MC68332CFC16 Motorola, MC68332CFC16 Datasheet

MC68332CFC16
Specifications of MC68332CFC16
Available stocks
Related parts for MC68332CFC16
MC68332CFC16 Summary of contents
Page 1
... CPU32 instruction set includes a low-power stop (LPSTOP) command that efficiently implements this capability. This document contains information on a new product. Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice. © MOTOROLA INC., 1993, 1996 Order this document by MC68332TS/D Rev. 2 MC68332 ...
Page 2
... MHz 2 pc tray 36 pc tray Order Number SPAKMC332GCFC16 MC68332GCFC16 SPAKMC332GCFC20 MC68332GCFC20 SPAKMC332GVFC16 MC68332GVFC16 SPAKMC332GVFC20 MC68332GVFC20 SPAKMC332GMFC16 MC68332GMFC16 SPAKMC332GMFC20 MC68332GMFC20 SPAKMC332CFC16 MC68332CFC16 SPAKMC332CFC20 MC68332CFC20 SPAKMC332VFC16 MC68332VFC16 SPAKMC332VFC20 MC68332VFC20 SPAKMC332MFC16 MC68332MFC16 SPAKMC332MFC20 MC68332MFC20 SPAKMC332ACFC16 MC68332ACFC16 SPAKMC332ACFC20 MC68332ACFC20 SPAKMC332AVFC16 MC68332AVFC16 SPAKMC332AVFC20 MC68332AVFC20 ...
Page 3
... Order Number SPAKMC332GCFV16 MC68332GCFVV16 SPAKMC332GCFV20 MC68332GCFV20 SPAKMC332GVFV16 MC68332GVFV16 SPAKMC332GVFV20 MC68332GVFV20 SPAKMC332GMFV16 MC68332GMFV16 SPAKMC332GMFV20 MC68332GMFVV20 SPAKMC332CFV16 MC68332CFV16 SPAKMC332CFVV20 MC68332CFV20 SPAKMC332VFV16 MC68332VFV16 SPAKMC332VFV20 MC68332VFV20 SPAKMC332MFV16 MC68332MFV16 SPAKMC332MFV20 MC68332MFV20 SPAKMC332ACFV16 MC68332ACFV16 SPAKMC332ACFV20 MC68332ACFV20 SPAKMC332AVFV16 MC68332AVFV16 SPAKMC332AVFC20 MC68332AVFV20 SPAKMC332AMFV16 MC68332AMFV16 SPAKMC332AMFV20 MC68332AMFV20 MOTOROLA 3 ...
Page 4
... Address Map .............................................................................................................................65 6.3 Pin Function ..............................................................................................................................66 6.4 QSM Registers ..........................................................................................................................66 6.5 QSPI Submodule .......................................................................................................................71 6.6 SCI Submodule .........................................................................................................................79 7 Standby RAM with TPU Emulation RAM 7.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................84 7.2 TPURAM Register Block ...........................................................................................................84 7.3 TPURAM Registers ...................................................................................................................84 7.4 TPURAM Operation ..................................................................................................................85 8 Summary of Changes MOTOROLA 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page MC68332 MC68332TS/D ...
Page 5
... Enhanced Serial Communication Interface — Queued Serial Peripheral Interface — One 8-Bit Dual Function Port • Static RAM Module with TPU Emulation Capability (TPURAM) — 2-Kbytes of Static RAM — May be Used as Normal RAM or TPU Microcode Emulation RAM MC68332 MC68332TS/D MOTOROLA 5 ...
Page 6
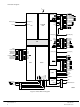
... RXD PQS7/TXD TXD PQS6/PCS3 PCS3 QS5/PCS2 PCS2 PQS4/PCS1 PCS1 PQS3/PCS0/SS PCS0/SS PQS2/SCK SCK PQS1/MOSI MOSI PQS0/MISO MISO BKPT/DSCLK IFETCH/DSI IPIPE/DSO MOTOROLA 6 V STBY SELECTS 2 KBYTES TPU RAM EBI IMB QSM CPU 32 Figure 1 MCU Block Diagram CHIP CSBOOT BR ADDR23/CS10 BG PC6/ADDR22/CS9 BGACK PC5/ADDR21/CS8 ...
