STPCI2HDYI STMicroelectronics, STPCI2HDYI Datasheet - Page 105

STPCI2HDYI
Manufacturer Part Number
STPCI2HDYI
Description
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.STPCI2HDYI.pdf
(108 pages)
Specifications of STPCI2HDYI
Operating Temperature (min)
-40C
Operating Temperature (max)
115C
Processing Unit
Microprocessor
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.45/3V
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
2.5/3.3V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
2.7/3.6V
Package Type
BGA
Screening Level
Industrial
Pin Count
516
Mounting
Surface Mount
Rad Hardened
No
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Supplier Unconfirmed
6.6.3.3. POST code
Once the 16 first bytes are fetched and decoded,
the CPU core continue its execution depending on
the content of these first data. Usually, it
corresponds to a JUMP instruction and the code
fetching continues, generating read cycles on the
ISA bus.
Most of the BIOS and boot loaders are reading the
content of the flash, decompressing it in SDRAM,
and then continue the execution by jumping to the
entry point in RAM. This boot process ends with a
JUMP to the entry point of the OS launcher.
These various steps of the booting sequence are
codified by the so-called POST codes (Power-On
Self-Test). A 8-bit code is written to the port 80H at
the beginning of each stage of the booting process
(I/O write to address 0080H) and can be displayed
on two 7-segment display, enabling a fast visual
check of the booting completion level.
Usually, the last POST code is 0x00 and
corresponds to the jump into the OS launcher.
When the execution fails or hangs, the lastest
written code stays visible on that display,
indicating either the piece of code to analyse,
either the area of the hardware not working
properly.
6.6.4. LOCAL BUS MODE
As the Local Bus controller is located into the Host
interface, there is no access to the cycles on the
PCI, reducing the amount of signals to check.
6.6.4.1. First code fetches
When booting on the Local Bus, the key signal to
check at the very beginning is FCS0#. This signal
is a Chip Select for the boot flash and should
toggle together with PRD# to fetch the first 16
bytes of code. This corresponds to the loading of
the first line of the CPU cache.
In case FCS0# does not toggle, then one of the
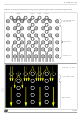
1
2
3
(Power Good)
14.318 MHz
SYSRSTI#
supplies
Check:
Power
Verify that voltage is within specs:
- this must include HF & LF noise
- avoid full range sweep
Refer to Table 4-1 for values
Verify OSC14M speed
Measure SYSRSTI# of STPC
See
Figure 4-3
for waveforms.
How?
previous steps has not been done properly, like
HCLK speed and CPU clock multiplier (x1, x2).
6.6.4.2. Boot Flash size
The Local Bus support 8-bit and 16-bit boot
memory devices only.
6.6.4.3. POST code
Like in ISA mode, POST codes can be
implemented on the Local Bus. The difference is
that an IOCS# must be programmed at I/O
address 80H prior to writing these code, the POST
display being connected to this IOCS# and to the
lower 8 bits of the bus.
6.6.5. SUMMARY
Here is a check-list for the STPC board debug
from power-on to CPU execution.
For each step, in case of failure, verify first the
corresponding balls of the STPC:
- check if the voltage or activity is correct
- search for potential shortcuts.
For troubleshooting in steps 5 to 10, verify the
related strap options:
- value & connection. Refer to Section 3.
- see
Steps 8a and 9a are for debug in ISA mode while
steps 8b and 9b are for Local Bus mode.
6.6.6. PCMCIA mode
As the STPC uses the RMRTCCS# signal for
booting in that mode, the methodology is the same
as for the ISA bus. The PCMCIA cards being 3.3V
or 5V, the boot flash device must be 5V tolerant
when directly connected on the address and data
busses. An other solution is to isolate the flash
from the PCMCIA lines using 5V tolerant LVTTL
buffers.
Figure 4-3
Measure voltage near STPC balls:
- use very low GND connection.
Add some decoupling capacitor:
- the smallest, the nearest to STPC balls.
The 2 capacitors used with the quartz must
match with the capacitance of the crystal.
Try other values.
Verify reset generation circuit:
- device reference
- components value
for timing constraints
Troubleshooting
STPC® ATLAS
105/108