LTC4006 Linear Technology, LTC4006 Datasheet - Page 9

LTC4006
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC4006
Description
Standalone Li-Ion Battery Charger
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC4006.pdf
(16 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-2
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-2
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-2#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-4
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-4#PBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
64
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-4#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-6
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-6
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-6#PBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
120
Company:
Part Number:
LTC4006EGN-6#TRPBF
Manufacturer:
LTC
Quantity:
2 830
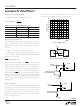
OPERATIO
off for about 300ns at 40 s intervals. This is done to
prevent audible noise when using ceramic capacitors at
the input and output.
Charger Startup
When the charger is enabled, it will not begin switching
until the I
current will be positive. This threshold is 5% to 15% of the
maximum programmed current. After the charger begins
switching, the various loops will control the current at a
level that is higher or lower than the initial current. The
duration of this transient condition depends upon the loop
compensation but is typically less than 100 s.
Thermistor Detection
The thermistor detection circuit is shown in Figure 3. It
requires an external resistor and capacitor in order to
function properly.
The thermistor detector performs a sample-and-hold func-
tion. An internal clock, whose frequency is determined by
the timing resistor connected to R
closed to sample the thermistor:
The external RC network is driven to approximately 4.5V
and settles to a final value across the thermistor of:
t
for R
V
SAMPLE
RTH FINAL
RT
(
TH
= 309k
= 127.5 • 20 • R
voltage exceeds a threshold that assures initial
0.6
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.2
0.4
0
)
0
U
I
4 5
Figure 2. I
CHARGE
R
.
0.309V
20
TH
V R
(% OF MAXIMUM CURRENT)
•
R
40
TH
9
MON
RT
60
• 17.5pF = 13.8ms,
vs I
1.19V
CHARGE
80
T
, keeps switch S1
4006 F02
100
This voltage is stored by C7. Then the switch is opened for
a short period of time to read the voltage across the
thermistor.
When the t
testing is stored in the D flip-flop (DFF). If the voltage at
NTC is within the limits provided by the resistor divider
feeding the comparators, then the NOR gate output will be
low and the DFF will set T
continue. If the voltage at NTC is outside of the resistor
divider limits, then the DFF will set T
will be shut down, and the timer will be suspended until
T
BAD
NTC
R
10k
(NOT TO
TH
t
for R
SCALE)
HOLD
V
CLK
NTC
returns to zero (see Figure 4).
RT
= 10 • R
VOLTAGE ACROSS THERMISTOR
= 309k
HOLD
32.4k
C7
0.47 F
R9
interval ends the result of the thermistor
RT
6
LTC4006
NTC
• 17.5pF = 54 s,
Figure 3
Figure 4
S1
D
C
BAD
Q
COMPARATOR LOW LIMIT
to zero and charging will
COMPARATOR HIGH LIMIT
t
HOLD
BAD
+
–
–
+
t
SAMPLE
–
+
to one, the charger
LTC4006
~4.5V
60k
45k
15k
4006 F03
sn4006 4006is
CLK
T
BAD
4006 F04
9