Page 7
... DATA0 110 DATA1 109 DATA2 108 DATA3 V DD 107 V SS 106 105 DATA4 104 DATA5 103 DATA6 102 DATA7 V SS 101 100 DATA8 99 DATA9 98 DATA10 97 DATA11 DATA12 93 DATA13 92 DATA14 91 DATA15 90 ADDR0 89 PE0/DSACK0 88 PE1/DSACK1 87 PE2/AVEC 86 PE3/RMC 85 PE5/ 332 132-PIN QFP MOTOROLA 7 ...
Page 8
... V DDE 25 V SSE 26 27 TPUCH7 28 TPUCH6 TPUCH5 29 30 TPUCH4 31 TPUCH3 32 TPUCH2 33 TPUCH1 TPUCH0 Figure 3 MC68332 144-Pin QFP Pin Assignments MOTOROLA 8 MC68332 109 108 107 106 PE4/AS 105 PE6/SIZ0 104 PE7/SIZ1 103 R/W 102 PF0/MODCLK 101 PF1/IRQ1 100 PF2/IRQ2 99 PF3/IRQ3 98 PF4/IRQ4 ...
Page 9
... The standardized modules in the MCU communi- cate with one another and with external components through the IMB. The IMB in the MCU uses 24 address and 16 data lines. MC68332 MC68332TS/D SIM 2-KBYTE TPURAM ARRAY QSM TPU Figure 4 MCU Address Map 332 ADDRESS MAP MOTOROLA 9 ...
Page 10
... BGACK/CS2 BKPT/DSCLK BR/CS0 CLKOUT CSBOOT 1 DATA[15:0] DS DSACK1 DSACK0 DSI/IFETCH DSO/IPIPE 2 EXTAL FC[2:0]/CS[5:3] FREEZE/QUOT HALT IRQ[7:1] MISO 1 MODCLK MOSI PCS0/SS PCS[3:1] R/W RESET RMC RXD SCK SIZ[1:0] MOTOROLA 10 Table 2 MCU Pin Characteristic Output Input Input Driver Synchronized Hysteresis — — — ...
Page 11
... Standby RAM Power/Clock Synthesizer Power Clock Synthesizer Power External Periphery Power (Source and Drain) Internal Module Power (Source and Drain) Table 4 MCU Driver Types Description Discrete Port I/O Designation — — — — — — I/O PQS7 Special — Special — MOTOROLA 11 ...
Page 12
... IRQ[7:1] MISO MODCLK MOSI PC[6:0] PCS[3:0] PE[7:0] PF[7:0] PQS[7:0] QUOT RESET RMC R/W RXD SCK SIZ[1:0] SS T2CLK TPUCH[15:0] MOTOROLA 12 Table 5 MCU Signal Characteristics MCU Module SIM SIM SIM SIM SIM SIM CPU32 SIM SIM SIM SIM SIM SIM SIM CPU32 CPU32 ...
Page 13
... SIM digital output port signals PCS[3:0] QSPI peripheral chip selects PE[7:0] SIM digital I/O port signals PF[7:0] SIM digital I/O port signals PQS[7:0] QSM digital I/O port signals Signal Type Active State Input — Output — Input — Output — Function MOTOROLA 13 ...
Page 14
... SCI Receive Data QSPI Serial Clock Size Slave Select TCR2 Clock TPU Channel Pins TPUCH[15:0] Three-State Control SCI Transmit Data External Filter Capacitor MOTOROLA 14 Mnemonic QUOT Provides the quotient bit of the polynomial divider RESET System reset RMC Indicates an indivisible read-modify-write instruction R/W ...
Page 15
... SUPV bit in the SIMCR. MC68332 MC68332TS/D CLKOUT EXTAL MODCLK CHIP SELECTS EXTERNAL BUS RESET TSC FREEZE/QUOT Figure 5 SIM Block Diagram S(C)IM BLOCK MOTOROLA 15 ...
Page 16
... S $YFFA48 S $YFFA4A S $YFFA4C S $YFFA4E S $YFFA50 S $YFFA52 S $YFFA54 MOTOROLA 16 Table 7 SIM Address Map 8 7 SIM CONFIGURATION (SIMCR) FACTORY TEST (SIMTR) CLOCK SYNTHESIZER CONTROL (SYNCR) NOT USED RESET STATUS REGISTER (RSR) MODULE TEST E (SIMTRE) NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED ...
