LTC1553LCSW#TRMPBF Linear Technology, LTC1553LCSW#TRMPBF Datasheet - Page 11

LTC1553LCSW#TRMPBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1553LCSW#TRMPBF
Description
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC1553LCSWTRMPBF.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of LTC1553LCSW#TRMPBF
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
APPLICATIONS
Soft Start and Current Limit
The LTC1553L includes a soft start circuit which is used
for initial start-up and during current limit operation. The
SS pin requires an external capacitor to GND with the value
determined by the required soft start time. An internal
11 A current source is included to charge the external SS
capacitor. During start-up, the COMP pin is clamped to a
diode drop above the voltage at the SS pin. This prevents
the error amplifier, ERR, from forcing the loop to maxi-
mum duty cycle. The LTC1553L will begin to operate at low
duty cycle as the SS pin rises above about 1.2V (V
1.8V). As SS continues to rise, Q
amplifier begins to regulate the output. The MIN compara-
tor is disabled when soft start is active to prevent it from
overriding the soft start function.
The LTC1553L includes yet another feedback loop to
control operation in current limit. Just before every falling
edge of G1, the current comparator, CC, samples and
holds the voltage drop measured across the external
MOSFET, Q1, at the I
to the voltage at the I
measured voltage across Q1 increases due to the drop
across the R
below I
ceeded the maximum level, CC starts to pull current out of
the external soft start capacitor, cutting the duty cycle and
controlling the output current level. The CC comparator
pulls current out of the SS pin in proportion to the voltage
difference between I
conditions, the SS pin will fall gradually, creating a time
delay before current limit takes effect. Very short, mild
overloads may not affect the output voltage at all. More
significant overload conditions will allow the SS pin to
reach a steady state, and the output will remain at a
reduced voltage until the overload is removed. Serious
overloads will generate a large overdrive at CC, allowing it
to pull SS down quickly and preventing damage to the
output components.
By using the R
the current limiting circuit eliminates an expensive dis-
crete sense resistor that would otherwise be required. This
MAX
, indicating that Q1’s drain current has ex-
DS(ON)
DS(ON)
U
of Q1. When the voltage at I
MAX
FB
FB
of Q1 to measure the output current,
pin. CC compares the voltage at I
and I
pin. As the peak current rises, the
INFORMATION
U
MAX
SS
. Under minor overload
turns off and the error
W
U
FB
COMP
drops
FB
helps minimize the number of components in the high
current path. Due to switching noise and variation of
R
accurate. The current limiting circuitry is primarily meant
to prevent damage to the power supply circuitry during
fault conditions. The exact current level where the limiting
circuit begins to take effect will vary from unit to unit as the
R
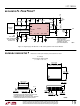
For a given current limit level, the external resistor from
I
where,
I
I
f
L
R
I
MAX
LOAD
RIPPLE
OSC
IMAX
O
DS(ON)
DS(ON)
DS(ON)Q1
LTC1553L
R
= Inductor value
I
LMAX
IMAX
= LTC1553L oscillator frequency = 300kHz
to V
= Internal 180 A sink current at I
= Maximum load current
CC
= Inductor ripple current
, the actual current limit trip point is not highly
of Q1 varies.
IN
–
+
= Hot on-resistance of Q1 at I
V
can be determined by:
I
IN
LOAD
f
I
OSC
LMAX
Figure 5. Current Limit Setting
180 A
V
OUT
L
I
IMAX
O
I
R
RIPPLE
DS ON Q
I
MAX
I
V
V
2
7
FB
8
OUT
IN
(
20
) 1
R
G1
G2
IMAX
V
IN
Q2
Q1
MAX
LTC1553L
LMAX
L
O
+
+
11
1553L F05
C
C
IN
OUT
V
OUT