ad8426 Analog Devices, Inc., ad8426 Datasheet - Page 11

ad8426
Manufacturer Part Number
ad8426
Description
Wide Supply Range, Rail-to-rail Output Instrumentation Amplifier
Manufacturer
Analog Devices, Inc.
Datasheet
1.AD8426.pdf
(20 pages)
Preliminary Technical Data
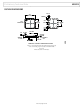
THEORY OF OPERATION
ARCHITECTURE
The
topology has two stages: a gain stage (preamplifier) to provide
differential amplification, followed by a difference amplifier to
remove the common-mode voltage. Figure 7 shows a simplified
schematic of one of the instrumentation amplifiers in the AD8426.
The first stage works as follows: to maintain a constant voltage
across the bias resistor, R
diode drop above the positive input voltage. Similarly, A2 keeps
Node 4 at a constant diode drop above the negative input voltage.
Therefore, a replica of the differential input voltage is placed
across the gain setting resistor, R
this resistance must also flow through the R1 and R2 resistors,
creating a gained differential signal between the A2 and A1 out-
puts. Note that, in addition to a gained differential signal, the
original common-mode signal, shifted a diode drop up, is also
still present.
The second stage is a difference amplifier, composed of A3 and
four 50 kΩ resistors. The purpose of this stage is to remove the
common-mode signal from the amplified differential signal.
The transfer function of the
where:
GAIN SELECTION
Placing a resistor across the R
AD8426, which can be calculated by referring to Table 7 or by
using the following gain equation:
AD8426
V
G
R
OUT
G
1
= G × (V
49.4
+IN
G
49.4
is based on the classic three op amp topology. This
R
kΩ
1
G
kΩ
IN+
OVERVOLTAGE
PROTECTION
ESD AND
− V
B
IN−
, A1 must keep Node 3 at a constant
) + V
AD8426
G
terminals sets the gain of the
G
REF
. The current that flows across
Q1
NODE 3
R
is
B
24.7kΩ
R1
A1
NODE 1
+V
–V
S
S
GAIN STAGE
R
G
Figure 7. Simplified Schematic
V
BIAS
Rev. PrD | Page 11 of 20
+V
–V
S
S
–V
A2
S
NODE 2
R2
24.7kΩ
NODE 4
Q2
Table 7. Gains Achieved Using 1% Resistors
1% Standard Table Value of R
49.9 kΩ
12.4 kΩ
5.49 kΩ
2.61 kΩ
1.00 kΩ
499 Ω
249 Ω
100 Ω
49.9 Ω
The
The tolerance and gain drift of the R
to the
racy of the system. When the gain resistor is not used, gain
error and gain drift are minimal.
REFERENCE TERMINAL
The output voltage of the
the potential on the reference terminal. This is useful when the
output signal needs to be offset to a precise midsupply level. For
example, a voltage source can be tied to the REF pin to level-
shift the output so that the
ADC. The REF pin is protected with ESD diodes and should
not exceed either +V
For the best performance, source impedance to the REF
terminal should be kept below 2 Ω. As shown in Figure 8,
the reference terminal, REF, is at one end of a 50 kΩ resistor.
Additional impedance at the REF terminal adds to this 50 kΩ
resistor and results in amplification of the signal connected to
the positive input. The amplification from the additional R
can be computed by 2 × (50 kΩ + R
R
B
AD8426
AD8426
OVERVOLTAGE
PROTECTION
ESD AND
defaults to G = 1 when no gain resistor is used.
specifications to determine the total gain accu-
S
or −V
50kΩ
50kΩ
–IN
R4
R5
AD8426
AD8426
S
by more than 0.3 V.
AMPLIFIER STAGE
G
50kΩ
R6
DIFFERENCE
50kΩ
A3
R3
is developed with respect to
REF
can drive a single-supply
+V
–V
G
Calculated Gain
1.990
4.984
9.998
19.93
50.40
100.0
199.4
495.0
991.0
S
S
resistor should be added
)/100 kΩ + R
+V
–V
S
S
V
REF
OUT
REF
AD8426
.
REF