Page 17
... CHIP-SELECT BASE 7 (CSBAR7) CHIP-SELECT OPTION 7 (CSOR7) CHIP-SELECT BASE 8 (CSBAR8) CHIP-SELECT OPTION 8 (CSOR8) CHIP-SELECT BASE 9 (CSBAR9) CHIP-SELECT OPTION 9 (CSOR9) CHIP-SELECT BASE 10 (CSBAR10) CHIP-SELECT OPTION 10 (CSOR10) NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED 0 NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED NOT USED MOTOROLA 17 ...
Page 18
... RESET DATA11 The SIM configuration register controls system configuration. It can be read or written at any time, ex- cept for the module mapping (MM) bit, which can be written only once. MOTOROLA 18 MODULE CONFIGURATION AND TEST RESET STATUS HALT MONITOR BUS MONITOR SPURIOUS INTERRUPT MONITOR SOFTWARE WATCHDOG TIMER ...
Page 19
... SIM interrupts from being discarded during initialization. MC68332 MC68332TS/D Action Show cycles disabled, external arbitration enabled Show cycles enabled, external arbitration disabled Show cycles enabled, external arbitration enabled Show cycles enabled, external arbitration enabled, internal activity is halted by a bus grant MOTOROLA 19 ...
Page 20
... BME — Bus Monitor External Enable 0 = Disable bus monitor function for an internal to external bus cycle Enable bus monitor function for an internal to external bus cycle. BMT[1:0] — Bus Monitor Timing This field selects a bus monitor time-out period as shown in the following table. MOTOROLA ...
Page 21
... The watchdog clock rate is affected by SWP and SWT in SYPCR. When SWT[1:0] are modified, a watchdog service sequence must be performed before the new time-out period takes effect. The reset value of SWP is affected by the state of the MODCLK pin on the rising edge of reset, as shown in the following table. MC68332 MC68332TS MODCLK SWP $YFFA27 MOTOROLA 21 ...
Page 22
... This is an 8-bit timing modulus. The period of the timer can be calculated as follows: where PIT Period = Periodic interrupt timer period PITM = Periodic interrupt timer register modulus (PITR[7:0]) EXTAL Frequency = Crystal frequency Prescale = 512 or 1 depending on the state of the PTP bit in the PITR MOTOROLA PIRQL ...
Page 23
... External system clock signal frequency must be less than or equal to maximum specified system clock frequency. MC68332 MC68332TS/D V DDSYN XFC 1 0.1 F 0 DDSYN XFC PIN LOW-PASS FILTER W FEEDBACK DIVIDER Y X SYSTEM CLOCK CONTROL V SSI VCO CLKOUT SYSTEM CLOCK SYS CLOCK BLOCK 32KHZ MOTOROLA 23 ...
Page 24
... MCU. The VCO frequency is twice the system clock frequency four times the system clock frequency The reset state of SYNCR ($3F00) produces a modulus-64 count. MOTOROLA 24 Minimum external clock period = minimum external clock high/low time pin to ensure stable operating frequency. ...
Page 25
... STEXT — Stop Mode External Clock 0 = When LPSTOP is executed, the CLKOUT signal is held negated to conserve power When LPSTOP is executed, the CLKOUT signal is driven from the SIM clock, as determined by the state of the STSIM bit. MC68332 MC68332TS EDIV $YFFA04 SLIMP SLOCK RSTEN STSIM STEXT MOTOROLA 25 ...
Page 26
... These spaces are designated as either user or supervisor, and program or data spaces. Address space 7 is designated CPU space. CPU space is used for control information not normally associated with read or write bus cycles. Function codes are valid while AS is asserted. MOTOROLA 26 Table 8 Size Signal Encoding ...
Page 27
... AVEC is ignored during all other bus cycles. MC68332 MC68332TS/D FC1 FC0 Address Space 0 0 Reserved 0 1 User Data Space 1 0 User Program Space 1 1 Reserved 0 0 Reserved 0 1 Supervisor Data Space 1 0 Supervisor Program Space 1 1 CPU Space MOTOROLA 27 ...
Page 28
... Positioning of bytes is determined by the size and address outputs. SIZ1 and SIZ0 indicate the remaining number of bytes to be transferred during the current bus cycle. The number of bytes trans- ferred is equal to or less than the size indicated by SIZ1 and SIZ0, depending on port width. MOTOROLA 28 Table 10 Effect of DSACK Signals ...
