MAX3292ESD+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX3292ESD+ Datasheet - Page 13

MAX3292ESD+
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX3292ESD+
Description
IC TXRX RS485/422 10MBPS 14-SOIC
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
Transceiverr
Datasheet
1.MAX3292EPD.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MAX3292ESD+
Number Of Drivers/receivers
1/1
Protocol
RS422, RS485
Voltage - Supply
4.75 V ~ 5.25 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
14-SOIC (3.9mm Width), 14-SOL
Operating Supply Voltage
5 V
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Product
RS-422/RS-485 Combination
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
3) Don’t overload the cable with too many receivers.
The MAX3291/ MAX3292 are centered for a load imped-
ance of 54Ω, which corresponds to the parallel combina-
tion of the cable impedance and termination resistors. If
your cable impedance deviates somewhat from this
value, you still get the preemphasis effect (although the
ideal preemphasis time, t
However, if your cable impedance is significantly differ-
ent, the preemphasis ratio DPER changes, resulting in
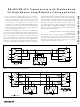
Figure 19. Typical Half-Duplex RS-485 Network
Figure 20. Typical Full-Duplex RS-485 Network
Even though the MAX3291/MAX3292 receives pre-
sent only 1/4-unit load, placing 128 receivers on the
cable will attenuate the signal if spaced out along
the cable and, in addition, cause reflections if
clumped in one spot. The MAX3291/MAX3292 suc-
cessfully drive the cables to correct RS-485/RS-422
levels with 128 receivers, but the preemphasis
effect is significantly diminished.
for High-Speed, Long-Distance Communication
RS-485/RS-422 Transceivers with Preemphasis
DE
RO
RE
DI
RO
RE
DE
DI
NOTE: RE AND DE ON.
D
D
MAX3291
MAX3292
R
______________________________________________________________________________________
R
A
B
Z
Y
R = Z
R = Z
PRE
O
O
Z
Y
B
A
, may need adjustment).
R = Z
Y
DI
O
D
Z
DE
B
RE
RO
R
A
DI
Z
D
Y
DE
significantly less preemphasis. Determine the preempha-
sis ratio versus load by referring to the Driver Differential
Output Voltage vs. R
Characteristics . Read the strong and normal levels from
the graph (remember that the horizontal units are half
your cable impedance) and divide the two numbers to
get DPER (DPER = V
Figures 19 and 20 show typical network application cir-
cuits with proper termination.
At low data rates (<1Msps), preemphasis operation is
not guaranteed because it is highly dependent on the
system power-supply noise. Minimize this noise by
increasing bypass capacitance and using a power
supply with a fast transient response.
B
R
RO
A
RE
Y
DI
D
Z
Preemphasis at Low Data Rates
DE
B
RE
R
R = Z
RO
DIFF
STRONG
O
A
graph in the Typical Operating
Y
B
A
Z
R = Z
R = Z
/ V
O
O
Y
B
A
Z
NORMAL
MAX3291
MAX3292
R
R
DE
D
D
= V
(MAX3292)
ODP
DI
DE
RE
RO
RO
DI
RE
/ V
OD
13
).