AD7663ASTRL Analog Devices Inc, AD7663ASTRL Datasheet - Page 19
AD7663ASTRL
Manufacturer Part Number
AD7663ASTRL
Description
IC ADC 16BIT CMOS 5V 48-LQFP
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
PulSAR®r
Datasheet
1.AD7663ASTZ.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of AD7663ASTRL
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Number Of Bits
16
Sampling Rate (per Second)
250k
Data Interface
Serial, Parallel
Number Of Converters
1
Power Dissipation (max)
41mW
Voltage Supply Source
Analog and Digital
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
48-LQFP
For Use With
EVAL-AD7663CBZ - BOARD EVALUATION FOR AD7663
SLAVE SERIAL INTERFACE
External Clock
The AD7663 is configured to accept an externally supplied
serial data clock on the SCLK pin when the EXT/INT pin is
held HIGH. In this mode, several methods can be used to read
the data. The external serial clock is gated by CS and the data
are output when both CS and RD are LOW. Thus, depending
on CS, the data can be read after each conversion or during the
following conversion. The external clock can be either a continu-
ous or discontinuous clock. A discontinuous clock can be either
normally high or normally low when inactive. Figures 19 and 21
show the detailed timing diagrams of these methods.
While the AD7663 is performing a bit decision, it is important
that voltage transients not occur on digital input/output pins or
degradation of the conversion result could occur. This is par-
ticularly important during the second half of the conversion
phase because the AD7663 provides error correction circuitry
that can correct for an improper bit decision made during the first
half of the conversion phase. For this reason, it is recommended
that when an external clock is being provided, it is a discontinuous
clock that is toggling only when BUSY is LOW or, more
importantly, that does not transition during the latter half of
BUSY HIGH.
External Discontinuous Clock Data Read after Conversion
This mode is the most recommended of the serial slave modes.
Figure 19 shows the detailed timing diagrams of this method.
After a conversion is complete, indicated by BUSY returning
LOW, the result of this conversion can be read while both CS and
RD are LOW. The data is shifted out, MSB first, with 16 clock
pulses and is valid on both the rising and falling edge of the clock.
Among the advantages of this method, the conversion performance
is not degraded because there are no voltage transients on the
digital interface during the conversion process.
REV. B
SDOUT
BUSY
SCLK
SDIN
CS
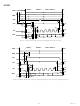
Figure 19. Slave Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read after Convert)
t
t
31
16
t
33
X
t
36
1
t
35
D15
t
X15
37
t
34
EXT/INT = 1
2
D14
X14
t
32
3
X13
D13
–19–
Another advantage is to be able to read the data at any speed up
to 40 MHz, which accommodates both slow digital host interface
and the fastest serial reading.
Finally, in this mode only, the AD7663 provides a “daisy-chain”
feature using the RDC/SDIN input pin for cascading multiple
converters together. This feature is useful for reducing component
count and wiring connections when desired as, for instance, in
isolated multiconverter applications.
An example of the concatenation of two devices is shown in
Figure 20. Simultaneous sampling is possible by using a com-
mon CNVST signal. It should be noted that the RDC/SDIN
input is latched on the opposite edge of SCLK of the one used
to shift out the data on SDOUT. Therefore, the MSB of the
“upstream” converter just follows the LSB of the “downstream”
converter on the next SCLK cycle.
Figure 20. Two AD7663s in a Daisy-Chain Configuration
INVSCLK = 0
CNVST IN
SCLK IN
14
CS IN
RDC/SDIN
(UPSTREAM)
AD7663
15
BUSY
#2
X1
D1
SDOUT
CNVST
SCLK
16
CS
RD = 0
D0
X0
17
X15
Y15
RDC/SDIN
18
(DOWNSTREAM)
AD7663
X14
Y14
BUSY
#1
SDOUT
CNVST
SCLK
AD7663
CS
BUSY
OUT
DATA
OUT