Page 29
... DSACK0 DATA DATA [15:8] [7: OP0 (OP0 OP0 (OP0 (OP0) OP0 1 0 OP0 (OP1 OP0 (OP0 OP0 OP1 0 X (OP0) OP0 1 0 OP0 (OP1 OP0 (OP0 OP0 OP1 0 X (OP0) OP0 1 0 OP0 (OP1 OP0 (OP0 OP0 OP1 0 X (OP0) OP0 MOTOROLA 29 ...
Page 30
... The following table lists allocation of chip-selects and discrete outputs on the pins of the MCU. Pin CSBOOT BR BG BGACK FC0 FC1 FC2 ADDR19 ADDR20 ADDR21 ADDR22 ADDR23 MOTOROLA 30 TIMING CONTROL OPTION COMPARE OPTION REGISTER PIN DSACK ASSIGNMENT GENERATOR REGISTER Chip Select Discrete Outputs CSBOOT ...
Page 31
... Chip Select (8-Bit Port) 11 Chip Select (16-Bit Port CSPA0[4] CSPA0[3] 1 DATA2 1 DATA1 1 DATA1 Alternate Signal CS5 FC2 CS4 FC1 CS3 FC0 CS2 BGACK CS1 BG CS0 BR CSBOOT — $YFFA44 CSPA0[2] CSPA0[1] CSBOOT 1 DATA1 1 1 DATA0 Discrete Output PC2 PC1 PC0 — — — — MOTOROLA 31 ...
Page 32
... Port size is determined when a pin is assigned as a chip select. When a pin is assigned to an 8-bit port, the chip select is asserted at all addresses within the block range pin is assigned to a 16-bit port, the upper/lower byte field of the option register selects the byte with which the chip select is associated. MOTOROLA 32 10 ...
Page 33
... ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR Block Size Address Lines Compared 2 K ADDR[23:11 ADDR[23:13 ADDR[23:14 ADDR[23:16] 128 K ADDR[23:17] 256 K ADDR[23:18] 512 K ADDR[23:19 ADDR[23:20] $YFFA48 ADDR ADDR BLKSZ $YFFA4C–$YFFA74 ADDR ADDR BLKSZ MOTOROLA 33 ...
Page 34
... Address strobe 1 = Data strobe This bit controls the timing for assertion of a chip select in asynchronous mode. Selecting address strobe causes chip select to be asserted synchronized with address strobe. Selecting data strobe caus- es chip select to be asserted synchronized with data strobe. MOTOROLA ...
Page 35
... Wait States 1101 13 Wait States 1110 Fast Termination 1111 External DSACK Address Space 00 CPU Space 01 User Space 10 Supervisor Space 11 Supervisor/User Space IPL Description 000 Any Level 001 IPL1 010 IPL2 011 IPL3 100 IPL4 101 IPL5 110 IPL6 111 IPL7 MOTOROLA 35 ...
Page 36
... The bits in this register control the direction of the pin drivers when the pins are configured as I/O. Any bit in this register set to one configures the corresponding pin as an output. Any bit in this register cleared to zero configures the corresponding pin as an input. This register can be read or written at any time. MOTOROLA ...
Page 37
... Port E Signal PE7 PE6 PE5 PE4 PE3 PE2 PE1 PE0 PF7 PF6 PF5 DDF7 DDF6 DDF5 0 0 $YFFA17 Bus Control Signal SIZ1 SIZ0 AS DS RMC AVEC DSACK1 DSACK0 $YFFA19, $YFFA1B PF4 PF3 PF2 PF1 PF0 $YFFA1D DDF4 DDF3 DDF2 DDF1 DDF0 MOTOROLA 37 ...
Page 38
... The logic states of certain data bus pins during reset determine SIM operating configuration. In addition, the state of the MODCLK pin determines system clock source and the state of the BKPT pin determines what happens during subsequent breakpoint assertions. The following table is a summary of reset mode selection options. Mode Select Pin MOTOROLA ...
Page 39
... PORTE PORTF Test Mode Enabled EXTAL = System Clock Background Mode Enabled Function DSI/IFETCH DSO/IPIPE BKPT/DSCLK Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Output Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input Discrete Input RXD MOTOROLA 39 ...
Page 40
... Worst case is approximately 20 milliseconds from TSC assertion. When an external clock signal is applied (MODCLK held low during reset), pins go to high-imped- ance state as soon after TSC assertion as ten clock pulses have been applied to the EXTAL pin. MOTOROLA 40 is applied before and during reset. This mini- DDSYN ...
