DS485M National Semiconductor, DS485M Datasheet - Page 7

DS485M
Manufacturer Part Number
DS485M
Description
IC, RS422/RS485 TRANSCEIVER 5.25V NSOIC8
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DS485M.pdf
(9 pages)
Specifications of DS485M
Device Type
Transceiver
Ic Interface Type
RS422, RS485
No. Of Drivers
1
Supply Voltage Range
4.75V To 5.25V
Driver Case Style
SOIC
No. Of Pins
8
Operating Temperature Range
0°C To +70°C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
DS485M
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS485MX
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DS485MX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
VTI
Quantity:
6 218
Applications Information
The DS485 is a low power transceiver designed for use in
RS-485 multipoint applications. The DS485 can transmit
data up to 2.5 Mbps based on a ratio of driver transition time
to the unit interval (bit time) of 10%. This maximum data rate
may be further limited by the interconnecting media. The
DS485 provides a standard unit load to the RS-485 bus
across the common mode range of −7V to +12V. This allows
up to 32 transceivers (standard unit load) to be connected to
the bus. More transceivers may be connected to the bus if
they support a reduced unit load (see DS36C278). The
DS485 also guarantees the driver’s output differential volt-
age into a worst case load that models standard termination
loads and 32 unit loads referenced to the maximum common
mode voltage extremes. With a minimum of 1.5V swing into
this load, a 1.3V differential noise margin is supported along
with the standard common mode rejection range of the
receivers.
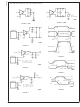
Multipoint RS-485 Application
7
Due to the multipoint nature of the bus, contention between
drivers may occur. This will not cause damage to the drivers
since they feature short-circuit protection and also thermal
shutdown protection. Thermal shutdown senses die tem-
perature and puts the driver outputs into TRI-STATE if a fault
condition occurs that causes excessive power dissipation
which can elevate the junction temperature to +150˚C.
A typical multipoint application is shown in the following
figure. Note that termination is typically required but is only
located at the two ends of the cable (not on every node).
Commonly pull up and pull down resistors may be required
at one end of the bus to provide a failsafe bias. These
resistors provide a bias to the line when all drivers are in
TRI-STATE. See National Application Note 847 for a com-
plete discussion of failsafe biasing of differention buses.
01288016
www.national.com