SI3200-GS Silicon Laboratories Inc, SI3200-GS Datasheet - Page 29
SI3200-GS
Manufacturer Part Number
SI3200-GS
Description
IC LINEFEED INTRFC 100V 16SOIC
Manufacturer
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Series
ProSLIC®r
Specifications of SI3200-GS
Function
Subscriber Line Interface Concept (SLIC), CODEC
Interface
GCI, PCM, SPI
Number Of Circuits
2
Voltage - Supply
3.3V, 5V
Current - Supply
110µA
Power (watts)
941mW
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Includes
Battery Switching, BORSCHT Functions, DTMF Generation and Decoding, FSK Tone Generation, Modem and Fax Tone Detection
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
SI3200-GS
Manufacturer:
SILICON
Quantity:
1
Part Number:
SI3200-GS
Manufacturer:
SILICON LABS/芯科
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
SI3200-GSR
Manufacturer:
SILICON
Quantity:
12 000
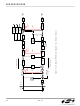
DC Feed Characteristics
The Si3220 and Si3225 offer programmable constant-
voltage and constant-current operating regions as
illustrated in Figure 14 and Figure . The constant
voltage region (defined by the open-circuit voltage, V
is programmable from 0 to 63.3 V in 1 V steps. The
constant current region (defined by the loop current
limit, I
0.87 mA steps. The Si3220 and Si3225 exhibit a
characteristic dc impedance of 640 Ω or 320 Ω during
Active mode. (See "Adaptive Linefeed" on page 32).
The TIP-RING voltage (V
programmable voltage (V
voltage headroom to the most positive terminal
(typically the TIP lead in normal polarity or the RING
lead in reverse polarity) for carrying audio signals. A
similar programmable voltage (V
between the most negative terminal and the battery
supply rail for carrying audio signals. (See Figure 14.)
The user-supplied battery voltage must have sufficient
amplitude under all operating states to ensure sufficient
headroom. The Si3200 may be powered by a lower
secondary battery supply (V
dissipation when driving short-loop lengths.
Calculating Overhead Voltages
The two programmable overhead voltages (V
V
V
normal operating conditions, these overhead voltages
are sufficiently low to maintain the desired TIP-RING
voltage (V
under which the user must exercise care in providing a
battery supply with enough amplitude to supply the
required TIP-RING voltage and enough margin to
accommodate these overhead voltages. The V
voltage is programmed for a given operating condition.
Therefore, the open-circuit voltage (V
CM
BAT
Figure 14. DC Linefeed Overhead Voltages
) represent one portion of the total voltage between
and ground as illustrated in Figure 14. Under
LIM
V
) is programmable from 18 to 45 mA in
OC
Constant I Region
Secondary V
V
BATL
). However, there are certain conditions
Selected
V
OV
(Forward State)
BAT
V
CM
OC
Constant V Region
CM
) is offset from ground by a
BATL
Loop Closure Threshold
V
) to provide sufficient
OV
) to reduce total power
V
OC
OV
V
V
V
RING
) is an offset
BATH
TIP
R
LOOP
OC
) varies
OV
and
OC
CM
Rev. 1.0
)
according to the required overhead voltage (V
the supplied battery voltage (V
pay attention to the maximum V
be required for each operating state.
In the off-hook active state, sufficient V
maintained to correctly power the phone from the
battery supply that is provided. Because the battery
supply depends on the state of the input supply (i.e.,
charging, discharging, or battery backup mode), the
user must decide how much loop current is required and
determine the maximum loop impedance that can be
driven based on the battery supply provided. The
minimum battery supply required can be calculated with
the following equation:
where V
The default V
overhead for a 3.1 dBm signal into a 600 Ω loop
impedance with an I
setting of 4 mA. A V
headroom to source a maximum I
3.1 dBm audio signal and an ABIAS setting of 16 mA.
For a typical operating condition of V
I
These conditions apply when the dc-sensing inputs
(STIPDCa/b and SRINGDCa/b) are placed on the SLIC
side of any protection resistance placed in series with
the TIP and RING leads. If line-side sensing is desired,
both V
equal to R
protection resistor. Other safety precautions may also
apply.
See "Linefeed Overhead Voltage Considerations During
Ringing" on page 50 for details on calculating the
overhead voltage during the ringing state.
The Dual ProSLIC chipset uses both voltage and
current information to control TIP and RING. Sense
resistor R
RING; Capacitor C
the TIP and RING leads to be measured. The Si3220
and Si3225 both use the Si3200 to drive TIP and RING
and isolate the high-voltage line from the low-voltage
CMOS devices.
The Si3220 and Si3225 measure voltage at various
nodes to monitor the linefeed current. R
provide these measuring points. The sense circuitry is
calibrated on-chip to guarantee measurement accuracy.
See "Linefeed Calibration" on page 35 for details.
LIM
= 22 mA:
OV
CM
V
PROT
DC
and V
and V
OC MAX
,
measures dc line voltages on TIP and
CM
x I
V
OV
CM
BAT
LIM
AC
=
value of 3 V provides sufficient
LIM
are provided in Table 8 on page 13.
OV
≥
must be increased by a voltage
56 V
where R
couples the ac line voltages on
V
Si3220/Si3225
setting of 22 mA and an ABIAS
value of 4 V provides sufficient
OC
–
+
(
3 V
V
PROT
CM
+
BAT
OV
+
LOOP
4 V
V
). The user should
and V
is the value of each
OV
)
=
BAT
of 45 mA with a
49 V
CM
DC
OC
= –56 V and
that might
and R
must be
OV
) and
BAT
29