Page 41
... The CPU space read cycle performs two functions: it places a mask value corresponding to the highest priority interrupt request on the address bus, and it acquires an exception vector number from the inter- rupt source. The mask value also serves two purposes latched into the CCR IP field in order to MC68332 MC68332TS/D MOTOROLA 41 ...
Page 42
... ADDR[3:1]. If the request level of at least one interrupting module or device is the same as the value in ADDR[3:1], interrupt arbitration contention takes place. When there is no conten- tion, the spurious interrupt monitor asserts BERR, and a spurious interrupt exception is pro- cessed. E. After arbitration, the interrupt acknowledge cycle can be completed in one of three ways: MOTOROLA 42 MC68332 MC68332TS/D ...
Page 43
... The test submodule supports scan-based testing of the various MCU modules integrated into the SIM to support production testing. Test submodule registers are intended for Motorola use. Register names and addresses are provided to indicate that these addresses are occupied. SIMTR —System Integration Test Register SIMTRE — ...
Page 44
... Central Processor Unit Based on the powerful MC68020, the CPU32 processing module provides enhanced system perfor- mance and also uses the extensive software base for the Motorola M68000 family. 4.1 Overview The CPU32 is fully object code compatible with the M68000 Family, which excels at processing calcu- lation-intensive algorithms and supporting high-level languages ...
Page 45
... Figure 11 Supervisor Programming Model Supplement MC68332 MC68332TS (USP CCR 0 A7' (SSP (CCR VBR 2 0 SFC DFC Data Registers Address Registers User Stack Pointer Program Counter Condition Code Register Supervisor Stack Pointer Status Register Vector Base Register Alternate Function Code Registers MOTOROLA 45 ...
Page 46
... Included in the register indirect addressing modes are the capabilities to post-increment, predecrement, and offset. The program counter relative mode also has index and offset capabilities. In addition to these addressing modes, many instructions implicitly specify the use of the status register, stack point- er, or program counter. MOTOROLA ...
Page 47
... Operation X Destination 10 Destination Destination Destination Destination Destination Destination X Destination Destination Destination CCR bit of destinatio (SSP); (SSP); (vector (SP Source), CCR shows results Source), CCR shows results Data), CCR shows results Source), CCR shows results Rn Upper bound, CCR shows result MOTOROLA 47 ...
Page 48
... MOVE to SR <ea> MOVE USP USP, An An, USP 1 MOVEC Rc, Rn Rn, Rc MOVEM list, <ea> <ea>, list MOVEP Dn, (d16, An) (d16, An), Dn MOVEQ #<data>, Dn MOTOROLA 48 Operand Size If condition false, then 1), then Destination / Source 32/16 (signed or unsigned) 64/ Destination / Source 32/32 32 (signed or unsigned) 32/ Source Destination ...
Page 49
... Data SR; STOP 16 8, 16, 32 Destination Source Destination Source 16, 32 Destination Data 8, 16, 32 Destination Data 8, 16 16, 32 Destination Source 8, 16, 32 Operation Rn Destination Destination Destination Destination Destination SP; (SP) PC; SP; (SP) PC Destination Destination Destination Destination Destination X Destination MOTOROLA 49 ...
Page 50
... TBLS/TBLU <ea>, Dn Dym : Dyn, Dn TBLSN/TBLUN <ea>, Dn Dym : Dyn, Dn TRAP #<data> TRAPcc none #<data> TRAPV none TST <ea> UNLK An 1. Privileged instruction. MOTOROLA 50 Operand Size 16 Destination Tested Condition Codes bit Destination Dyn Dym Temp 8, 16, 32 (Temp 0]) (Dym 256) Temp Dyn Dym Temp ...
Page 51
... Current program counter is stacked at the location of the current stack pointer. Instruction execution begins at user patch code. RST Asserts RESET for 512 clock cycles. The CPU is not reset by this command. Synonymous with the CPU RESET instruction. NOP performs no operation and can be used as a null command. Description MOTOROLA 51 ...
Page 52
... The programmer can choose one of the three fol- lowing conditions to update the parameter: 1) when a transition occurs, 2) when the CPU makes a re- quest when a rate specified in another parameter is matched. When a pin is used as a discrete output set high or low only upon request by the CPU. MOTOROLA 52 SCHEDULER SERVICE REQUESTS ...
