LTC2412IGN Linear Technology, LTC2412IGN Datasheet - Page 20

LTC2412IGN
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC2412IGN
Description
IC CONV A/D 24B 2CH DIFF 16-SSOP
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC2412CGNPBF.pdf
(36 pages)
Specifications of LTC2412IGN
Number Of Bits
24
Sampling Rate (per Second)
7.5
Data Interface
MICROWIRE™, Serial, SPI™
Number Of Converters
1
Power Dissipation (max)
1mW
Voltage Supply Source
Single Supply
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-SSOP (0.150", 3.90mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC2412IGN
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LTC2412IGN
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LTC2412IGN#TRPBF
Manufacturer:
LTNEAR
Quantity:
20 000
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
LTC2412
device returns to the sleep state and the conversion result
is held in the internal static shift register.
If CS remains LOW longer than t
edge of SCK will occur and the conversion result is serially
shifted out of the SDO pin. The data output cycle concludes
after the 32nd rising edge. Data is shifted out the SDO pin
on each falling edge of SCK. The internally generated serial
clock is output to the SCK pin. This signal may be used to
shift the conversion result into external circuitry. EOC can
be latched on the first rising edge of SCK and the last bit
of the conversion result on the 32nd rising edge of SCK.
After the 32nd rising edge, SDO goes HIGH (EOC = 1), SCK
stays HIGH and a new conversion starts.
Typically, CS remains LOW during the data output state.
However, the data output state may be aborted by pulling
CS HIGH anytime between the first and 32nd rising edge
of SCK, see Figure 9. On the rising edge of CS, the device
aborts the data output state and immediately initiates a
new conversion. This is useful for systems not requiring
all 32 bits of output data, aborting an invalid conversion
cycle, or synchronizing the start of a conversion. If CS is
pulled HIGH while the converter is driving SCK LOW, the
internal pull-up is not available to restore SCK to a logic
20
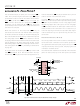
(INTERNAL)
SDO
SCK
CS
CONVERSION
Hi-Z
U
SLEEP
(OPTIONAL)
TEST EOC
U
SLEEP
Hi-Z
<t
EOCtest
EOCtest
BIT 31
Figure 8. Internal Serial Clock, Single Cycle Operation
W
EOC
, the first rising
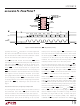
CH0/CH1
ANALOG INPUT RANGE
BIT 30
–0.5V
REF
U
TO 0.5V
0.1V TO V
REFERENCE
BIT 29
SIG
VOLTAGE
1 F
2.7V TO 5.5V
REF
CC
BIT 28
MSB
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
V
REF
REF
CH0
CH0
CH1
CH1
CC
LTC2412
HIGH state. This will cause the device to exit the internal
serial clock mode on the next falling edge of CS. This can
be avoided by adding an external 10k pull-up resistor to
the SCK pin or by never pulling CS HIGH when SCK is LOW.
Whenever SCK is LOW, the LTC2412’s internal pull-up at
pin SCK is disabled. Normally, SCK is not externally driven
if the device is in the internal SCK timing mode. However,
certain applications may require an external driver on SCK.
If this driver goes Hi-Z after outputting a LOW signal, the
LTC2412’s internal pull-up remains disabled. Hence, SCK
remains LOW. On the next falling edge of CS, the device is
switched to the external SCK timing mode. By adding an
external 10k pull-up resistor to SCK, this pin goes HIGH
once the external driver goes Hi-Z. On the next CS falling
edge, the device will remain in the internal SCK timing
mode.
A similar situation may occur during the sleep state when
CS is pulsed HIGH-LOW-HIGH in order to test the
conversion status. If the device is in the sleep state (EOC
= 0), SCK will go LOW. Once CS goes HIGH (within the time
period defined above as t
activated. For a heavy capacitive load on the SCK pin, the
+
–
+
–
+
–
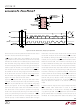
BIT 27
GND
SDO
SCK
DATA OUTPUT
CS
F
O
14
13
12
11
8, 9, 10, 15, 16
BIT 26
3-WIRE
SPI INTERFACE
V
CC
= 50Hz REJECTION
= EXTERNAL OSCILLATOR
= 60Hz REJECTION
LSB
BIT 5
24
EOCtest
), the internal pull-up is
V
CC
10k
BIT 0
CONVERSION
Hi-Z
TEST EOC
2412 F08
Hi-Z
2412f