AT90LS4433-4AC Atmel, AT90LS4433-4AC Datasheet
AT90LS4433-4AC
Specifications of AT90LS4433-4AC
Available stocks
Related parts for AT90LS4433-4AC
AT90LS4433-4AC Summary of contents
Page 1
... PDIP and 32-lead TQFP • Operating Voltage – 2.7V - 6.0V for the AT90LS4433 – 4.0V - 6.0V for the AT90S4433 • Speed Grades – MHz for the AT90LS4433 – MHz for the AT90S4433 ® 8-bit RISC Architecture 8-bit Microcontroller with 4K Bytes of ...
Page 2
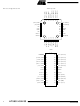
Pin Configurations AT90S/LS4433 2 TQFP Top View (INT1) PD3 1 (T0) PD4 VCC 4 GND XTAL1 7 XTAL2 8 PDIP RESET 1 28 (RXD) PD0 2 27 (TXD) PD1 3 26 (INT0) PD2 4 ...
Page 3
... The AT90S4433 AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system development tools including: C Compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, In-Cir- cuit Emulators and evaluation kits. Table 1. Comparison Table Device Flash EEPROM AT90S4433 4K 256B AT90LS4433 4K 256B AT90S/LS4433 SRAM Voltage Range Frequency 128B 4. MHz 128B 2 ...
Page 4
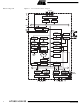
Block Diagram AT90S/LS4433 4 Figure 1. The AT90S4433 Block Diagram VCC GND DATA REGISTER PORTC AVCC ANALOG MUX ADC AGND AREF PROGRAM STACK COUNTER POINTER PROGRAM SRAM FLASH INSTRUCTION GENERAL REGISTER PURPOSE REGISTERS X INSTRUCTION Y DECODER Z CONTROL ALU ...
Page 5
Pin Descriptions VCC GND Port B (PB5..PB0) Port C (PC5..PC0) Port D (PD7..PD0) RESET XTAL1 XTAL2 AVCC AREF AGND 1042H–AVR–04/03 Supply voltage. Ground. Port 6-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors. The Port B output buffers ...
Page 6
Clock Options Crystal Oscillator External Clock AT90S/LS4433 6 XTAL1 and XTAL2 are input and output, respectively inverting amplifier, which can be configured for use as an On-chip Oscillator, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Either a ...
Page 7
Architectural Overview 1042H–AVR–04/03 The fast-access Register File concept contains 32 x 8-bit general purpose working reg- isters with a single clock cycle access time. This means that during one single clock cycle, one Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) operation is executed. ...
Page 8
AT90S/LS4433 8 The I/O memory space contains 64 addresses for CPU peripheral functions such as Control Registers, Timer/Counters, A/D Converters and other I/O functions. The I/O memory can be accessed directly the Data Space locations following those of ...
Page 9
Figure 6. AT90S4433 Memory Maps Program Memory Program Flash (2K x 16) A flexible interrupt module has its control registers in the I/O space with an additional Global Interrupt Enable bit in the Status Register. All the different interrupts ...
Page 10
General Purpose Register File X-register, Y-register and Z- register AT90S/LS4433 10 Figure 7 shows the structure of the 32 general purpose working registers in the CPU. Figure 7. AVR CPU General Purpose Working Registers 7 General Purpose Working Registers All ...
Page 11
ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit In-System Programmable Flash Program Memory SRAM Data Memory 1042H–AVR–04/03 In the different addressing modes, these address registers have functions as fixed dis- placement, automatic increment and decrement (see the descriptions for the different instructions). The ...
Page 12
Program and Data Addressing Modes Register Direct, Single Register Rd Register Direct, Two Registers Rd and Rr AT90S/LS4433 12 The direct addressing reaches the entire data space. The Indirect with Displacement mode features 63 address locations reached from the base ...
Page 13
I/O Direct Data Direct Data Indirect with Displacement 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 12. I/O Direct Addressing Operand address is contained in six bits of the instruction word the destination or source register address. Figure 13. Direct Data Addressing 20 19 ...
Page 14
Data Indirect Data Indirect with Pre- decrement Data Indirect with Post- increment AT90S/LS4433 14 Figure 15. Data Indirect Addressing REGISTER Operand address is the contents of the X-, Y-, or the Z-register. Figure 16. ...
Page 15
Constant Addressing Using the LPM Instruction Indirect Program Addressing, IJMP and ICALL Relative Program Addressing, RJMP and RCALL 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 18. Code Memory Constant Addressing Constant byte address is specified by the Z-register contents. The 15 MSBs select word address ...