Page 53
... TCR2 is reset to $FFFF. Alternatively, a byte at an address specified by a channel parameter can be read and used as a flag. A nonzero value of the flag indicates that TCR2 reset to $FFFF once the next additional transition is detected. MC68332 MC68332TS/D Offset = Period Ratio MOTOROLA 53 ...
Page 54
... The user specifies a starting channel of the block and number of channels within the block. Gen- eration of links depends on the mode of operation. Any channel can be used to measure an accumulated number of periods of an input signal. A maximum of 24 bits can be used for the accumu- MOTOROLA 54 P( – ...
Page 55
... The times of the most recent two transitions are maintained in parameter RAM. A channel can perform input captures continually channel can detect a single transition or specified number of transitions, ceasing channel activity until reinitialization. After each transition or specified number of transitions, the channel can generate a link to other channels. MC68332 MC68332TS/D MOTOROLA 55 ...
Page 56
... The state sequence is implemented as a user-configurable state machine, thus providing a flexible ap- proach with other general applications. A CPU offset parameter is provided to allow all the switching angles to be advanced or retarded on the fly by the CPU. This feature is useful for torque maintenance at high speeds. MOTOROLA 56 MC68332 MC68332TS/D ...
Page 57
... HOST SEQUENCE REGISTER 0 (HSQR0) HOST SEQUENCE REGISTER 1 (HSQR1) HOST SERVICE REQUEST REGISTER 0 (HSRR0) HOST SERVICE REQUEST REGISTER 1 (HSRR1) CHANNEL PRIORITY REGISTER 0 (CPR0) CHANNEL PRIORITY REGISTER 1 (CPR1) CHANNEL INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER (CISR) LINK REGISTER (LR) SERVICE GRANT LATCH REGISTER (SGLR) DECODED CHANNEL NUMBER REGISTER (DCNR MOTOROLA 57 ...
Page 58
... Channel Control and Status Registers Development Support and Test Verification Registers 5.5.1 System Configuration Registers TPUMCR — TPU Module Configuration Register STOP TCR1P TCR2P RESET STOP — Stop Bit 0 = TPU operating normally 1 = Internal clocks shut down MOTOROLA 58 Base Parameter Address Address $YFFFF $YFFFF $YFFFF $YFFFF## ...
Page 59
... PSCK = 0 Number of Rate at Clocks 16 MHz 128 8 ms 256 MUX CONTROL B (T2CG CONTROL BIT) 0 – – B Divide By Internal Clock Divided TCR1 PRESCALER CTL BLOCK 1 PSCK = 1 Number of Rate at Clocks 16 MHz 4 250 ns 8 500 TCR2 PRESCALER TCR2 PRESCALER CTL BLOCK 2 External Clock Divided MOTOROLA 59 ...
Page 60
... The TPU is assigned 16 unique interrupt vector numbers, one vector number for each channel. The CIBV field specifies the most significant nibble of all 16 TPU channel interrupt vector numbers. The low- er nibble of the TPU interrupt vector number is determined by the channel number on which the interrupt occurs. MOTOROLA ...
Page 61
... CHANNEL[15:0] — Encoded Time Function for each Channel Encoded 4-bit fields in the channel function select registers specify one of 16 time functions to be exe- cuted on the corresponding channel. MC68332 MC68332TS CHANNEL14 CHANNEL13 CHANNEL10 CHANNEL9 CHANNEL6 CHANNEL5 CHANNEL2 CHANNEL1 $YFFE0A $YFFE20 $YFFE0C CHANNEL12 $YFFE0E CHANNEL8 $YFFE10 CHANNEL4 $YFFE12 CHANNEL0 MOTOROLA 61 ...
Page 62
... TPU clears the service request to %00 before the CPU changes any parameters or issues a new service request to the channel. CPR0 — Channel Priority Register CH13 RESET CPR1 — Channel Priority Register RESET CH[15:0] — Encoded One of Three Channel Priority Levels MOTOROLA ...
Page 63
... DCNR — Decoded Channel Number Register TCR — Test Configuration Register The TCR is used for factory test of the MCU. MC68332 MC68332TS/D Service Guaranteed Time Slots Disabled — Low 4 out of 7 Middle 2 out of 7 High 1 out of 7 $YFFE04 $YFFE06 $YFFE22 $YFFE24 $YFFE26 $YFFE02 MOTOROLA 63 ...
