MAX9451 Maxim, MAX9451 Datasheet - Page 10

MAX9451
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX9451
Description
The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 clock generators provide high-precision clocks for timing in SONET/SDH systems or Gigabit Ethernet systems
Manufacturer
Maxim
Datasheet
1.MAX9450.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MAX9451EHJ+
Manufacturer:
Microsemi Consumer Medical Product Group
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MAX9451EHJ+T
Manufacturer:
Microsemi Consumer Medical Product Group
Quantity:
10 000
When the device switches from one input reference to
the other or reverts to an input reference from holdover,
the output phase changes smoothly during the transition
due to the narrowband external PLL filter. The narrower
the filter bandwidth is, the smoother the phase
transition. However, if bandwidth is too narrow, it can
cause some degradation on output jitter performance.
The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 allow external setting
of the charge-pump current in the PLL. Connect a resis-
tor from RJ to GNDA to set the PLL charge-pump current:
where R
current is in µA. Use R
to meet individual application requirements. The
charge-pump current and the external filter compo-
nents change the PLL bandwidth. Table 11 shows the
charge-pump current vs. the resistor’s value.
The loop response equation is defined as:
where I
R
back divider.
The two inputs can be disabled separately by SEL0
and SEL1 or the 2 bits in CR5[3:2]. Table 2 shows the
state map.
Upon power-up, default frequency divider rates and the
states of the monitor, inputs, and outputs are set
according to Table 10. Setting MR high or CR6[4] to 1
also resets the device. When the device resets, INT
and CR7[5:6] go low and all the registers revert to their
default values.
High-Precision Clock Generators
with Integrated VCXO
Table 2. Input Activation by SEL0, SEL1,
or CR5[3:2]
10
FILT
SEL1
unity-gain bandwidth = (I
______________________________________________________________________________________
X
X
X
0
0
1
1
is the external filter resistance, and M is the feed-
charge-pump current (µA) = 2.48 x 1000 /
CP
SET
is the charge-pump current set by REXT,
is in kΩ and the value of the charge-pump
SEL0
0
1
0
1
X
X
X
(R
Power-Up and Master Reset
SET
SET
Charge-Pump Current Setting
(kΩ) + 0.375)
CR5[3:2]
00
00
00
00
01
10
11
to adjust the loop response
CP
External Loop Filter
x R
FILT
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
IN1
Input Disable
x 12kHz) / M
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
IN0
The control interface of the MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452
is an I
AD1. Drive both AD0 and AD1 high to active SPI mode.
Otherwise, I
slave that sends and receives data through the clock
line, SCL, and data line, SDA, to achieve bidirectional
communication with the masters. A master (typically a
microcontroller) initiates all data transfers to and from
slaves, and generates the SCL clock that synchronizes
the data transfer. Figure 4 shows the timing of SCL and
SDA. The SDA line operates as both an input and an
open-drain output. SDA requires a pullup resistor, typi-
cally 4.7kΩ. The SCL line operates only as an input. A
pullup resistor, typically 4.7kΩ, is required on SCL if there
are multiple masters on the 2-wire bus, or if the master in
a single-master system has an open-drain SCL output.
Every I
address is the slave (MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452)
ID for the master to write and read. In the MAX9450/
MAX9451/MAX9452, the first 4 bits (1101) of the
address are hard coded into the device at the factory.
See Table 3. The last 3 bits of the address are input
programmable by the three-level AD0 and AD1. This
configuration provides eight selectable addresses for
the MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452, allowing eight
devices to be connected to one master.
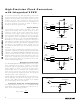
Both SCL and SDA remain high when the interface is
not busy. The active master signals the beginning of a
transmission with a START (S) condition by transitioning
SDA from high to low while SCL is high. When the master
has finished communicating with the slave, it issues a
STOP (P) condition by transitioning SDA from low to
high while SCL is high. The bus is then free for another
transmission (Figure 3). The interval between a START
and a STOP is called a session.
Figure 3. START and STOP Conditions
SDA
SCL
CONDITION
START
2
2
S
C or SPI depending on the states of AD0 and
C port has a 7-bit device address. This 7-bit
2
C is activated. The device operates as a
START and STOP Conditions
I
2
C Device Address
I
2
C Interface
CONDITION
STOP
P