Page 16
EEPROM Data Memory Memory Access Times and Instruction Execution Timing AT90S/LS4433 16 The AT90S4433 contains 256 bytes of data EEPROM memory organized as a sep- arate data space, in which single bytes can be read and written. The ...
Page 17
I/O Memory 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 23. On-chip Data SRAM Access Cycles T1 System Clock Ø Address Prev. Address Data WR Data RD The I/O space definition of the AT90S4433 is shown in Table 2. (1) Table 2. AT90S4433 I/O Space I/O ...
Page 18
AT90S/LS4433 18 (1) Table 2. AT90S4433 I/O Space I/O Address (SRAM Address) Name Function $17 ($37) DDRB Data Direction Register, Port B $16 ($36) PINB Input Pins, Port B $15 ($35) PORTC Data Register, Port C $14 ($34) DDRC Data ...
Page 19
Status Register – SREG 1042H–AVR–04/03 The AVR Status Register (SREG) at I/O space location $3F ($5F) is defined as: Bit $3F ($5F Read/Write R/W R/W R/W Initial Value • Bit 7 ...
Page 20
Stack Pointer – SP Reset and Interrupt Handling AT90S/LS4433 20 The AT90S4433 Stack Pointer is implemented as an 8-bit register in the I/O space loca- tion $3D ($5D). As the AT90S4433 data memory has $0DF locations, eight bits are used. ...
Page 21
Reset Sources 1042H–AVR–04/03 The most typical program setup for the Reset and Interrupt Vector addresses are: Address Labels Code $000 rjmp RESET $001 rjmp EXT_INT0 $002 rjmp EXT_INT1 $003 rjmp TIM1_CAPT $004 rjmp TIM1_COMP $005 rjmp TIM1_OVF $006 rjmp TIM0_OVF ...
Page 22
AT90S/LS4433 22 Figure 24. Reset Logic Power-on Reset V CC Circuit Brown-out BODEN Reset Circuit BODLEVEL RESET Reset Circuit Watchdog Timer On-chip RC Oscillator Table 4. Reset Characteristics (V CC Symbol Parameter Power-on Reset Threshold Voltage, rising (1) V POT ...
Page 23
Power-on Reset 1042H–AVR–04/03 Table 5. Reset Delay Selections CKSEL Start-up Time, [2: 2.7V t TOUT CC TOUT 000 001 6 CK 010 256 ms + 16K 16K ...
Page 24
External Reset AT90S/LS4433 24 Figure 25. MCU Start-up, RESET Tied POT VCC V RST RESET t TOUT TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET Figure 26. MCU Start-up, RESET Controlled Externally V POT VCC RESET TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET An External Reset ...
Page 25
Brown-out Detection Watchdog Reset 1042H–AVR–04/03 AT90S4433 has an On-chip Brown-out Detection (BOD) circuit for monitoring the V level during the operation. The power supply must be decoupled with 100 nF capacitor if the BOD function is ...
Page 26
MCU Status Register – MCUSR Interrupt Handling AT90S/LS4433 26 The MCU Status Register provides information on which reset source caused an MCU Reset. Bit $34 ($54) – – – Read/Write Initial Value 0 0 ...
Page 27
General Interrupt Mask Register – GIMSK General Interrupt Flag Register – GIFR 1042H–AVR–04/03 Note that the Status Register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt rou- tine or restored when returning from an interrupt routine. This must be handled ...
Page 28
Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register – TIMSK AT90S/LS4433 28 • Bit 6 – INTF0: External Interrupt Flag0 When an edge on the INT0 pin triggers an interrupt request, the corresponding Interrupt Flag, INTF0 becomes set (one). If the I-bit in SREG ...
Page 29
Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register – TIFR 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit 7 6 $38 ($58) TOV1 OCF1 Read/Write R/W R/W Initial Value 0 0 • Bit 7 – TOV1: Timer/Counter1 Overflow Flag The TOV1 is set (one) when an overflow occurs in Timer/Counter1. ...
Page 30
External Interrupts Interrupt Response Time MCU Control Register – MCUCR AT90S/LS4433 30 The External Interrupts are triggered by the INT1 and INT0 pins. Observe that, if enabled, the interrupts will trigger even if the INT0/INT1 pins are configured as outputs. ...
