DS275 Maxim Integrated Products, DS275 Datasheet - Page 2
DS275
Manufacturer Part Number
DS275
Description
IC TXRX LINE-PWR RS232 8-DIP
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
Transceiverr
Datasheet
1.DS275.pdf
(8 pages)
Specifications of DS275
Number Of Drivers/receivers
1/1
Protocol
RS232
Voltage - Supply
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DS275
Manufacturer:
DALLAS
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
DS2751E
Manufacturer:
MAXIM
Quantity:
361
Part Number:
DS2751E
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2751E+TR
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2751E/T
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2751R
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2756E
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DS275E
Manufacturer:
SIPEX
Quantity:
6 851
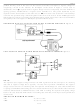
DS275 BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
OPERATION
Designed for the unique requirements of battery-backed systems, the DS275 provides a low-power half-
duplex interface to an RS-232 serial port. Typically, a designer must use an RS-232 device which uses
system power during both negative and positive transitions of the transmit signal to the RS-232 port. If
the connector to the RS-232 port is left connected for an appreciable time after the communication
session has ended, power will statically flow into that port, draining the battery capacity. The DS275
eliminates this static current drain by stealing current from the receive line (RX
when that line is at a negative level (marking). Since most asynchronous communication over an RS-232
connection typically remains in a marking state when data is not being sent, the DS275 will not consume
system power in this condition. System power would only be used when positive-going transitions are
needed on the transmit RS-232 output (TX
communication sessions typically exhibit a very low duty-cycle, overall system power consumption
remains low.
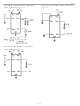
RECEIVER SECTION
The RX
negative data signal is called a mark while a positive data signal is called a space. These signals are
inverted and then level
with RX
RX
The input threshold of RX
noise rejection. Therefore, an input positive-going signal must exceed 1.8 volts to cause RX
states. A negative-going signal must now be lower than 1.3 volts (typically) to cause RX
again. An open on RX
TRANSMITTER SECTION
TX
produces a mark (negative data signal) at TX
As mentioned earlier, the transmitter section employs a unique driver design that uses the RX
swinging to negative levels. The RX
design; if RX
a positive level, it uses the V
IN
OUT
is the CMOS/TTL-compatible input for digital data from the user system. A logic 1 at TX
; a space produces a logic 0.
IN
IN
pin is the receive input for an RS
is RX
IN
is in a spacing state, TX
OUT
which swings from +V
IN
-
shifted to normal +5-volt CMOS/TTL logic levels. The logic output associated
is interpreted as a mark, producing a logic 1 at RX
IN
DRV
is typically around 1.8 volts with 500 millivolts of hysteresis to improve
power pin for this level. V
IN
OUT
line must be in a marking or idle state to take advantage of this
CC
will only swing to ground. When TX
-
232 signal whose levels can range from 3 to 15 volts. A
OUT
to ground. Therefore, a mark on RX
OUT
while a logic 0 produces a space (positive data signal).
2 of 8
) when data is sent. However, since synchronous
DRV
can be a voltage supply between 5 to 12
OUT
.
OUT
IN
IN
) of the RS-232 port
produces a logic 1 at
needs to transition to
OUT
OUT
IN
to switch
to switch
line for
DS275
IN