AD8042AN Analog Devices Inc, AD8042AN Datasheet - Page 15

AD8042AN
Manufacturer Part Number
AD8042AN
Description
IC OPAMP VF R-R DUAL LP 8DIP
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD8042ARZ.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of AD8042AN
Slew Rate
225 V/µs
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Design Resources
Single-Ended-to-Differential Converters for Voltage Output and Current Output DACs Using AD8042 (CN0143)
Amplifier Type
Voltage Feedback
Number Of Circuits
2
Output Type
Rail-to-Rail
-3db Bandwidth
170MHz
Current - Input Bias
1.2µA
Voltage - Input Offset
3000µV
Current - Supply
6mA
Current - Output / Channel
50mA
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
3 V ~ 12 V, ±1.5 V ~ 6 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Op Amp Type
Voltage Feedback
No. Of Amplifiers
2
Bandwidth
160MHz
Supply Voltage Range
3V To 12V
Amplifier Case Style
DIP
No. Of Pins
8
Gain Bandwidth Product
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
AD8042ANZ
Manufacturer:
ADI
Quantity:
9 115
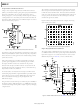
The circuit was tested with a 1 MHz input signal and clocked
at 10 MHz. An FFT response of the digital output is shown in
Figure 42.
Pin 5 is biased at 2.5 V by the voltage divider and bypassed.
This biases each output at 2.5 V. V
V
the negative direction. The opposite happens for a negative
going V
HDSL Line Driver
High bit rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) is a popular means
of providing data communication at DS1 rates (1.544 Mbps)
over moderate distances via conventional telephone twisted pair
wires. In these systems, the transceiver at the customer’s end is
powered sometimes via the twisted pair from a power source at
the central office. Sometimes, it is required to raise the dc voltage
of the power source to compensate for IR drops in long lines or
lines with narrow gauge wires.
Because of the IR drop, it is highly desirable to keep the power
consumption of the customer’s transceiver as low as possible.
One means to realize significant power savings is to run
the transceiver from a ±5 V supply instead of the more
conventional ±12 V.
The high output swing and current drive capability of the
AD8042 make it ideally suited to this application. Figure 43
shows a circuit for the analog portion of an HDSL transceiver
using the AD8042 as the line driver.
IN
going positive makes VINA go positive and VINB go in
Figure 42. FFT of the
IN
FUND FRQ 1000977
SMPL FRQ 10000000 SNR
.
1
9
AD9220
THD
SINAD 70.79
SFDR
HARMONICS (dBc)
2
8
–82.00
71.13
–86.74
Output When Driven by the AD8042
IN
2ND –88.34
3RD –86.74
4TH –99.26
5TH –90.67
is ac-coupled such that
3
7
6TH –99.47
7TH –91.16
8TH –97.25
9TH –91.61
6
4
5
Rev. E | Page 15 of 16
LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
The specified high speed performance of the AD8042 requires
careful attention to board layout and component selection.
Proper RF design techniques and low-pass parasitic component
selection are necessary.
The PCB should have a ground plane covering all unused
portions of the component side of the board to provide a low
impedance path. The ground plane should be removed from
the area near the input pins to reduce the stray capacitance.
Chip capacitors should be used for the supply bypassing. One
end should be connected to the ground plane and the other
within ⅛-inch of each power pin. An additional large (0.47 μF
to 10 μF) tantalum electrolytic capacitor should be connected in
parallel, but not necessarily so close to supply current, for fast,
large signal changes at the output.
The feedback resistor should be located close to the inverting
input pin to keep the stray capacitance at this node to a
minimum. Capacitance variations of less than 1 pF at the
inverting input significantly affect high speed performance.
Stripline design techniques should be used for long signal
traces (greater than approximately one inch). These should be
designed with a characteristic impedance of 50 Ω or 75 Ω and
be properly terminated at each end.
V
IN
0.001µF
232Ω
2kΩ
2kΩ
6
5
2
3
Figure 43. HDSL Line Driver
3kΩ
3kΩ
AD8042
0.0027µF
AD8042
0.001µF
1/2
1/2
912Ω
2kΩ
7
1
2kΩ
34Ω
10
2
9
2kΩ
1
2718AF
93DJ39
ATT
3
2kΩ
2
4
5
7
6
AD8044
2kΩ
1/4
1
V
AD8042
OUT
249Ω
V
REC