Page 31
Sleep Modes 1042H–AVR–04/03 • Bits 3, 2 – ISC11, ISC10: Interrupt Sense Control 1 Bit 1 and Bit 0 The External Interrupt 1 is activated by the external pin INT1 if the SREG I-flag and the corresponding interrupt mask in ...
Page 32
Idle Mode Power-down Mode AT90S/LS4433 32 When the SM bit is cleared (zero), the SLEEP instruction forces the MCU into the Idle mode stopping the CPU but allowing Timer/Counters, Watchdog and the interrupt sys- tem to continue operating. This enables ...
Page 33
Timer/Counters Timer/Counter Prescaler 8-bit Timer/Counter0 1042H–AVR–04/03 The AT90S4433 provides two general purpose Timer/Counters – one 8-bit T/C and one 16-bit T/C. Timer/Counters0 and 1 have individual prescaling selection from the same 10-bit prescaling timer. These Timer/Counters can either be used ...
Page 34
Timer/Counter0 Control Register – TCCR0 AT90S/LS4433 34 Figure 31. Timer/Counter0 Block Diagram Bit $33 ($53) – – – Read/Write Initial Value • Bits 7 – 3 – Res: Reserved Bits These ...
Page 35
Timer Counter0 – TCNT0 16-bit Timer/Counter1 1042H–AVR–04/03 The Stop condition provides a Timer Enable/Disable function. The prescaled CK modes are scaled directly from the CK Oscillator clock. If the external pin modes are used for Timer/Counter0, transitions on PD4/(T0) will ...
Page 36
AT90S/LS4433 36 Interrupt Flag Register (TIFR). The interrupt enable/disable settings for Timer/Counter1 are found in the Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register (TIMSK). When Timer/Counter1 is externally clocked, the external signal is synchronized with the Oscillator frequency of the CPU. To assure ...
Page 37
Timer/Counter1 Control Register A – TCCR1A 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit $2F ($4F) COM11 COM10 – Read/Write R/W R/W R Initial Value • Bits 7, 6 – COM11, COM10: Compare Output Mode1, Bits 1, and 0 The ...
Page 38
Timer/Counter1 Control Register B – TCCR1B AT90S/LS4433 38 Bit $2E ($4E) ICNC1 ICES1 – Read/Write R/W R/W R Initial Value • Bit 7 – ICNC1: Input Capture1 Noise Canceler (4 CKs) When the ICNC1 ...
Page 39
Timer/Counter1 – TCNT1H and TCNT1L 1042H–AVR–04/03 • Bits – CS12, CS11, CS10: Clock Select1, Bits 2, 1, and 0 The Clock Select1 bits 2, 1, and 0 define the prescaling source of Timer/Counter1. Table 12. Clock 1 ...
Page 40
Timer/Counter1 Output Compare Register – OCR1H and OCR1L AT90S/LS4433 40 the TEMP Register. Consequently, the Low Byte TCNT1L must be accessed first for a full 16-bit register read operation. The Timer/Counter1 is realized up/down (in PWM ...
Page 41
Timer/Counter1 Input Capture Register – ICR1H and ICR1L Timer/Counter1 in PWM Mode 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit $27 ($47) MSB $26 ($46 Read/Write Initial Value ...
Page 42
AT90S/LS4433 42 Table 14. Compare1 Mode Select in PWM Mode COM11 COM10 Effect on OC1 0 0 Not connected 0 1 Not connected Cleared on compare match, up-counting. Set on compare match, down counting (non-inverted PWM). Cleared on ...
Page 43
Watchdog Timer Watchdog Timer Control Register – WDTCR 1042H–AVR–04/03 The Watchdog Timer is clocked from a separate On-chip Oscillator. By controlling the Watchdog Timer prescaler, the Watchdog Reset interval can be adjusted as shown in Table 6. See characterization data ...
Page 44
AT90S/LS4433 44 • Bits 2..0 – WDP2, WDP1, WDP0: Watchdog Timer Prescaler 2, 1, and 0 The WDP2, WDP1, and WDP0 bits determine the Watchdog Timer prescaling when the Watchdog Timer is enabled. The different prescaling values and their corresponding ...
Page 45
EEPROM Read/Write Access EEPROM Address Register – EEAR EEPROM Data Register – EEDR EEPROM Control Register – EECR 1042H–AVR–04/03 The EEPROM Access Registers are accessible in the I/O space. The write access time is in the range of 2.5 - ...