Page 64
... Optional parity generation and detection provide either even or odd parity check capability. Ad- vanced error detection circuitry catches glitches 1/ bit time in duration. Wakeup functions allow the CPU to run uninterrupted until meaningful data is available. An address map of the QSM is shown below. MOTOROLA 64 QSPI PORT QS ...
Page 65
... PQS PIN ASSIGNMENT (PQSPAR) SPI CONTROL 0 (SPCR0) SPI CONTROL 1 (SPCR1) SPI CONTROL 2 (SPCR2) SPI CONTROL 3 (SPCR3) NOT USED RECEIVE RAM (RR[0:F]) TRANSMIT RAM (TR[0:F]) COMMAND RAM (CR[0:F]) 0 QSM INTERRUPT VECTOR (QIVR) PQS DATA (PORTQS) PQS DATA DIRECTION (DDRQS) SPI STATUS (SPSR) MOTOROLA 65 ...
Page 66
... STOP places the QSM in a low-power state by disabling the system clock in most parts of the module. The QSMCR is the only register guaranteed to be readable while STOP is asserted. The QSPI RAM is not readable. However, writes to RAM or any register are guaranteed to be valid while STOP is assert- ed. STOP can be negated by the CPU and by reset. MOTOROLA 66 Pin Mode ...
Page 67
... ILSCI determines the priority of SCI interrupts. This field must be given a value between $0 (interrupts disabled (highest priority). If ILQSPI and ILSCI are the same nonzero value, and both submodules simultaneously request inter- rupt service, QSPI has priority. MC68332 MC68332TS ILSCI $YFFC02 $YFFC04 0 QIVR MOTOROLA 67 ...
Page 68
... DDRQS — PORT QS Data Direction Register PQSPA6 PQSPA5 PQSPA4 PQSPA3 RESET Clearing a bit in the PQSPAR assigns the corresponding pin to general-purpose I/O; setting a bit as- signs the pin to the QSPI. The PQSPAR does not affect operation of the SCI. MOTOROLA PQS7 PQS6 PQS5 RESET: 0 ...
Page 69
... DDRQS affects both QSPI function and I/O function. MC68332 MC68332TS/D Table 25 QSPAR Pin Assignments PQSPAR Bit Pin Function 0 PQS0 1 MISO 0 PQS1 1 MOSI 0 PQS2 1 SCK 0 PQS3 1 PCS0/SS 0 PQS4 1 PCS1 0 PQS5 1 PCS2 0 PQS6 1 PCS3 0 PQS7 1 TXD 1 2 MOTOROLA 69 ...
Page 70
... PQS7 is a digital I/O pin unless the SCI transmitter is enabled (TE in SCCR1 = 1), in which case it be- comes SCI serial output TXD. DDRQS determines the direction of the TXD pin only when the SCI transmitter is disabled. When the SCI transmitter is enabled, the TXD pin is an output. MOTOROLA 70 Mode DDRQS ...
Page 71
... QSPI Submodule The QSPI submodule communicates with external devices through a synchronous serial bus. The QSPI is fully compatible with the serial peripheral interface (SPI) systems found on other Motorola products. A block diagram of the QSPI is shown below. QUEUE CONTROL BLOCK QUEUE 4 POINTER COMPARATOR ...
Page 72
... MSTR WOMQ BITS RESET SPCR0 contains parameters for configuring the QSPI before it is enabled. The CPU can read and write this register. The QSM has read-only access. MOTOROLA 72 Mnemonics Mode MISO Master Slave MOSI Master Slave SCK Master Slave PCS[3:1] ...
Page 73
... SPBR field. The following equation determines the MC68332 MC68332TS/D BITS Bits per Transfer 0000 16 0001 Reserved 0010 Reserved 0011 Reserved 0100 Reserved 0101 Reserved 0110 Reserved 0111 Reserved 1000 8 1001 9 1010 10 1011 11 1100 12 1101 13 1110 14 1111 15 MOTOROLA 73 ...
Page 74
... If DT equals zero, a standard delay is inserted. Standard Delay after Transfer = [17/System Clock] Delay after transfer can be used to provide a peripheral deselect interval. A delay can also be inserted between consecutive transfers to allow serial A/D converters to complete conversion. MOTOROLA 74 SCK Baud Rate = System Clock/(2SPBR) or ...
