h Def/EE 5Ah Def/EE 5Bh Def/EE 5Ch ...
Page 67
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers PAGE ADDRESS Def/EE 76h Def/EE 77h Def/EE 78h Def/EE 79h Def/EE 7Ah Def/EE 7Bh Def/EE 7Ch Def/EE 7Dh Def/EE 7Eh–93h EEPROM 9Ch–FFh * MAX16046 only Note: Ext refers to registers contained in ...
Page 68
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers TOP VIEW MON1 MON2 MON3 MON4 MON5 MON6 MON7 MON8 MON9 MON10 MON11 MON12 RESET A0 MON1 MON2 MON3 MON4 MON5 MON6 MON7 MON8 N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. RESET A0 *EP = ...
Page 69
EEPROM-Programmable System Managers with Nonvolatile Fault Registers TOP VIEW MON1 1 MON2 2 MON3 3 MON4 4 MON5 5 MON6 6 MON7 7 N.C. 8 N.C. 9 MON8 10 MON9 11 MON10 12 MON11 13 MON12 14 N.C. 15 ...
Page 70
... Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time. 70 ____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 © 2010 Maxim Integrated Products ...