LM2595T-ADJ National Semiconductor, LM2595T-ADJ Datasheet - Page 23

LM2595T-ADJ
Manufacturer Part Number
LM2595T-ADJ
Description
DC/DC Converter IC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM2595T-ADJ.pdf
(29 pages)
Specifications of LM2595T-ADJ
Input Voltage
40V
Output Current
1A
Output Voltage
37V
No. Of Pins
5
Termination Type
Through Hole
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Voltage Regulator Type
Buck Switching
Output Current Max
1A
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM2595T-ADJ
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LM2595T-ADJ/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
8 784
Application Information
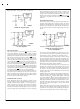
DELAYED STARTUP
The circuit in Figure 21 uses the the ON /OFF pin to provide
a time delay between the time the input voltage is applied
and the time the output voltage comes up (only the circuitry
pertaining to the delayed start up is shown). As the input volt-
age rises, the charging of capacitor C1 pulls the ON /OFF pin
high, keeping the regulator off. Once the input voltage
reaches its final value and the capacitor stops charging, and
resistor R
cuit to start switching. Resistor R
maximum voltage applied to the ON /OFF pin (maximum of
25V), reduces power supply noise sensitivity, and also limits
the capacitor, C1, discharge current. When high input ripple
voltage exists, avoid long delay time, because this ripple can
be coupled into the ON /OFF pin and cause problems.
This delayed startup feature is useful in situations where the
input power source is limited in the amount of current it can
deliver. It allows the input voltage to rise to a higher voltage
before the regulator starts operating. Buck regulators require
less input current at higher input voltages.
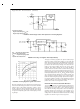
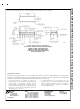
UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
Some applications require the regulator to remain off until
the input voltage reaches a predetermined voltage. An und-
ervoltage lockout feature applied to a buck regulator is
shown in Figure 22 , while Figure 23 and Figure 24 applies
the same feature to an inverting circuit. The circuit in Figure
23 features a constant threshold voltage for turn on and turn
off (zener voltage plus approximately one volt). If hysteresis
2
FIGURE 22. Undervoltage Lockout
pulls the ON /OFF pin low, thus allowing the cir-
FIGURE 21. Delayed Startup
for Buck Regulator
1
is included to limit the
(Continued)
DS012565-36
DS012565-37
23
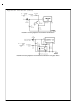
is needed, the circuit in Figure 24 has a turn ON voltage
which is different than the turn OFF voltage. The amount of
hysteresis is approximately equal to the value of the output
voltage. If zener voltages greater than 25V are used, an ad-
ditional 47 k resistor is needed from the ON /OFF pin to the
ground pin to stay within the 25V maximum limit of the ON
/OFF pin.
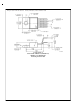
INVERTING REGULATOR
The circuit in Figure 25 converts a positive input voltage to a
negative output voltage with a common ground. The circuit
operates by bootstrapping the regulator’s ground pin to the
negative output voltage, then grounding the feedback pin,
the regulator senses the inverted output voltage and regu-
lates it.
This circuit has an ON/OFF threshold of approximately 13V.
This example uses the LM2595-5.0 to generate a −5V out-
put, but other output voltages are possible by selecting other
output voltage versions, including the adjustable version.
Since this regulator topology can produce an output voltage
that is either greater than or less than the input voltage, the
maximum output current greatly depends on both the input
and output voltage. The curve shown in Figure 26 provides a
guide as to the amount of output load current possible for the
different input and output voltage conditions.
The maximum voltage appearing across the regulator is the
absolute sum of the input and output voltage, and this must
be limited to a maximum of 40V. For example, when convert-
ing +20V to −12V, the regulator would see 32V between the
input pin and ground pin. The LM2595 has a maximum input
voltage spec of 40V.
Additional diodes are required in this regulator configuration.
Diode D1 is used to isolate input voltage ripple or noise from
coupling through the C
or no load conditions. Also, this diode isolation changes the
topology to closley resemble a buck configuration thus pro-
viding good closed loop stability. A Schottky diode is recom-
mended for low input voltages, (because of its lower voltage
drop) but for higher input voltages, a fast recovery diode
could be used.
Without diode D3, when the input voltage is first applied, the
charging current of C
eral volts for a short period of time. Adding D3 prevents the
output from going positive by more than a diode voltage.
FIGURE 23. Undervoltage Lockout
for Inverting Regulator
IN
IN
can pull the output positive by sev-
capacitor to the output, under light
www.national.com
DS012565-46