Page 75
... HMIE — HALTA and MODF Interrupt Enable 0 = HALTA and MODF interrupts disabled 1 = HALTA and MODF interrupts enabled HMIE controls CPU interrupts caused by the HALTA status flag or the MODF status flag in SPSR. MC68332 MC68332TS ENDQP LOOPQ HMIE HALT $YFFC1C NEWQP $YFFC1E 0 SPSR MOTOROLA 75 ...
Page 76
... CPU. The RAM is divided into three segments: receive data, transmit data, and command control data. Receive data is information received from a serial device external to the MCU. Transmit data is infor- mation stored by the CPU for transmission to an external peripheral. Command control data is used to perform the transfer. Refer to the following illustration of the organization of the RAM. MOTOROLA ...
Page 77
... TRF D4F WORD Figure 15 QSPI RAM DSCK PCS3 — — — DT DSCK PCS3 PERIPHERAL CHIP SELECT CR0 CR1 CR2 COMMAND RAM CRD CRE CRF BYTE QSPI RAM MAP $YFFD00 $YFFD20 $YFFD40 PCS2 PCS1 PCS0* — — — PCS2 PCS1 PCS0* MOTOROLA 77 ...
Page 78
... A mode fault flag (MODF) indicates a request for SPI master arbitration. System software must provide arbitration. Note that unlike previous SPI systems, MSTR is not cleared by a mode fault being set, nor are the QSPI pin output drivers disabled. The QSPI and associated output drivers must be dis- abled by clearing SPE in SPCR1. MOTOROLA 78 MC68332 MC68332TS/D ...
Page 79
... SCI Submodule The SCI submodule is used to communicate with external devices through an asynchronous serial bus. The SCI is fully compatible with the SCI systems found on other Motorola MCUs, such as the M68HC11 and M68HC05 Families. 6.6.1 SCI Pins There are two unidirectional pins associated with the SCI. The SCI controls the transmit data (TXD) pin when enabled, whereas the receive data (RXD) pin remains a dedicated input pin to the SCI ...
Page 80
... Long idle-line detect (start count on first one after stop bit(s)) PT — Parity Type 0 = Even parity 1 = Odd parity When parity is enabled, PT determines whether parity is even or odd for both the receiver and the trans- mitter. MOTOROLA 80 Table 27 SCI Baud Rates SCBR Value 64.0 $1FFF 110 ...
Page 81
... WAKE). When in wakeup mode, the receiver status flags are not set, and interrupts are inhibited. This bit is cleared automatically (returned to normal mode) when the receiver is awakened. MC68332 MC68332TS/D PE Result 0 8 Data Bits 1 7 Data Bits, 1 Parity Bit 0 9 Data Bits 1 8 Data Bits, 1 Parity Bit MOTOROLA 81 ...
Page 82
... RAF — Receiver Active Flag 0 = SCI receiver is idle 1 = SCI receiver is busy RAF indicates whether the SCI receiver is busy set when the receiver detects a possible start bit and is cleared when the chosen type of idle line is detected. RAF can be used to reduce collisions in systems with multiple masters. MOTOROLA ...
Page 83
... SCDR is read, or the first eight data bits to be transmitted when SCDR is written. R8/T8 are used when the SCI is configured for 9-bit operation. When it is configured for 8-bit operation, they have no meaning or effect. MC68332 MC68332TS R8/T8 R7/T7 R6/T6 R5/ $YFFC0E R4/T4 R3/T3 R2/T2 R1/T1 R0/ MOTOROLA 83 ...
Page 84
... RAM array enters low-power stop mode. This bit controls whether the RAM array is in stop mode or normal operation. Reset state is zero, for normal operation. In stop mode, the array retains its contents, but cannot be read or written by the CPU. MOTOROLA TPURAM MODULE CONFIGURATION REGISTER (TRAMMCR) ...
Page 85
... ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR Circuitry within the TPURAM module switches to the higher STBY falls below V DD STBY $YFFB02 $YFFB04 ADDR ADDR NOT USED RAMDS The array can be accessed DD is removed. TPURAM DD , access to the array STBY during stop mode, internal circuitry MOTOROLA 85 ...
Page 86
... Expanded and revised QSM section. Made all register diagrams and bit mnemon- ics consistent. Added information concerning SPI and SCI operation. Page 93-95 Revised Standby RAM with TPU Emulation RAM section. Made all register dia- grams and bit mnemonics consistent. MOTOROLA 86 MC68332 MC68332TS/D ...
Page 87
... MC68332 MC68332TS/D MOTOROLA 87 ...
Page 88
... Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “ ...