LTC6602IUF#PBF Linear Technology, LTC6602IUF#PBF Datasheet - Page 22

LTC6602IUF#PBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC6602IUF#PBF
Description
IC FILTER BANDPASS/LOWPASS 24QFN
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC6602IUFPBF.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of LTC6602IUF#PBF
Filter Type
Bandpass
Frequency - Cutoff Or Center
300kHz
Number Of Filters
2
Max-order
5th
Voltage - Supply
2.7 V ~ 3.6 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
24-QFN
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
LTC6602
Power Supply Current
The power supply current depends on the state of the
lowpass cutoff frequency controls (LPF1, LPF0) and the
value of R
lowest lowpass cutoff frequency (LPF1 = LPF0 = ‘0’), the
supply current is reduced by about 35% relative to the
supply current for the higher bandwidth settings. Power
supply current vs. cutoff frequency for various bandwidth
settings is shown in the Typical Performance Characteris-
tics section. The LTC6602 can be programmed through the
serial interface to enter into a low power shutdown mode
as described in the Serial Interface section. The power
supply current during shutdown is less than 235µA.
Supply Current Versus Noise Tradeoff
The passband of the LTC6602 is determined by the master
clock frequency (which is set by R
oscillator is used), HPF1, HPF0, LPF1 and LPF0. The
LTC6602 is optimized for use with R
between 200k and 54.9k to set the internal oscillation
22
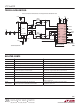
Table 5. Total Input Referred Integrated Noise Voltage (Passband Gain = 30dB)
Figure 15. f
BIAS
100
10
. When the LTC6602 is programmed for the
1k
LPF1
0
0
1
HPF1 = 0
HPF0 = 0
FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY (Hz)
CLK
vs Filter Cutoff Frequencies
10k
HPF1 = 0
HPF0 = 1
HPF1 = 1
HPF0 = 0
100k
BIAS
LPF1 = 0
LPF0 = 0
LPF1 = 0
LPF0 = 1
LPF0
0
1
X
BIAS
LPF1 = 1
when the internal
6602 F15
having a value
1M
HPF1
0
0
1
frequency from 24.705MHz to 90MHz. Both lowpass
and highpass corner frequencies are proportional to the
clock frequency (internal or external). To extend the filter’s
operational frequency range, the master clock is divided
down before reaching the filter. LPF1 and LPF0 set the divi-
sion ratio of the lowpass clock while HPF1 and HPF0 set
the division ratio of the highpass clock. Figure 15 shows
the possible cutoff frequencies versus f
LPF1 and LPF0. Overlapping frequency ranges allow more
than one possible choice of bandwidth settings for some
cutoff frequencies. Figure 16 shows supply current as a
function of the lowpass cutoff frequency, LPF1 and LPF0.
Note that the higher bandwidth setting always gives the
minimum supply current for a given cutoff frequency. The
total integrated noise voltage for a passband gain of 30dB
is shown in Table 5. Note that the noise is higher for the
higher bandwidth settings. This creates a tradeoff between
supply current and noise. For a given cutoff frequency,
using the highest possible bandwidth setting gives the
minimum supply current at the expense of higher noise.
Figure 16. Supply Current vs Lowpass Cutoff Frequency
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
10k
T
V
CLKCNTL PIN FLOATING
HPF1 = 0
HPF0 = 1
GAIN = 0dB
A
S
= 25°C
= 3V
LPF1 = 0
LPF0 = 0
HPF0
LOWPASS CUTOFF FREQUENCY (Hz)
0
1
0
LPF1 = 0
LPF0 = 1
100k
LPF1 = 1
Noise Voltage
–90dBm
–89dBm
–82dBm
CLK
6602 F16
, HPF1, HPF0,
1M
6602fc