MCP6546-I/SN Microchip Technology, MCP6546-I/SN Datasheet - Page 16

MCP6546-I/SN
Manufacturer Part Number
MCP6546-I/SN
Description
IC COMP OPENDRN 1.6V SNGL 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Type
General Purposer
Specifications of MCP6546-I/SN
Output Type
CMOS, Open-Drain, Rail-to-Rail, TTL
Package / Case
8-SOIC (0.154", 3.90mm Width)
Number Of Elements
1
Voltage - Supply
1.6 V ~ 5.5 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Number Of Channels
1 Channel
Product
Analog Comparators
Response Time
4 us
Offset Voltage (max)
7 mV
Input Bias Current (max)
1 pA
Supply Voltage (max)
5.5 V
Supply Voltage (min)
1.6 V
Supply Current (max)
1 uA
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Comparator Type
Low Power
No. Of Comparators
1
Supply Voltage Range
1.6V To 5.5V
Amplifier Case Style
SOIC
No. Of Pins
8
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To +85°C
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
MCP6546I/SN
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MCP6546-I/SN
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
MCP6546/6R/6U/7/8/9
EQUATION 4-1:
Using this simplified circuit, the trip voltage can be
calculated using the following equation:
EQUATION 4-2:
Figure 2-21
typical values for V
output current I
can be determined using the equation below:
EQUATION 4-3:
V
EQUATION 4-4:
As explained in Section 4.1 “Comparator Inputs”, it
is important to keep the non-inverting input below
V
4.5
With this family of comparators, the power supply pin
(V
capacitor (i.e., 0.01 µF to 0.1 µF) within 2 mm for good
edge rate performance.
DS21714F-page 16
V
V
V
OH
DD
THL
DD
TLH
THL
+0.3V when V
can be calculated using the equation below:
for single supply) should have a local bypass
=
= trip voltage from low to high
= trip voltage from high to low
V
V
TLH
V
Supply Bypass
OH
PU
I
OL
and
=
⎛
⎜
⎝
=
--------------------------------------- -
R
=
OL
23
V
(
V
Figure 2-24
V
OL
⎛
⎝
+
PU
23
as shown in
PU
V
------------------------- -
OL
I
⎛
⎜
⎝
R
PU
R F
OL
R
---------------------- -
R
=
. This voltage is dependent on the
–
23
> V
R
23
23
–
PU
V
+
R
=
------------------
R
=
23
+
V
23
DD
2
R
I
R
OL
)
R F
+
PU
------------------
R
PU
×
.
3
R
2
R
⎞
⎠
can be used to determine
⎛
⎝
⎞
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎟
⎠
2
+
+
3
+
------------------------------------- -
R
R
Figure
+
+
×
I
R
⎛
⎝
23
3
RF
V
------------------------
3
V
V
V
R
R
+
23
23
DD
23
23
23
R
⎛
⎝
⎛
⎝
–
+
+
F
---------------------------------------
R
--------------------- -
R
4-4. This current
V
23
23
R
R
+
OL
R
R
F
F
R
+
+
F
F
⎞
⎠
PU
R
R
+
F
F
⎞
⎠
R
⎞
⎠
+
PU
R
PU
⎞
⎠
4.6
Reasonable capacitive loads (e.g., logic gates) have
little impact on propagation delay (see
The supply current increases with increasing toggle
frequency
capacitive loads.
4.7
In order to maximize battery life in portable
applications, use large resistors and small capacitive
loads. Avoid toggling the output more than necessary.
Do not use Chip Select (CS) too frequently in order to
conserve power. Capacitive loads will draw additional
power at start-up.
4.8
In applications where low input bias current is critical,
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) surface leakage effects
need to be considered. Surface leakage is caused by
humidity, dust or other contamination on the board.
Under low-humidity conditions, a typical resistance
between nearby traces is 10
would cause 5 pA of current to flow. This is greater
than the MCP6546/6R/6U/7/8/9 family’s bias current at
25°C (1 pA, typ.).
The easiest way to reduce surface leakage is to use a
guard ring around sensitive pins (or traces). The guard
ring is biased at the same voltage as the sensitive pin.
An example of this type of layout is shown in
Figure
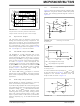
FIGURE 4-7:
for Inverting Circuit.
1.
Inverting Configuration (Figures
a.
b.
4-7.
Capacitive Loads
Battery Life
PCB Surface Leakage
Connect the guard ring to the non-inverting
input pin (V
to the same reference voltage as the
comparator (e.g., V
Connect the inverting pin (V
pad without touching the guard ring.
(Figure
V
2-30),
IN
IN
Guard Ring
+). This biases the guard ring
Example Guard Ring Layout
-
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
DD
especially
/2 or ground).
V
12
IN
Ω. A 5V difference
+
IN
4-4
–) to the input
and 4-7):
Figure
with
V
SS
higher
2-27).