Page 46
AT90S/LS4433 46 • Bit 3 – EERIE: EEPROM Ready Interrupt Enable When the I-bit in SREG and EERIE are set (one), the EEPROM Ready Interrupt is enabled. When cleared (zero), the interrupt is disabled. The EEPROM Ready Interrupt generates a ...
Page 47
Prevent EEPROM Corruption 1042H–AVR–04/03 During periods of low V , the EEPROM data can be corrupted because the supply volt- CC age is too low for the CPU and the EEPROM to operate properly. These issues are the same as ...
Page 48
Serial Peripheral Interface – SPI AT90S/LS4433 48 The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) allows high-speed synchronous data transfer between the AT90S4433 and peripheral devices or between several AVR devices. The AT90S4433 SPI features include the following: • Full Duplex, Three-wire Synchronous ...
Page 49
SS Pin Functionality 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 37. SPI Master-slave Interconnection The system is single buffered in the transmit direction and double buffered in the receive direction. This means that bytes to be transmitted cannot be written to the SPI Data Register ...
Page 50
Data Modes AT90S/LS4433 50 pins are inputs. When SS is driven high, externally all pins are inputs and the SPI is passive, which means that it will not receive incoming data. Note that the SPI logic will be reset once ...
Page 51
SPI Control Register – SPCR 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit $0D ($2D) SPIE SPE DORD Read/Write R/W R/W R/W Initial Value • Bit 7 – SPIE: SPI Interrupt Enable This bit causes the SPI interrupt to be ...
Page 52
SPI Status Register – SPSR SPI Data Register – SPDR AT90S/LS4433 52 Bit $0E ($2E) SPIF WCOL – Read/Write Initial Value • Bit 7 – SPIF: SPI Interrupt Flag When a ...
Page 53
UART Data Transmission 1042H–AVR–04/03 The AT90S4433 features a full duplex (separate Receive and Transmit Registers) Uni- versal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART). The main features are: • Baud Rate Generator Generates any Baud Rate • High Baud Rates at Low ...
Page 54
Data Reception AT90S/LS4433 54 data is transferred from UDR to the 10(11)-bit Shift Register, bit 0 of the Shift Register is cleared (start bit) and bit set (stop bit). If 9-bit data word is selected (the ...
Page 55
The Receiver front-end logic samples the signal on the RXD pin at a frequency 16 times the baud rate. While the line is idle, one single sample of logical “0” will be interpreted as the falling edge of a ...
Page 56
Multi-processor Communication Mode AT90S/LS4433 56 The Multi-processor Communication mode enables several slave MCUs to receive data from a Master MCU. This is done by first decoding an address byte to find out which MCU has been addressed particular ...
Page 57
UART Control UART I/O Data Register – UDR UART Control and Status Register A – UCSRA 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit $0C ($2C) MSB Read/Write R/W R/W R/W Initial Value The UDR Register is actually two physically ...
Page 58
UART Control and Status Register B – UCSRB AT90S/LS4433 58 • Bit 4 – FE: Framing Error This bit is set if a Framing Error condition is detected, i.e., when the stop bit of an incom- ing character is zero. ...
Page 59
Baud Rate Generator 1042H–AVR–04/03 • Bit 3 – TXEN: Transmitter Enable This bit enables the UART Transmitter when set (one). When disabling the Transmitter while transmitting a character, the Transmitter is not disabled before the character in the Shift Register ...
Page 60
Table 19. UBR Settings at Various Crystal Frequencies Baud Rate 1 MHz %Error 2400 UBR= 25 4800 UBR= 12 9600 UBR= 14400 UBR= 19200 UBR= 28800 UBR= 38400 UBR= 57600 UBR= 76800 UBR= 115200 UBR= Baud Rate 3.2768 MHz %Error ...
Page 61
UART Baud Rate Register – UBRR 1042H–AVR–04/03 Bit $03 ($23) – – – $09 ($29) MSB Read/Write R/W R/W R/W Initial Value This is a ...
Page 62
Analog Comparator Analog Comparator Control and Status Register – ACSR AT90S/LS4433 62 The Analog Comparator compares the input values on the positive input PD6 (AIN0) and negative input PD7 (AIN1). When the voltage on the positive input PD6 (AIN0) is ...
Page 63
Bit 4 – ACI: Analog Comparator Interrupt Flag This bit is set (one) when a comparator output event triggers the interrupt mode defined by ACI1 and ACI0. The Analog Comparator Interrupt routine is executed if the ACIE bit ...
