ad8426 Analog Devices, Inc., ad8426 Datasheet - Page 12

ad8426
Manufacturer Part Number
ad8426
Description
Wide Supply Range, Rail-to-rail Output Instrumentation Amplifier
Manufacturer
Analog Devices, Inc.
Datasheet
1.AD8426.pdf
(20 pages)
AD8426
Only the positive signal path is amplified; the negative path
is unaffected. This uneven amplification degrades the CMRR of
the amplifier.
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
The three op amp architecture of the
first stage before removing common-mode voltage in the
difference amplifier stage. In addition, the input transistors in
the first stage shift the common-mode voltage up one diode
drop. Therefore, internal nodes between the first and second
stages (Node 1 and Node 2 in Figure 7) experience a combina-
tion of gained signal, common-mode signal, and a diode drop.
This combined signal can be limited by the voltage supplies even
when the individual input and output signals are not.
Equation 1 to Equation 3 can be used to understand how the
gain (G), common-mode input voltage (V
voltage (V
for the constants, V
atures are shown in Table 8. These three formulas, along with
the input and output range specifications in Table 2 and Table 3,
set the operating boundaries of the part.
Table 8. Input Voltage Range Constants for Various
Temperatures
Temperature
−40°C
+25°C
+85°C
+125°C
The common-mode input voltage range shifts upward with temp-
erature. At cold temperatures, the part requires extra headroom
from the positive supply, whereas operation near the negative
V
REF
INCORRECT
AD8426
V
V
(
V
CM
CM
DIFF
2
DIFF
)(
(
(
V
V
G
), and reference voltage (V
DIFF
DIFF
)
2
2
2
V
)(
)(
Figure 8. Driving the Reference Pin
−LIMIT
G
G
CM
V
)
)
V
−0.55
−0.35
−0.15
−0.05
REF
−LIMIT
V
, V
REF
+
OP1177
–
V
V
CORRECT
+LIMIT
S
S
AD8426
V
V
, and V
V
LIMIT
S
LIMIT
V
+0.8
+0.7
+0.65
+0.6
V
+LIMIT
REF
REF_LIMIT
AD8426
_
REF
LIMIT
V
CM
) interact. The values
REF
, at different temper-
), differential input
applies gain in the
+
AD8426
–
CORRECT
V
+1.3
+1.15
+1.05
+0.9
REF_LIMIT
AD8426
Rev. PrD | Page 12 of 20
(1)
(2)
(3)
supply has more margin. Conversely, at hot temperatures, the part
requires less headroom from the positive supply but is subject
to the worst-case conditions for input voltages near the negative
supply.
A typical part functions up to the boundaries described in this
section. However, for best performance, designing with a few
hundred millivolts extra margin is recommended. As signals
approach the boundary, internal transistors begin to saturate,
which can affect frequency and linearity performance.
LAYOUT
To ensure optimum performance of the
level, care must be taken in the design of the board layout.
The
this task.
Package Considerations
The
no exposed paddle. The footprint from another 4 mm × 4 mm
LFCSP part should not be copied because it may not have the
correct lead pitch and lead width dimensions. Refer to the
Outline Dimensions section for the correct dimensions.
Hidden Paddle Package
The
paddle. Unlike chip scale packages where the pad limits routing
capability, this package allows routes and vias directly beneath
the chip, so that the full space savings of the small LFCSP can be
realized. Although the package has no metal in the center of the
part, the manufacturing process leaves a very small section of
exposed metal at each of the package corners, as shown in
Figure 10 and in Figure 17 in the Outline Dimensions section.
This metal is connected to – V
possibility of a short, vias should not be placed underneath
these exposed metal tabs.
AD8426
AD8426
AD8426
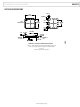
is available in a 16-lead, 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP with
pins are arranged in a logical manner to aid in
is available in an LFCSP package with a hidden
–IN1
+IN1
RG1
RG1
1
2
3
4
AD8426
Preliminary Technical Data
Figure 9. Pinout Diagram
16
5
15
6
S
through the part. Because of the
14
7
13
8
AD8426
12
11
10
9
RG2
RG2
–IN2
+IN2
at the PCB