Page 64
Analog-to-Digital Converter Features AT90S/LS4433 64 • 10-bit Resolution • ±2 LSB Absolute Accuracy • 0.5 LSB Integral Non-linearity • 260 µs Conversion Time • kSPS • Six Multiplexed Input Channels • Rail-to-Rail Input Range • ...
Page 65
Operation Prescaling 1042H–AVR–04/03 The ADC can operate in two modes: Single Conversion and Free Run mode. In Single Conversion mode, each conversion will have to be initiated by the user. In Free Run mode, the ADC is constantly sampling and ...
Page 66
Table 21. ADC Conversion Time Sample Cycle Condition Number 1st Conversion, Free Run 13.5 1st Conversion, Single 13.5 Free Run Conversion Single Conversion AT90S/LS4433 66 keeps running for as long as the ADEN bit is set and is continuously reset ...
Page 67
ADC Noise Canceler Function 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 47. ADC Timing Diagram, Single Conversion Cycle Number ADC Clock ADSC ADIF ADCH ADCL Sample & Hold MUX and REFS Update Figure 48. ADC Timing Diagram, Free Run Conversion ...
Page 68
ADC Multiplexer Select Register – ADMUX ADC Control and Status Register – ADCSR AT90S/LS4433 68 Bit $07 ($27) – ADCBG – Read/Write R R/W R Initial Value • Bit 7 – Res: Reserved Bit ...
Page 69
ADC Data Register – ADCL AND ADCH 1042H–AVR–04/03 • Bit 5 – ADFR: ADC Free Run Select When this bit is set (one), the ADC operates in Free Run mode. In this mode, the ADC samples and updates the Data ...
Page 70
Scanning Multiple Channels ADC Noise Canceling Techniques AT90S/LS4433 70 Since change of analog channel always is delayed until a conversion is finished, the Free Run mode can be used to scan multiple channels without interrupting the con- verter. Typically, the ...
Page 71
ADC Characteristics T = -40°C to 85°C A Symbol Parameter Resolution Absolute Accuracy Absolute Accuracy Absolute Accuracy Integral Non-linearity Differential Non-linearity Zero Error (Offset) Conversion Time Clock Frequency AVCC Analog Supply Voltage V Reference Voltage REF R Reference Input Resistance ...
Page 72
I/O Ports Port B Port B Data Register – PORTB Port B Data Direction Register – DDRB Port B Input Pins Address – PINB AT90S/LS4433 72 All AVR ports have true Read-Modify-Write functionality when used as general digital I/O ports. ...
Page 73
Port B as General Digital I/O Alternate Functions of Port B 1042H–AVR–04/03 The Port B Input Pins address (PINB) is not a register; this address enables access to the physical value on each Port B pin. When reading PORTB, the ...
Page 74
AT90S/LS4433 74 controlled by DDB2. When the pin is forced input, the pull-up can still be con- trolled by the PORTB2 bit. See the description of the SPI port for further details. • OC1 – Port B, ...
Page 75
Figure 51. Port B Schematic Diagram (Pin PB1) PB1 WP: WRITE PORTB WD: WRITE DDRB RL: READ PORTB LATCH RP: READ PORTB PIN RD: READ DDRB Figure 52. Port B Schematic Diagram (Pin PB2) MOS PULL- UP PB2 WP: ...
Page 76
AT90S/LS4433 76 Figure 53. Port B Schematic Diagram (Pin PB3) MOS PULL- UP PB3 WRITE PORTB WP: WD: WRITE DDRB RL: READ PORTB LATCH RP: READ PORTB PIN READ DDRB RD: SPI ENABLE SPE: MSTR MASTER SELECT Figure 54. Port ...
Page 77
Port C 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 55. Port B Schematic Diagram (Pin PB5) MOS PULL- UP PB5 WRITE PORTB WP: WRITE DDRB WD: READ PORTB LATCH RL: READ PORTB PIN RP: READ DDRB RD: SPI ENABLE SPE: MSTR MASTER SELECT Port C ...
Page 78
Port C Data Register – PORTC Port C Data Direction Register – DDRC Port C Input Pins Address – PINC Port C as General Digital I/O AT90S/LS4433 78 Bit $15 ($35) – – PORTC5 Read/Write R R ...
Page 79
Port C Schematics 1042H–AVR–04/03 Note that all port pins are synchronized. The synchronization latch is, however, not shown in the figure. Figure 56. Port C Schematic Diagrams (Pins PC0 - PC5) MOS PULL- UP PCn PWRDN WP: WRITE PORTC WD: ...
Page 80
Port D Port D Data Register – PORTD Port D Data Direction Register – DDRD Port D Input Pins Address – PIND AT90S/LS4433 80 Port 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors. Three I/O memory address ...
Page 81
Port D as General Digital I/O Alternate Functions of Port D 1042H–AVR–04/03 PDn, General I/O pin: The DDDn bit in the DDRD Register selects the direction of this pin. If DDDn is set (one), PDn is configured as an output ...
Page 82
Port D Schematics AT90S/LS4433 82 • TXD – Port D, Bit 1 Transmit Data (Data Output pin for the UART). When the UART Transmitter is enabled, this pin is configured as an output, regardless of the value of DDD1. • ...
Page 83
Figure 58. Port D Schematic Diagram (Pin PD1) MOS PULL- UP PD1 WP: WRITE PORTD WD: WRITE DDRD RL: READ PORTD LATCH RP: READ PORTD PIN READ DDRD RD: UART TRANSMIT DATA TXD: UART TRANSMIT ENABLE TXEN: Figure 59. ...
Page 84
AT90S/LS4433 84 Figure 60. Port D Schematic Diagram (Pins PD4 and PD5) PDn WP: WRITE PORTD WD: WRITE DDRD RL: READ PORTD LATCH RP: READ PORTD PIN RD: READ DDRD Figure 61. Port D Schematic Diagram (Pins ...
Page 85
... CKSEL2..0: See Table 5 on page 23 for which combination of CKSEL2..0 to use. Default value is “010”. All Atmel microcontrollers have a 3-byte signature code that identifies the device. This code can be read in both serial and parallel mode. The three bytes reside in a separate address space ...
Page 86
... Serial Programming mode. During program- ming, the supply voltage must be in accordance with Table 29. Table 29. Supply Voltage during Programming Part Serial Programming AT90LS4433 2.7 - 6.0V AT90S4433 4.0 - 6.0V This section describes how to Parallel program and verify Flash Program memory, EEPROM Data memory, Lock bits and Fuse bits in the AT90S4433 ...
Page 87
Enter Programming Mode 1042H–AVR–04/03 Table 30. Pin Name Mapping Signal Name in Programming Mode Pin Name RDY/BSY PD1 OE PD2 WR PD3 BS PD4 XA0 PD5 XA1 PD6 DATA PC1 - 0, PB5 - 0 Table 31. XA1 and XA0 ...
Page 88
Chip Erase Programming the Flash AT90S/LS4433 88 The Chip Erase command will erase the Flash and EEPROM memories and the Lock bits. The Lock bits are not reset until the Flash and EEPROM have been completely erased. The Fuse bits ...
Page 89
G: Write Data High Byte 1. Set BS to “1”. This selects high data. 2. Give WR a negative pulse. This starts programming of the data byte. RDY/BSY goes low. 3. Wait until RDY/BSY goes high to program the ...
Page 90
Reading the Flash Programming the EEPROM Reading the EEPROM AT90S/LS4433 90 Figure 64. Programming the Flash Waveforms (Continued) DATA DATA HIGH XA1 XA0 BS XTAL1 WR RDY/BSY RESET +12V OE The algorithm for reading the Flash memory is as follows ...
Page 91
Programming the Fuse Bits Programming the Lock Bits Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits 1042H–AVR–04/03 The algorithm for programming the Fuse bits is as follows (refer to “Programming the Flash” for details on command and data loading): A: Load Command ...
Page 92
Reading the Signature Bytes Parallel Programming Characteristics AT90S/LS4433 92 The algorithm for reading the signature bytes is as follows (refer to “Programming the Flash” for details on command and address loading): A: Load Command “0000 1000”. B: Load Address Low ...
Page 93
... Wait for at least 20 ms and enable serial programming by sending the Program- ming Enable serial instruction to pin MOSI/PB3. 3. The serial programming instructions will not work if the communication is out of synchronization. When in sync, the second byte ($53) will echo back when issu- AT90S/LS4433 4.0 - 6.0 V (AT90S4433) AT90S/LS4433 2.7 - 6.0 V (AT90LS4433) VCC 93 ...
Page 94
Data Polling EEPROM AT90S/LS4433 94 ing the third byte of the Programming Enable instruction. Whether or not the echo is correct, all four bytes of the instruction must be transmitted. If the $53 did not echo back, give SCK a ...
Page 95
Data Polling Flash 1042H–AVR–04/03 When a byte is being programmed into the Flash, reading the address location being programmed will give the value $FF. At the time the device is ready for a new byte, the programmed value will read ...
Page 96
Table 35. Serial Programming Instruction Set Instruction Byte 1 1010 1100 Programming Enable 1010 1100 Chip Erase 0010 H000 Read Program Memory 0100 H000 Write Program Memory Read EEPROM 1010 0000 Memory Write EEPROM 1100 0000 Memory 1010 1100 Write ...
Page 97
Serial Programming Characteristics 1042H–AVR–04/03 Figure 68. Serial Programming Timing MOSI t OVSH SCK MISO Table 36. Serial Programming Characteristics, T (unless otherwise noted) Symbol Parameter 1/t Oscillator Frequency (V CLCL t Oscillator Period (V = 2.7 - 6.0V) CLCL CC ...
Page 98
Electrical Characteristics Absolute Maximum Ratings* Operating Temperature.................................. -55°C to +125°C Storage Temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C Voltage on Any Pin except RESET with Respect to Ground .............................-1. Voltage on RESET with Respect to Ground ....-1.0V to +13.0V Maximum ...
Page 99
DC Characteristics (Continued -40°C to 85° 2.7V to 6.0V (unless otherwise noted Symbol Parameter Analog Comparator Input V ACIO Offset Voltage Analog Comparator Input I ACLK Leakage A Analog Comparator t ACPD Propagation Delay ...
Page 100
External Clock Drive Waveforms AT90S/LS4433 100 Figure 69. External Clock VIH1 VIL1 Table 39. External Clock Drive Symbol Parameter 1/t Oscillator Frequency CLCL t Clock Period CLCL t High Time CHCX t Low Time CLCX t Rise Time CLCH t ...
Page 101
Typical Characteristics 1042H–AVR–04/03 The following charts show typical behavior. These figures are not tested during manu- facturing. All current consumption measurements are performed with all I/O pins configured as inputs and with internal pull-ups enabled. A sine wave generator with ...
Page 102
AT90S/LS4433 102 Figure 71. Active Supply Current vs. V ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs 2.5 3 Figure 72. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY ...
Page 103
Figure 73. Idle Supply Current vs. V IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs 2.5 3 Figure 74. Power-down Supply Current vs. V POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. V WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED 25 20 ...
Page 104
AT90S/LS4433 104 Figure 75. Power-down Supply Current vs. V POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. V 120 100 2.5 3 Figure 76. Power-down Supply Current vs. V POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. V BROWN-OUT DETECTOR ENABLED 140 ...
Page 105
Figure 77. Analog Comparator Current vs. V ANALOG COMPARATOR CURRENT vs. V 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0 2.5 3 Analog Comparator offset voltage is measured as absolute offset. Figure 78. Analog Comparator Offset ...
Page 106
AT90S/LS4433 106 Figure 79. Analog Comparator Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Voltage ANALOG COMPARATOR OFFSET VOLTAGE vs. COMMON MODE VOLTAGE 0.5 1 Figure 80. Analog Comparator Input Leakage Current ANALOG COMPARATOR INPUT LEAKAGE ...
Page 107
Figure 81. Watchdog Oscillator Frequency vs. V WATCHDOG OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY vs 2.5 3 Sink and source capabilities of I/O ports are measured on one pin at a time. Figure ...
Page 108
AT90S/LS4433 108 Figure 83. Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Input Voltage PULL-UP RESISTOR CURRENT vs. INPUT VOLTAGE 25˚ 85˚ 0.5 Figure 84. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. ...
Page 109
Figure 85. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage I/O PIN SOURCE CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE 0.5 1 1.5 Figure 86. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. Output Voltage ...
Page 110
AT90S/LS4433 110 Figure 87. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage I/O PIN SOURCE CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE 0.5 1 Figure 88. I/O Pin Input Threshold Voltage vs. V I/O PIN INPUT ...
Page 111
Figure 89. I/O Pin Input Hysteresis vs. V I/O PIN INPUT HYSTERESIS vs. V 0.18 0.16 0.14 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 2.7 AT90S/LS4433 25˚ 5.0 111 ...
Page 112
Register Summary Address Name Bit 7 $3F ($5F) SREG I $3E ($5E) Reserved – $3D ($5D) SP SP7 $3C ($5C) Reserved $3B ($5B) GIMSK INT1 $3A ($5A) GIFR INTF1 $39 ($59) TIMSK TOIE1 $38 ($58) TIFR TOV1 $37 ($57) Reserved ...
Page 113
Notes: 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. Some of the Status Flags are cleared by writing a logical “1” to them. Note ...
Page 114
Instruction Set Summary Mnemonic Operands Description ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC INSTRUCTIONS ADD Rd, Rr Add Two Registers ADC Rd, Rr Add with Carry Two Registers ADIW Rdl, K Add Immediate to Word SUB Rd, Rr Subtract Two Registers SUBI Rd, K ...
Page 115
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) Mnemonic Operands Description LD Rd, Y Load Indirect LD Rd, Y+ Load Indirect and Post-inc. LD Rd, -Y Load Indirect and Pre-dec. LDD Rd,Y+q Load Indirect with Displacement LD Rd, Z Load Indirect LD Rd, Z+ ...
Page 116
... Speed (MHz) 2.7 - 6.0V 4 4.0 - 6.0V 8 32A 32-lead, Thin (1.0 mm) Plastic Quad Flat Package (TQFP) 28P3 28-lead, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP) AT90S/LS4433 116 Ordering Code Package AT90LS4433-4AC 32A AT90LS4433-4PC 28P3 AT90LS4433-4AI 32A AT90LS4433-4PI 28P3 AT90S4433-8AC 32A AT90S4433-8PC 28P3 AT90S4433-8AI ...
Page 117
Packaging Information 32A PIN 0˚~7˚ L Notes: 1. This package conforms to JEDEC reference MS-026, Variation ABA. 2. Dimensions D1 and E1 do not include mold protrusion. Allowable protrusion is 0.25 mm per side. Dimensions D1 and ...
Page 118
A SEATING PLANE Note: 1. Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold Flash or Protrusion. Mold Flash or Protrusion shall not exceed 0.25 mm (0.010"). 2325 Orchard Parkway San Jose, CA 95131 R AT90S/LS4433 118 ...
Page 119
Errata for AT90S/LS4433 Rev. Rev. C/D/E/F 1042H–AVR–04/03 • BOD Keeps the Device in Reset at Low Temperature • Fuses and Programming Mode • Incorrect Channel Change in Free Running Mode • Bandgap Reference Stabilizing Time • Brown-out Detection Level • ...
Page 120
AT90S/LS4433 120 3. Brown-out Detection Level The Brown-out Detection level can increase when there is heavy I/O-activity on the device. The increase can be significant when some of the I/O pins are driving heavy loads. Problem Fix/Workaround Select a V ...
Page 121
Data Sheet Change Log for AT90S/LS4433 Changes from Rev. 1042E-09/01 to Ref. 1042F-03/02 Changes from Rev. 1042F-03/02 to Ref. 1042G-09/02 Changes from Rev. 1042G-09/02 to Ref. 1042H-04/03 1042H–AVR–04/03 This section containes a log on the changes made to the data ...
Page 122
AT90S/LS4433 122 1042H–AVR–04/03 ...
Page 123
Table of Contents 1042H–AVR–04/03 Features................................................................................................. 1 Pin Configurations................................................................................ 2 Description ............................................................................................ 3 Block Diagram ...................................................................................................... 4 Pin Descriptions.................................................................................................... 5 Clock Options ....................................................................................................... 6 Architectural Overview......................................................................... 7 General Purpose Register File ........................................................................... 10 ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit................................................................................ 11 In-System Programmable ...
Page 124
AT90S/LS4433 ii Analog-to-Digital Converter............................................................... 64 Features.............................................................................................................. 64 Operation ............................................................................................................ 65 Prescaling ........................................................................................................... 65 ADC Noise Canceler Function............................................................................ 67 Scanning Multiple Channels ............................................................................... 70 ADC Noise Canceling Techniques ..................................................................... 70 ADC Characteristics T = -40°C to 85°C ............................................................ 71 A I/O ...
Page 125
Data Sheet Change Log for AT90S/LS4433.................................... 121 Changes from Rev. 1042E-09/01 to Ref. 1042F-03/02 .................................... 121 Changes from Rev. 1042F-03/02 to Ref. 1042G-09/02.................................... 121 Changes from Rev. 1042G-09/02 to Ref. 1042H-04/03 ................................... 121 Table of Contents .................................................................................. i AT90S/LS4433 ...
Page 126
... No licenses to patents or other intellectual property of Atmel are granted by the Company in connection with the sale of Atmel products, expressly or by implication. Atmel’s products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems. ...